Amoeba sisters a and b PDF
| Title | Amoeba sisters a and b |
|---|---|
| Course | Introductory Biology |
| Institution | Ohio State University |
| Pages | 2 |
| File Size | 293.4 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 13 |
| Total Views | 199 |
Summary
Amoeba sisters for days...
Description
Amoeba Sisters Answer Key
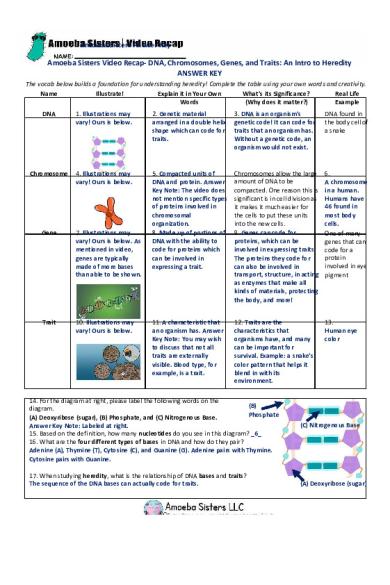
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap- DNA, Chromosomes, Genes, and Traits: An Intro to Heredity ANSWER KEY The vocab below builds a foundation for understanding heredity! Complete the table using your own words and creativity. Name Illustrate! Explain it in Your Own What’s its Significance? Real Life Words (Why does it matter?) Example DNA
1. Illustrations may vary! Ours is below.
2. Genetic material arranged in a double helix shape which can code for traits.
3. DNA is an organism’s genetic code! It can code for traits that an organism has. Without a genetic code, an organism would not exist.
DNA found in the body cell of a snake
Chromosome
4. Illustrations may vary! Ours is below.
5. Compacted units of DNA and protein. Answer Key Note: The video does not mention specific types of proteins involved in chromosomal organization. 8. Made up of portions of DNA with the ability to code for proteins which can be involved in expressing a trait.
Chromosomes allow the large amount of DNA to be compacted. One reason this is significant is in cell division as it makes it much easier for the cells to put these units into the new cells. 9. Genes can code for proteins, which can be involved in expressing traits. The proteins they code for can also be involved in transport, structure, in acting as enzymes that make all kinds of materials, protecting the body, and more!
6. A chromosome in a human. Humans have 46 found in most body cells. One of many genes that can code for a protein involved in eye pigment
11. A characteristic that an organism has. Answer Key Note: You may wish to discuss that not all traits are externally visible. Blood type, for example, is a trait.
12. Traits are the characteristics that organisms have, and many can be important for survival. Example: a snake’s color pattern that helps it blend in with its environment.
13. Human eye color
Gene
7. Illustrations may vary! Ours is below. As mentioned in video, genes are typically made of more bases than able to be shown.
Trait
10. Illustrations may vary! Ours is below.
14. For the diagram at right, please label the following words on the (B) diagram. Phosphate (A) Deoxyribose (sugar), (B) Phosphate, and (C) Nitrogenous Base. Answer Key Note: Labeled at right. 15. Based on the definition, how many nucleotides do you see in this diagram? _6_ 16. What are the four different types of bases in DNA and how do they pair? Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G). Adenine pairs with Thymine. Cytosine pairs with Guanine. 17. When studying heredity, what is the relationship of DNA bases and traits? The sequence of the DNA bases can actually code for traits.
(C) Nitrogenous Base
(A) Deoxyribose (sugar)
Amoeba Sisters Answer Key Amoeba Sisters Video Recap- DNA, Chromosomes, Genes, and Traits: An Intro to Heredity ANSWER KEY A Picture Says It! 18. Explain what this image represents regarding where your entire DNA code can be found. In eukaryotes, the entire DNA code can be found in [nearly] all of the body cells, which is what this image shows. [Answer Key Note: The video mentions that genes are regulated. It may be helpful to emphasize that despite having the full DNA code, not all genes may be “turned on” in a cell. For example, a stomach cell may have genes activated that are involved in producing stomach acid. Skin cells may have those genes “turned off” in gene regulation] 19. Apply Your Understanding Spike is not a clone of his father. He inherited DNA from both of his parents. Chromosomes are condensed units of DNA. If Spike has 36 chromosomes, you would expect that Spike would have inherited __18__ chromosomes from his mother and __18___ chromosomes from his father. 20. How did you determine the chromosome numbers and how does that relate to heredit
Offspring receive half of their chromosomes from each parent. Since Spike has 36 chromosomes, he received ½ of that (18) from his mother and ½ of that (18) from his Heredity involves the passing of traits down from parent to offspring. DNA can code for those traits, and that DNA is condensed into chromosomes that the offspring inherits from its parents. 21. As mentioned in the video, the environment can also affect an organism’s traits. The example of nourishment was used in the case for Spike, as this could affect his growth and size. This can also occur in humans. UV light was not mentioned in the video. How could UV light potentially affect an organism’s trait? Provide one example. Examples may vary, especially since the question allows it to be any organism. Here are a few examples: -UV light can affect the size of plants, since plants require light for growth. -UV light can affect human skin color as pigmentation can change with UV light exposure. -UV light exposure can be involved in vitamin D synthesis in some organisms, and a severe deficiency could affect bone density (and more). 22. Recap the Vocab Nitrogenous Base Identify some of the vocabulary you worked with Gene by labeling them on this illustration: DNA
DNA Gene – NOTE: Green portion of DNA. As mentioned in video, genes are typically made of more bases than able to be shown. Chromosome Nucleotide Phosphate Deoxyribose (sugar) Nitrogenous Base
Phosphate Deoxyribose (sugar)...
Similar Free PDFs

Amoeba sisters a and b
- 2 Pages

Bio Notes- Amoeba Sisters
- 2 Pages

Amoeba Sisters - work
- 2 Pages

Amoeba sisters worksheets
- 4 Pages

Amoeba Sisters Carb Nitro Cycle
- 2 Pages

My sisters keeper - Grade: B
- 9 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu









