Managerial Economics Tutorial Paper PDF

| Title | Managerial Economics Tutorial Paper |
|---|---|
| Course | Bachelor of Science in Accountancy |
| Institution | Polytechnic University of the Philippines |
| Pages | 5 |
| File Size | 142.3 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 206 |
| Total Views | 859 |
Summary
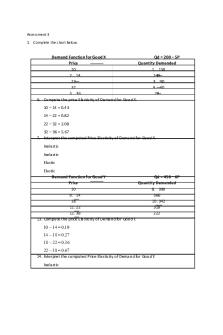
Assessment 3 Complete the chart below. Demand Function for Good X Qd = 200 – 5PPrice Quantity Demanded10 1. 1502. 14 13022 3. 9032 4. 405. 36 206. Compute the price Elasticity of Demand for Good X.10 – 14 = 0.14 – 22 = 0.22 – 32 = 2.32 – 36 = 5.7. Interpret the computed Price Elasticity of Demand fo...
Description
Assessment 3 1. Complete the chart below.
Demand Function for Good X Qd = 200 – 5P Price Quantity Demanded 10 1. 150 2. 14 130 22 3. 90 32 4. 40 5. 36 20 6. Compute the price Elasticity of Demand for Good X. 10 – 14 = 0.43 14 – 22 = 0.82 22 – 32 = 2.08 32 – 36 = 5.67 7. Interpret the computed Price Elasticity of Demand for Good X. Inelastic Inelastic Elastic Elastic Demand Function for Good Y Qd = 450 – 6P Price Quantity Demanded 10 8. 390 9. 14 366 18 10. 342 11. 22 318 12. 38 222 13. Compute the price Elasticity of Demand for Good Y. 10 – 14 = 0.19 14 – 18 = 0.27 18 – 22 = 0.36 22 – 38 = 0.67 14. Interpret the computed Price Elasticity of Demand for Good Y. Inelastic
Inelastic Inelastic Inelastic 15. Compute the Cross Elasticity of Demand for Good X to Y using the price of 18 and 22. – Bonus 16. Which type of good is Good Y to X? – Bonus 17. Compute the Income Elasticity of Demand for Good X when the income for the price of 18 is 18000 and for the price of 22 is 26000. Answer: Ei = -0.55 18. Which type of good is Good X? Answer: Good X is an inferior good. 19. Compute the Income Elasticity of Demand for Good Y when the income for the price of 18 is 18000 and for the price of 22 is 26000. Answer: Ei = -0.20 20. Which type of good is Good Y? Answer: Good Y is an inferior good. 2. You are given market data that says when the price of pesto bread is P4, the quantity demanded of pesto bread is 60 pieces and the quantity demanded of cheese bread is 100 pieces. When the price of pesto bread is P2, the quantity demanded of pesto bread is 80 pieces and the quantity demanded of cheese bread is 70 pieces. Calculate the price elasticity of demand for pesto bread. If the producer of pesto bread wants to increase its revenue, is it correct to increase/to decrease the price? Why?
Answer:
Qd 2−Qd 1 P 2− P 1 /¿ ÷ Qd 2+ Qd 1 P 2+P1 2 2 80 −60 2− 4 /¿ PED=¿ ÷ 80 + 60 2+4 2 2 20 −2 PED=¿ /¿ ÷ 70 3 PED =0.14−inelastic PED=¿
(
)(
(
)( )
)
If the producer of the pesto bread wants to increase its revenue, it is preferable to decrease its price. In my own perspective, decreasing the price of the pesto bread may attract customers. Even though it is in its decreased price, if the demand will increase, it will gain more profit.
3. Gary operates an automobile detailing business in his town in Laguna. An automobile detailer restores a car to the level of cleanliness and perfection that it had when it was new. His fastidious nature, attention to detail, and ability to effectively manage employees have helped to make his business profitable, but he believes that more information about the market would allow him to operate more efficiently. He uses regression analysis to estimate the demand function for his business and gets the following result: Qx = 235 - 3PX + 40A - 20U + 8PW The number of detailing jobs he gets per month (QX) depends on the price he charges per job (PX), his monthly advertising expenditures (A) measured in P1,000, the regional percentage unemployment rate (U), and the average price charged by local car wash businesses (PW) for a standard wash and wax. Use the estimated demand function given above to solve Problems 3.1 and 3.2. 3.1. Is a wash and wax at the local car wash a complement or a substitute for automobile detailing? How can you tell?
It was that a wash and wax at the local car wash is a substitute for automobile detailing. Using the cross-price elasticity of demand, which measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded for a good to a change in the price of another good, a negative cross elasticity denotes two products that are considered as complements, while a positive cross elasticity denotes two substitute products. In our case if Pw increases, then Qx increases too, so cross-price elasticity is positive, so a wash and wax at the local car wash is a substitute for automobile detailing.
3.2. Interpret the coefficients of the price he charges per job (PX), his monthly advertising expenditures (A) measured in P1,000, the regional percentage unemployment rate (U), and the average price charged by local car wash businesses (PW) for a standard wash and wax.
It means that Automobile detailing business is a normal good business. The slope coefficient associated with the variable U (the regional unemployment rate measured as a percentage) is an indirect, or proxy, measure of income. If the unemployment rate increases, then per capita income will generally decrease. Thus, since the slope coefficient is negative, an increase in unemployment (and decrease in income) will cause demand to decrease, which means that the good is normal.
3.3. Gary is currently charging P650 per detailing job and spending P3,500 per month on advertising. The regional unemployment rate is 7.5% and the average price of a wash and wax at a local car wash is P150. How many detailing jobs per month can Gary expect under these conditions?
Qx=235−3 PX + 40 A−20U + 8 PW Qx=235−3( 650)+ 40 (3500 )−20 U (7.5 % )+ 8(150 )
Qx=139 483.5
4. CASE STUDY A. LalaFast 21 LalaFast 21 is a major carrier based in the Philippines and has made a strategy of cutting fares drastically on certain routes with large effects on traffic in those markets. For example, on the Baguio-Cubao route the entry of LalaFast into the market caused average fares to fall by 48 percent and increased market revenue from P21,327,008 to P47,064,782 annually. On the Tuguegarao-Caloocan route, however, the average fare cut in the market when LalaFaST entered was 70 per cent and market revenue fell from an annual P66,201,553 to P33,101,514. Questions 1. Calculate the PEDs for the Baguio-Cubao route and Tuguegarao-Caloocan route. Answer: Total Revenue = (Quantity Demanded) (Price) % Change in Total Revenue = (% Change in Quantity) (% Change in Price) Baguio – Cubao Route % Change in Quantity = % Change in Total Revenue / % Change in Price % Change in Quantity = 75.27 / 48% % Change in quantity = 156.81 Price Elasticity of Demand = % Change in Quantity / % Change in Price Price Elasticity of Demand = 156.81 / 48 Price Elasticity of Demand = 3.27 Tuguegarao – Caloocan Route % Change in Quantity = % Change in Total Revenue / % Change in Price % Change in Quantity = 66.66 / 70% % Change in quantity = 95.23 Price Elasticity of Demand = % Change in Quantity / % Change in Price Price Elasticity of Demand = 95.23/ 70 Price Elasticity of Demand = 1.36 2. Explain why the above market elasticities might not apply specifically to Lalafast 21. It is because of the services provided by the Lalafast21. 3. If LalaFast 21 does experience a highly elastic demand on the Baguio-Cubao route, what is the profit implication of this? When they decreased the price total revenue will increases when the demand is elastic. Additional units that are sold are enough to make up for the lower price even though the price per unit is lower. It is because elastic demand rises from price
elasticity, the agency or company's price reduction resulted in an increase in revenue or profit. 4. Explain why the fare reduction on the Tuguegarao-Caloocan route a profitable strategy for LalaFast may still be. Tuguegarao – Caloocan Route have elastic demand but its earnings for the year decreased. Maybe, it is because they found another replacement service. Even though it has an elastic demand, it may still have a positive impact on their income growth. Furthermore, it is believed that the majority of people thinks that pricing is one of the most important aspects for consumers when making purchases. B. Nickey and Aididas Nickey and Aididas produce trainers in the sports-shoe market. For one of their main products they have the following demand curves: Nickey : Pn = 175 – 1.2Qn Aididas = Pa = 125 – 0.8Qa Where P is in Pesos and Q is in pairs per week. Questions: The firms are currently selling 80 and 75 pairs of their products per week respectively. 1. What are the current price elasticities for the products?
Nickey is 0.82 – inelastic, while for Adidas is 1.08 – elastic.
2. Assume that Nickey reduces its price and increases its sales to 90 pairs and that this also causes a fall in Aididas’s sales to 70 pairs per week. What is the cross-elasticity between the two products? Qx = 90 (Final) Px = 175 – 1.2(90) = 67
Qx = 80 (Initial) Px = 175 – 1.2(80) = 79
Change in Price of Nickey = 79 – 67 = 12 Change in Quantity of Nickey = 90 – 80 = 10
Qy = 70 (Final) Py = 125 – 0.8(70) = 69
Qy = 75 (Initial) Py = 125 – 0.8(75) = 65
Change in Price of Aididas = 69 – 65 = 4 Change in Quantity of Aididas = 75 – 70 = 5
Cross Elasticity = Py/Qx × ∆Qx/∆Px = 65/80 × 10/4 3. Is the above price reduction by Nickey to be recommended? Explain your answer. It is not recommended because of its elasticity which is inelastic of 0.82. When the demand for a product is inelastic, dropping the price causes the demand to vary less. As a result, total income is reduced. The result may mean that the company should not cut the price of its products because it would have negative impact....
Similar Free PDFs

Managerial Economics
- 8 Pages

managerial economics
- 44 Pages

Managerial Economics 2019 2020
- 6 Pages

Managerial-economics-principles
- 167 Pages

Managerial economics HM
- 4 Pages

BE 313 Managerial Economics
- 72 Pages

BUSN2043 - Managerial Economics
- 14 Pages

Managerial Economics MBA MCQ
- 27 Pages

Managerial Economics Assessment
- 4 Pages

Managerial economics tutor
- 3 Pages

Definition of Managerial Economics
- 11 Pages

Managerial Economics Lecture Notes
- 72 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu