Bjt1 - bjt notes PDF

| Title | Bjt1 - bjt notes |
|---|---|
| Author | mike faky |
| Course | Electronics I |
| Institution | University of Miami |
| Pages | 3 |
| File Size | 181 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 23 |
| Total Views | 154 |
Summary
bjt notes...
Description
Summary of Bipolar Junction T ransistors
SUMMARY OF BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS SYMBOLS Collector
Collector Base
Base
Emitter
Emitter
npn phototransistor
pnp
npn
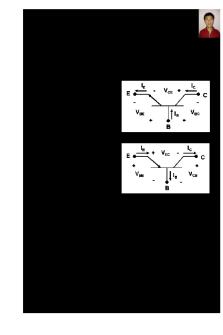
CURRENTS AND VOLTAGES IC IB
IC
VCB +
IB
– +
IE
+
VBE – (0.7 V)
IE
VCB –
+ –
VCE
–
VBE + (–0.7 V)
– VCE
+
IE = IC + IB
AMPLIFICATION +VCC
Vc
IB
C
DC current gain IC = bDCIB
◆
Vb
AC voltage gain
RB VBB
Vs
IC
◆
RC
IE
Av =
Vc RC = Vb r9e
BE junction forward-biased BC junction reverse-biased
SWITCHING +VCC RC IB = 0 0V RB
RC
IC = 0
+ – –
IB
VC = VCC OPEN
+
+VBB RB
+ +
IC(sat) IB > – bDC
IE = 0
Cutoff: BE junction reverse-biased BC junction reverse-biased
+VCC
+VCC
+VCC
Ideal switch equivalent for cutoff
–
IC
RC
IC ù
VCC RC
VC = 0 V CLOSED
–
IE
Saturation: BE junction forward-biased BC junction forward-biased
Ideal switch equivalent for saturation
◆
203
204
◆
Bipolar Junction Tr ansistors
SUMMARY Section 4–1
◆ The BJT (bipolar junction transistor) is constructed with three regions: base, collector, and emitter. ◆ The BJT has two pn junctions, the base-emitter junction and the base-collector junction. ◆ Current in a BJT consists of both free electrons and holes, thus the term bipolar. ◆ The base region is very thin and lightly doped compared to the collector and emitter regions. ◆ The two types of bipolar junction transistor are the npn and the pnp.
Section 4–2
◆ To operate as an amplifier, the base-emitter junction must be forward-biased and the base-
collector junction must be reverse-biased. This is called forward-reverse bias. ◆ The three currents in the transistor are the base current (IB), emitter current (IE), and collector
current (IC). ◆ IB is very small compared to IC and IE.
Section 4–3
◆ The dc current gain of a transistor is the ratio of IC to IB and is designated bDC. Values typically
range from less than 20 to several hundred. ◆ bDC is usually referred to as hFE on transistor datasheets. ◆ The ratio of IC to IE is called aDC. Values typically range from 0.95 to 0.99. ◆ There is a variation in bDC over temperature and also from one transistor to another of the same type.
Section 4–4
◆ When a transistor is forward-reverse biased, the voltage gain depends on the internal emitter
resistance and the external collector resistance. ◆ Voltage gain is the ratio of output voltage to input voltage. ◆ Internal transistor resistances are represented by a lowercase r.
Section 4–5
◆ A transistor can be operated as an electronic switch in cutoff and saturation. ◆ In cutoff, both pn junctions are reverse-biased and there is essentially no collector current. The
transistor ideally behaves like an open switch between collector and emitter. ◆ In saturation, both pn junctions are forward-biased and the collector current is maximum. The
transistor ideally behaves like a closed switch between collector and emitter. ◆ Transistors are used as switches in digital logic circuits.
Section 4–6
◆ In a phototransistor, base current is produced by incident light. ◆ A phototransistor can be either a two-lead or a three-lead device. ◆ An optocoupler consists of an LED and a photodiode or phototransistor. ◆ Optocouplers are used to electrically isolate circuits.
Section 4–7
◆ There are many types of transistor packages using plastic, metal, or ceramic. ◆ Two basic package types are through-hole and surface mount.
Section 4–8
◆ It is best to check a transistor in-circuit before removing it. ◆ Common faults in transistor circuits are open junctions, low bDC, excessive leakage currents,
and external opens and shorts on the circuit board.
KEY TERMS
Key terms and other bold terms in the chapter are defined in the end-of-book glossary. Amplification The process of increasing the power, voltage, or current by electronic means. AND gate A digital circuit in which the output is at a high level voltage when all of the inputs are at a high level voltage. Base One of the semiconductor regions in a BJT. The base is very thin and lightly doped compared to the other regions. Beta (B) The ratio of dc collector current to dc base current in a BJT; current gain from base to collector. BJT A bipolar junction transistor constructed with three doped semiconductor regions separated by two pn junctions. Collector The largest of the three semiconductor regions of a BJT.
True/False Quiz
◆
205
Cutoff The nonconducting state of a transistor. Emitter The most heavily doped of the three semiconductor regions of a BJT. Gain The amount by which an electrical signal is increased or amplified. Linear Characterized by a straight-line relationship of the transistor currents. Load Line A load line is a straight line that represents the voltage and current in the linear portion of circuit that is connected to a device (a transistor in this case). OR gate A digital circuit in which the output is at a high level voltage when one or more inputs are at a high level voltage. Phototransistor A transistor in which base current is produced when light strikes the photosensitive semiconductor base region. Saturation The state of a BJT in which the collector current has reached a maximum and is independent of the base current.
KEY FORMULAS IE 5 IC 1 IB IC BDC 5 IB
Transistor currents
4–3
VBE G 0.7 V
Base-to-emitter voltage (silicon)
4–4
VBB 2 VBE IB 5 RB
Base current
4–5
VCE 5 VCC 2 ICRC
Collector-to-emitter voltage (common-emitter)
4–6
VCB 5 VCE 2 VBE RC Av G r9 e
Collector-to-base voltage
4–1 4–2
4–7 4–8 4–9 4–10 4–11
TRUE/FALSE QUIZ
DC current gain
Approximate ac voltage gain
VCE(cutoff) 5 VCC VCC 2 V CE(sat) I C(sat) 5 RC IC(sat) I B(min) 5 BDC
Cutoff condition
IC 5 BDCIL
Phototransistor collector current
Collector saturation current Minimum base current for saturation
Answers can be found at www.pearsonhighered.com/floyd. 1. A bipolar junction transistor has three terminals. 2. The three regions of a BJT are base, emitter, and cathode. 3. For operation in the linear or active region, the base-emitter junction of a transistor is forwardbiased. 4. Two types of BJT are npn and pnp. 5. The base current and collector current are approximately equal. 6. The dc voltage gain of a transistor is designated bDC. 7. Cutoff and saturation are the two normal states of a linear transistor amplifier. 8. When a transistor is saturated, the collector current is maximum. 9. bDC and hFE are two different transistor parameters. 10. Voltage gain of a transistor amplifier depends on the collector resistor and the internal ac resistance. 11. Amplification is the output voltage divided by the input current. 12. A transistor in cutoff acts as an open switch....
Similar Free PDFs

Bjt1 - bjt notes
- 3 Pages

BJT 2021 - Lecture notes 2
- 11 Pages

BJT Fundamentals
- 22 Pages

Summary - Bjt formula
- 1 Pages

Curvas Características DEL BJT
- 7 Pages

Bias Junction Transistor (BJT
- 1 Pages

Transistor BJT - VIDEO CAPTIONS
- 11 Pages

Summary - Bjt device equations
- 19 Pages

Problems BJT dc analysis
- 2 Pages

Amplificadores BJT y JFET
- 5 Pages

BJT circuit analysis Tutorial
- 7 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu