Lab 4- Connective Tissue PDF

| Title | Lab 4- Connective Tissue |
|---|---|
| Author | Anonymous User |
| Course | Human Anatomy & Physiology l |
| Institution | Plymouth State University |
| Pages | 7 |
| File Size | 487.5 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 66 |
| Total Views | 134 |
Summary
Lab for understanding types of connective tissue...
Description
4.1
Lab 4: Connective Tissue Connective tissue is found through the body and is quite diverse in structure and function. It provides support and protection for vital organs as well as functioning as a connector between different structures. Additionally connective tissue functions as a space-filler between structures; has the ability to repair tissue damage, store fat and defends the body from infections. The main objective for this lab is to learn the structure and functional relationships of connective tissues. You will be viewing slides for identification of tissue, as well as structures associated with the tissue. Use the following table to guide you through the tissues. Please note: there may be more than one type of tissue on the slide. You need to make sure you know what you are looking at. Use your guide, text and following worksheet to assist you.
OBJECTIVES
To be identify connective tissue types and specific structures under the microscope. To know where these tissues may be found. To know the functions of connective tissues
MATERIALS
Prepared slides Lab Atlas Chapter 3 Attached pages
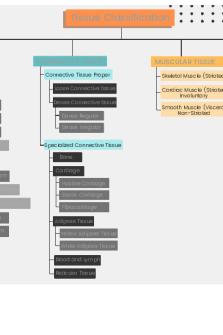
CONNECTIVE TISSUE General Information: The name connective tells what the function of the tissue is ... it binds other tissues and offers support and protection. EXAMPLE: cartilage, fat, tendons, and ligaments
All connective tissue types contains more or less of the following 3 components: o Fibers collagen - thicker fibers, non-stretchy, sturdy, flexible elastic - thin fibers, very stretchy, return to shape easily reticular - serves as a frame work for structure of organ o Ground substance (primarily water and protein) - forms extracellular matrix o Cells (many different types possible - type depends on tissue)
fibroblasts - produce fibers chondrocytes - produce cartilage adipocytes - fat-producing cells macrophages - cell eaters, remove foreign bodies from system
4.2
Often has lots of empty space. Generally named based on the fibers present as well as what the tissue looks like. Tissue: o Loose Connective (Areolar) - fibers are loosely arranged, vascular, with scattered fibroblasts o Dense Connective - tight fibers, few fibroblasts
regular (White Fibrous) - fibers tight, very organized, “neat” irregular - collagen fibers arranged in cris-crossed “pattern”
o Adipose - fat tissue, notice bags of empty space, squished nucleus o Cartilage - contains chondrocytes found in lacunae, ground substance
hyaline - very strong, no fibers elastic - contains elastic fibers, large lacunae
o Bone - very hard mostly matrix, contains osteocytes o Blood - we cover this next semester *** There are two other types of tissues ... III.
MUSCLE - We will cover muscle tissue later in the semester.
IV.
NERVES - We will cover this in the second semester.
TISSUE LOCATIONS Loose connective: under skin, under any epithelial White fibrous connective tissue: tendons, ligaments Adipose: anywhere there are clustered fat cells, around organs, under the Epidermis Hyaline cartilage: trachea, larynx, ribs, and ends of long bones (joints)
Elastic cartilage: external ear, epiglottis
4.3
Tissue Loose Connective Tissue/(Areolar) Contains three types of fibers Gel-like matrix/ ground substance Contains fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells and some blood cells Functions to cushion and bind organs Adipose Tissue
Matrix is sparse Packed with adipocytes with nuclei pushed to the side Functions to support and protect organs, provides insulation and stores fat.
Hyaline Cartilage
Contains chondrocytes interspersed throughout a network of collagen fibers. Firm gel-like matrix/ ground substance Functions to support, protect and provide a framework
Elastic Cartilage
Contains chondrocytes interspersed throughout threadlike elastic fibers. Firm gel-like matrix/ ground substance Provides strength and elasticity
Slide Name Areolar or Esophagus Trachea
Adipose or Trachea/ Esophagus
Hyaline Cartilage or Trachea/ Esophagus
Epiglottis
Tissue Found on the Slide
4.4 Dense Regular Connective Tissue
White fibrous Connective Tissue
Mainly uniform collagen fibers running in the same direction. Contains some elastic fibers Contains Fibroblasts Functions to bind body parts
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Disorganized collagen type 1 fibers Minimal amount of fibroblasts and other cells Amorphous ground substance http://www.pathguy.com/histo/052.htm
Compact Bone
Hard, calcified matrix. Contains osteocytes and collagen fibers Functions to protect and support, stores minerals and fat and location of blood cell formation.
Compact Bone
Assignment Instructions: for each of the tissues complete the following. Draw each tissue from what you see in the field of view of the microscope. Draw in color. Label each tissue with listed terms. Make sure your labels are clear. Answer the questions 1. Areolar (400x) 1. What is the function of this tissue? ________________________________________ ________________________________________ 2. Name two characteristics of this tissue. a) _________________________________ b) _________________________________
Label: Extracellular matrix/ ground
substance, Elastic Fibers, Collagen Fibers and Fibroblast Nucleus 2. Adipose Tissue (400x)
1. Name two places in the body where you would find this tissue. 1. ___________________________________ 2. ____________________________________
2. State two functions of this tissue. a) __________________________________ b) __________________________________ Label: Adipocyte and Cell Membrane
A-4.1
A-4.2
3. Hyaline Cartilage (400x) 1. Name two characteristics of this tissue. a) _________________________________ _________________________________ b) _________________________________ _________________________________ 2. Name one function of this tissue. _______________________________________ _______________________________________ Label: Lacunae, Chondrocyte, and
Extracellular matrix/ ground substance
4. Elastic Cartilage (400x) 1. Where in the body would you find this tissue? _____________________________________ 2. In regards to your answer for question 1, what is the advantage of having elastic cartilage in this location? _____________________________________ _____________________________________
Label: elastic fiber, lacunae, chondrocyte
A-4.3 5. Dense Regular Connective Tissue (100 or 400x)
1. What is the function of this tissue? _______________________________________ 2. What type of cells are found in this tissue? _______________________________________ _______________________________________
Label: individual fibers
6. Irregular Dense Connective Tissue (400X) 1. Where in the body would you find tissue? _______________________________________ _______________________________________
2. Name one function of this tissue. _______________________________________ _______________________________________ Label: collagen fibers and fibroblast 7. Compact Bone (400X) 1. What is the benefit to the concentric rings of connective bone? ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ 1b. What structure within bone contains the osteocyte?____________________________________
Label: osteon, central canal, lacunae and li li...
Similar Free PDFs

Lab 4- Connective Tissue
- 7 Pages

Connective tissue lab
- 3 Pages

Connective Tissue Table
- 1 Pages

Connective Tissue Chart
- 2 Pages

Connective Tissue Summary Table
- 3 Pages

Connective Tissue Reinforcement
- 1 Pages

Lab 3 Epithelial Tissue
- 7 Pages

Tissue and Skin Lab
- 17 Pages

Chapter 4 tissue review
- 39 Pages

Exercise 4 - Epithelial Tissue
- 5 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu