Hirarc AND Hazop PDF

| Title | Hirarc AND Hazop |
|---|---|
| Author | Syahir Amin |
| Course | Chemical Engineering |
| Institution | Universiti Teknologi MARA |
| Pages | 15 |
| File Size | 365.8 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 11 |
| Total Views | 146 |
Summary
.......
Description
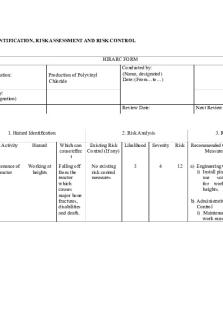
HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT AND RISK CONTROL
HIRARC FORM Company: Process/Location:
Production of Polyvinyl Chloride
Conducted by: (Name, designated) Date: (From…to…)
Approved by: (Name, designation) Date:
Review Date:
1. Hazard Identification
Next Review Date:
2. Risk Analysis
No.
Work Activity
Hazard
Which can cause/effec t
1.
Maintenance of Reactor
Working at heights
Falling off from the reactor which causes major bone fractures, disabilities and death.
Existing Risk Likelihood Control (If any) No existing risk control measures
3
3. Risk Control
Severity
Risk
Recommended Control Measures
4
12
a) Engineering Control i) Install platform or use scaffolding for working at heights. b) Administrative Control i) Maintenance work must be
PIC (Due date/status)
carried out by trained personnel. c) PPE Control i) Usage of safety harness. Working in confined space
Breathing difficulties
No existing risk control measures
3
2
6
a) Administrative Control i) Work must be performed by qualified and trained personnel. ii) Provide signage to identify confined spaces as a restricted access area only. b) PPE Control i) Wearing respiratory protection devices, eye protection and safety harness in confined space.
Low illumination
Limited vision and damage to eyesight
Fluorescent bulb or torch
3
3
9
a) Engineering Control i) Use more than one portable spot lights ii) Install torch at safety helmets.
Exposure to catalyst residue
Irritate and burn the skin and eyes
Safety helmet, gloves and eye protection
3
4
12 a) Engineering Control i) To enclose operations and install local exhaust ventilation.
Severe shortness of breath
b) Administrative Control i) Eye wash fountain should be provided in immediate work area c) PPE Control i) Provide clothing workers 2.
Maintenance of heater
Exposure to hot steam
Skin burn or first aid injury
Personal Protective Equipment
4
1
4
safety for
a) Administrative Control i) Provide heat
3.
Cleaning gas
Electrocution
compressor area
Potential
Personal
fatality or
Protective cloth
body
and equipment.
2
4
8
injuries
resistant gloves. a) Administrative Control i) Ensure electrical hand tool is in good condition. ii) Work must be performed by trained or competent personnel.
Inhalation of heavy smoke or exhaust fume
Chronic respiratory problems
Face mask and servicing
3
2
6
a) Administrative Control i) Ensure all workers used proper respiratory mask. ii) Briefing before start work.
Exposure to noise
4.
Moving heavy objects
Heavy objects falls
NoiseInduced hearing loss
Ear plugs or muffs and initial noise monitoring
3
Possible fatal and injuries
Forklift or slinging to move heavy objects
4
3
9
a) Administrative Control i) Ensure all workers must be inducted before commencing work. ii) Provide competent supervisor at site. iii) Ensure all workers properly equipped with ear plugs or muffs.
4
16
a) Administrative Control i) Ensure only trained personnel operates the forklift ii) Conduct lifting and slinging course for the workers.
5.
Walking on slippery floor
Slip and fall
Body injury and bone fracture
Usage of safety boots and avoid walking on greasy liquids
2
3
6
a) Engineering Control i) Install floor blower at places that are often slippery. ii) Install side bars or handles on staircase. b) Administrative Control i) Regular cleaning of floors from greasy liquids.
HAZARD AND OPERABILITY STUDY (HAZOP)
The technique of Hazard and Operability Studies, or in more common terms HAZOPS, has been used and developed over approximately four decades for 'identifying potential hazards and operability problems' caused by 'deviations from the design intent' of both new and existing process plants. Before progressing further, it might be as well to clarify some aspects of these statements.
HAZOP technique is accepted in the process industries for its intrinsic value as a safety management tool. While the structure of HAZOP is almost standard, the methods and techniques vary considerably. Increasingly, computers are being used to assist with the process of performing the HAZOP and for producing the documentation.
On conclusion of a HAZOP, there should be quality documentation to demonstrate that it was performed comprehensively, that the rationale was sound and that it provides an action plan. Statutory authorities now require, not only that HAZOP's be performed, but also that they be performed to some acceptable standards. This part discusses the issues of productivity in the performance of HAZOP and audibility of the results.
Productivity is an issue of interest to management, and audibility is an issue of interest to both management and statutory authorities. Accurate, quality documentation of HAZOP’s is important from the point of view of management accountability to satisfy both the statutory authorities and management’s own corporate responsibilities.
The Objectives of HAZOP
To identify hazards or deficiency and potential operability problems which may lead to hazards such as fire, explosion, toxic release or reduce productivity
To critically examine the inadequacies in systems by considering is as a fully integrated dynamic unit, rather than the ‘ad hoc’ design approach
To coordinate the various discipline involved in the project and provide a means for systematic analysis of the system
To reduce cost due to operability problems in increasingly larger and complexity plants so that profitability is increased.
To meet the legislative requirements for example, DOSH
To identify and prevent hazards in process plants that are growing in complexity with standards are no longer adequate.
HAZOP for Bubble Column Reactor (R-101) Project Name: Case Study of Bubble Column Reactor (R-101) Process: Production of polyvinyl chloride Section: No. Study Node Process Parameter Deviation 1. Reactor Vessel Pressure High
Low
Temperature
High
Possible Causes Pres sure controller failure. Thermal expansion in tank due to high temperature. L eaking of reactant feed. Valve not close tightly. Poor insulation. No cooling water flow. Uncontr olled reaction. Fire
Page: Date:
Assigned To:
Possible Consequence O verpressure in reactor. Ruptures of reactor vessel.
Action Required Install a pressure alarm. Install pressure relief valve.
Product produced Use a good material not followed the of construction at the standard required. pipeline.
Overheating at Install an the wall of reactor. excellent heat insulator. Ex plosion and Install rupture of vessel. cooling jacket. Instal l water sprinkler on top of the reactor. Start the cooling procedure
Low
2.
Cooling system (water)
Flow
Ver The gas y cold component can weather outside. become liquid. Excess Less reaction occurred. ive flow of cooling water. Incomplete reaction. .
Build a temperature alarm system where the system will notify the worker to readjust the system. Install a flow meter at the cooling water pipe.
High
Controller fails High pressure Install flow to operate. cause a pump control system to rupture. control the power Temperat used in pump. ure of the reactant Improve the and product will wiring system. drastically decrease.
Low
Leakage at High temperature of Improve pipeline. reactor. material of Minor construction for the failure at cooling pipeline. water system. Do troubleshoot and maintenance.
No
Temperature
High
Clogged in Temperature inside pipeline. the reactor increase. Flow controller fails to operate. Pu mp fail to pump the cooling water.
Malfunction of Temperature in the reactor increase. cooling water system.
Install backup
a
pump. Install flowmeter. Clean the pipeline. Observe the control system performance and so maintenance. Inst all high temperature alarm. Do troubleshoot and maintenance during shutdown period.
HAZOP for Evaporator (E-02) Project Name: Case Study of Evaporator (E-02) Process: Production of polyvinyl chloride Section: No. Study Node Process Parameter 1.
Heat Exchanger Flow
Page: Date: Deviation
Possible Consequence
Action Required
No
Pumping system fails Control valve not working Partially blockage in piping system.
Production failure Fail feed specification
Production failure. Fail feed specification
Low
Control valve not working Partially blockage in piping system. Pumping failure. Failure in valve. Too much pumping.
Production failure. Fail feed specification
Production failure. Fail feed specification
High temperature Less purity in product. Fail feed specification.
High temperature
Fail feed specification
High
Temperature
Possible Causes
Assigned To:
Less
Pipe leaking in transfer from shell
Fail feed specification
Less purity in product. Fail feed specification....
Similar Free PDFs
Hirarc AND Hazop
- 15 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu