Module 4 carbohydrates worksheet with answers PDF

| Title | Module 4 carbohydrates worksheet with answers |
|---|---|
| Course | Biochemistry And Molecular Biology |
| Institution | University of Melbourne |
| Pages | 4 |
| File Size | 242.4 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 80 |
| Total Views | 144 |
Summary
2021 tut...
Description
BCMB20002 Module 4 carbohydrates worksheet 1.
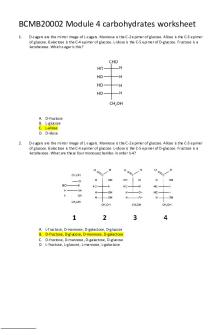
D-sugars are the mirror image of L-sugars. Mannose is the C-2 epimer of glucose. Allose is the C-3 epimer of glucose. Galactose is the C-4 epimer of glucose. L-idose is the C-5 epimer of D-glucose. Fructose is a ketohexose. Which sugar is this?
A. B. C. D. 2.
D-fructose L-glucose L-allose D-idose
D-sugars are the mirror image of L-sugars. Mannose is the C-2 epimer of glucose. Allose is the C-3 epimer of glucose. Galactose is the C-4 epimer of glucose. L-idose is the C-5 epimer of D-glucose. Fructose is a ketohexose. What are these four monosaccharides in order 1-4?
A. B. C. D.
L-fructose, D-mannose, D-galactose, D-glucose D-fructose, D-glucose, D-mannose, D-galactose D-fructose, D-mannose, D-galactose, D-glucose L-fructose, L-glucose, L-mannose, L-galactose
BCMB20002 Module 4 carbohydrates worksheet 3.
In the disaccharide below, 1 and 2 are both D-galactose.
Non-reducing end
Reducing end
A. Label the reducing and non-reducing ends of this disaccharide (1 mark) B. Name the glycosidic linkage that joins the two monosaccharides. (1 mark) α 1,4 C. Complete the diagram by drawing a D-glucose residue joined to monosaccharide 1 in a β1,3 linkage. (3 marks)
BCMB20002 Module 4 carbohydrates worksheet The next two questions relate to the image below:
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
What type of glycosidic linkage is shown? A.
α 1,4
B.
α 1,6
C.
β 1,4
D.
β 1,3
This image displays: A.
chitin, which is linked in the same way as cellulose but composed of modified monosaccharides.
B.
cellulose, which is stabilized by inter- and intra-chain hydrogen bonding.
C.
starch, which has an open helical structure.
D.
a branch point in glycogen.
Which one of the following statements about ABO blood groups is CORRECT? A.
Blood group A contains a terminal galactose residue.
B.
Blood group B has a terminal sialic acid residue.
C.
Blood groups A and B are synthesized by glycosyltransferases that recognise different carbohydrate acceptors.
D.
The O allele encodes an inactive enzyme.
Individuals with O type blood: A.
Have circulating antibodies against both the A and B blood group antigens.
B.
Do not have antibodies against either A, B or O blood group antigens.
C.
Are susceptible to infection because they lack circulating antibodies.
D.
Can safely receive A, B, AB and O type donor blood.
Which one of the following statements about carbohydrates is CORRECT? A.
Glucose residues in glycogen are joined by β-1,4 glycosidic linkages.
B.
Glycosyltransferases catalyse the biosynthesis of oligosaccharides by transfer of a monosaccharide from a nucleotide sugar to a carbohydrate acceptor.
BCMB20002 Module 4 carbohydrates worksheet
9.
10.
11.
C.
O-glycans are attached to the side chains of asparagine residues in proteins.
D.
Up to 11 different disaccharides can be generated using the two monosaccharides D-glucose and Dgalactose.
After a carbohydrate-rich meal, when the blood glucose concentration more than doubles, which of the following glucose transporters would be operating closest to its Vmax? A.
GLUT4, because its Kt is most similar to normal blood glucose levels.
B.
GLUT3, because it has a very low Kt, which protects the brain under starvation conditions.
C.
GLUT2, because it has a very high Kt, which helps regulate insulin production and removal of glucose from the blood.
D.
GLUT1, because it has a moderately low Kt, which provides a constant flow of glucose into most cells of the body to maintain their basal cellular functions.
If an individual inherits an O type blood group antigen allele from their mother and an A type blood group antigen allele from their father, they will have red cells expressing: A.
A type surface antigen only.
B.
O type surface antigen only.
C.
mixed A type and O type surface antigens.
D.
mixed A type and B type surface antigens.
Which of the following best describes the enzyme expressed from the O allele? A.
A fully folded inactive glcosyltransferase enzyme that does not recognise UDP-Gal
B.
A full-length, but unfolded glcosyltransferase enzyme
C.
An active glcosyltransferase enzyme that recognises the O antigen acceptor, but not UDP-gal or UDP-GalNAc
D.
A truncated glcosyltransferase enzyme that cannot fold....
Similar Free PDFs

Module 4 Carbohydrates
- 18 Pages

Carbohydrates worksheet
- 2 Pages

Protein Worksheet with Answers
- 4 Pages

Module 4 Worksheet
- 8 Pages

Module 4 Quiz Answers
- 1 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu