T03-tut Qanswers PDF
| Title | T03-tut Qanswers |
|---|---|
| Author | jiang yang |
| Course | Accounting and Financial Management 1B |
| Institution | University of New South Wales |
| Pages | 7 |
| File Size | 254.1 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 44 |
| Total Views | 136 |
Summary
T03-tut Qanswers...
Description
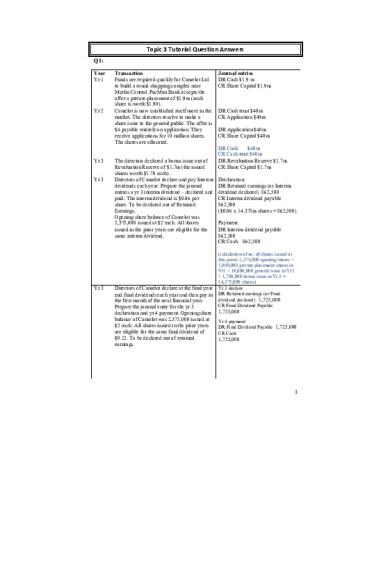
Topic 3 Tutorial Question Answers Q1: Year Yr 1
Yr 2
Yr 3
Yr 3
Yr 3
Transaction Funds are required quickly for Camelot Ltd to build a round shopping complex near Merlin Central. PacMan Bank accepts the offer a private placement of $1.9m (each share is worth $1.90). Camelot is now established itself more in the market. The directors resolve to make a share issue to the general public. The offer is $4 payable entirely on application. They receive applications for 10 million shares. The shares are allocated.
The directors declared a bonus issue out of Revaluation Reserve of $1.7m (the issued shares worth $1.70 each). Directors of Camelot declare and pay Interim dividends each year. Prepare the journal entries a yr 3 interim dividend – declared and paid. The interim dividend is $0.06 per share. To be declared out of Retained Earnings. Opening share balance of Camelot was 2,375,000 issued at $2 each. All shares issued in the prior years are eligible for the same interim dividend.
Directors of Camelot declare at the final year end final dividends each year and then pay in the first month of the next financial year. Prepare the journal entry for the yr 3 declaration and yr 4 payment. Opening share balance of Camelot was 2,375,000 issued at $2 each. All shares issued in the prior years are eligible for the same final dividend of $0.12. To be declared out of retained earnings.
Journal entries DR Cash $1.9 m CR Share Capital $1.9m
DR Cash trust $40m CR Application $40m DR Application $40m CR Share Capital $40m DR Cash $40m CR Cash trust $40m DR Revaluation Reserve $1.7m CR Share Capital $1.7m Declaration: DR Retained earnings (or Interim dividend declared) 862,500 CR Interim dividend payable 862,500 ($0.06 x 14.375m shares = 862,500) Payment: DR Interim dividend payable 862,500 CR Cash 862,500 (calculation of no. of shares issued at this point: 2,375,000 opening shares + 1,900,000 private placement shares in Yr1 + 10,000,000 general issue in Yr2 + 1,700,000 bonus issue in Yr 3 = 14,375,000 shares) Yr 3 declare DR Retained earnings (or Final dividend declared) 1,725,000 CR Final Dividend Payable
1,725,000 Yr 4 payment DR Final Dividend Payable 1,725,000 CR Cash
1,725,000
1
Year Yr 4
Yr 5
Yr 6
Every year
Transaction The directors of Camelot Ltd believe that it is difficult for institutional investors to obtain enough shares for a matched portfolio. The share price per share has also risen to $100 per share and they are concerned that this will deter investors from purchasing their shares compared to other industry shares. The directors resolve to do a 10 for 1 split and the balance of share capital is $18,350,000. Camelot’s management resolve to increase General Reserve with a transfer from Retained Earnings of $900,000. Camelot directors are now concerned that as a result of the share split they have too much issued share capital. It is resolved that a share-buy back of $1.9 million shares take place – on market with cash. The buy back takes place successfully. The issue price is equal to market price which the company paid to repurchase these shares. Transfer the following years profits and losses to the profit & loss statement Yr 1 Loss $40,000 Yr 6 Profit $998,000
Journal entries No journal entries
DR Retained Earnings 900,000 CR General Reserve 900,000 DR Share Capital CR Cash
$1.9 m $1.9 m
Yr 1 DR Retained Earnings $40,000 CR P&L Summary $40,000
Yr 6 DR P&L Summary $998,000 CR Retained Earnings $998,000
Q2: Cash Dividends, Bonus Issue and Share Split Indicate whether the following actions lead to an increase, decreases or have no effect on Company’s asset, liabilities or equity. A cash dividend of 5% of the share capital declared and paid out of retained profits. The company’s share capital is $500,000. The company declares and pay 1:5 bonus issue out of the company’s revaluation surplus. The company’s share capital is $500,000 and the value of the revaluation surplus is $200,000.
The company declares and perform a 3:1 share split. The company has 200,000 fully paid up shares.
Assets Decrease
Liabilities No Change
Equity Decrease
No Change
No Change
No Change
No Change
No change in total equity but revaluation surplus will decrease and share capital will increase. No Change
2
Q3: QUESTION 2 - Final Exam, 2013s1 (modified) The following transactions took place during the period ending 30 June 2016 for McKay Ltd: • • • • • • •
Transfer $15,000 from general reserve to retained profits Profit for the period was $780,000 Land was revalued upwards during the year by $45,000 for the year Bonus share issue from Revaluation Reserve of $50,000 Share issue received funds of $120,000 from investors and all shares applied for were allotted during the period. A bank loan of $34,000 was paid off with cash. Dividends declared and paid with cash during the period totalled $160,000.
Additional information: • •
Beginning balance of shareholder’s equity (1 July 2015) was $165,000. Assume there were no other transactions during the period than those mentioned above.
Required: PART A: Calculate the ending balance of shareholders’ equity using the information above. Shareholder’s Equity Dividend payable 1mrk C/b
160,000
165,000 780,000 45,000 120,000
o/b Profit 1mrk Revaluation upwards 1mrk Share issue 1mrk
950,000 . 1,110,000 1,110,000
DO NOT WRITE OUTSIDE THE BOX
3
PART B: Prepare the T-accounts for Retained Profits, Share Capital, General Reserve and Revaluation Reserve for McKay Ltd at 30 June 2016. The following balances are provided as at 1 July 2015: Retained Profits Share Capital Revaluation Reserve General Reserve Total Shareholder’s Equity
$ 40,000 49,000 56,000 20,000 $165,000
Retained Profits Dividend Payable 160 40 o/b 15 General Reserve c/b 675 780 Profit (Transferred In) 835 835 Share Capital a/c 49 o/b 50 Revaluation Reserve (bonus issue) c/b 219 120 (share issue) 219 219
Revaluation Reserve Share Capital 50 56 o/b c/b 51 45 Land 101 101
General Reserve 20 o/b c/b 35 15 Retained Profits 35 35 DO NOT WRITE OUTSIDE THE BOX
4
Q4 Part 1
Scenario Sussex Ltd receives a non-refundable upfront fee $90,000 from Harrington Ltd on 1 March 2012. Under the agreement with Harrington Ltd, Sussex Ltd must provide on-going advice services until 1 March 2016
Part 2
O’Neill Ltd’s Skiing gear shop sells skiing gear to a customer worth $1,000 for cash on 1 June 2012. The customer has the ability to return the goods during a 7 day return period.
Analysis? and Recognition This is because Sussex Ltd is obligated to provide on-going management services. Recognise as revenue and record as earned in a straightline-basis over the contract period. As there is a reliable estimate of any potential future returns. Revenue – recognize at point of sale – 1 June 2012
Journal entries for the REVENUE DR Cash 90,000 CR Unearned Advice Fee 90,000 (up front fee) Earn straight-line, sum of the entries: DR Unearned Advice Fees 90,000 CR Advice Fees Revenue 90,000
It is when the provision of the product is fully completed when shipped out to the customer. Revenue is recognized when shipped. Dell does not guarantee delivery. Thus their obligation is only up to the construction and shipping of the goods.
10/1/2013
Sale: 1 June 2012 DR Cash 1,000 CR Sales Revenue 1,000
Typically O’Neill Ltd estimates that 1% of customers will return the skiing gear as they have a strict returns policy – returns can only be made if the size is incorrect or the product is faulty and it only allows exchange of goods. Sales revenue for the year was $1.5 million. Part 3
A customer in Sydney places an online order for a laptop computer with Dell computers on 10 January 2013 for $599, and pays via direct bank account transfer. Assembly for the laptop is completed on 15 January 2013, and is shipped on 16 January 2013 from its assembly facility in Penang, Malaysia. The customer receives it on 22 January 2013. Dell always uses a third party shipping company, FedEx to deliver the products to their customers.
DR Cash 599 CR Unearned revenue 599 On 16 January 2013 for $599: DR Unearned revenue 599 CR Sales Revenue 599
5
What-if Analysis Q5
Scenario
Analysis of the accounting change
Accounts affected: COGS Part McKay Ltd, an electronic games store, has considering to switch from and Ending Inventories 1 weighted average to FIFO for inventory valuation. Prices are rising over this period and the cost per unit of GateGear Game is now $90, whereas the first units purchased for their period were $40. The increase is due to the release of the film by the same name. There were 1,000 units purchased at $40 and 100 purchased at $90. Ending inventory for the period contained 50 units. Sales price per unit is $200 and remained constant over the period. Part Granger Cause Wine company has currently been depreciating their 2 white-wine processing plant over a 30 year period. The directors of the company would like to compare with if they used a 10 year useful life. Assume that the company purchase price of the plant was $1,200,000 and you are depreciating for the financial year. They believe that there is evidence a newer model of processing plant is soon to be released.
Explanation: Weighted average (WA) would smooth out the cost per unit, rather than FIFO. FIFO would include the first unit cost in COGS and leave the later, more expense units in ending inventories.
Accounts affected: Depreciation expense will increase per period and Accumulated depreciation will be increased per period. Carrying amount will be reduced at higher amount each period. Net profit would be lower with the higher depreciation expense per period. This would reduce the tax payable as well on profits.
(1) What if
(2) What if
WA: Average cost = (($40 x 1000 units) + ($90 x 100units)) / 1,100 = $44.55 round Ending inventory = $44.55 x 50 = $2,227.50 COGS = (1,100 – 50) x $44.55 = 46,777.50 Gross Profit = ($200 x 1,050) $46,777.50 =163,222.50
FIFO Ending inventory = $90 x 50 units = $4,500 COGS = (1,000 x $40) + (50 x $90) = 44,500
Depreciation over a 30 year period: $1.2m / 30 years = $40,000 per annum
Depreciation over a 10 year period: $1.2m / 10 years = $120,000 per annum Net profit would be lower.
Gross Profit = ($200 x 1,050) -44,500 =$165,500
6
Q5
Scenario
Part Jackson Ltd constructs football 3 stadiums. The directors would like you to provide analysis if the company had used the completed contract method instead of the percentage of completion method for their New-Village Stadium (5 year completion of project).
Analysis of the accounting change Accounts: Retained Profits Revenue Income tax expense If the company had used completion of contract method instead of % completion they wouldn’t have been able to recognise profits except in the final year. Profits would be higher in years 1 to 4 in the % of completion method compared to Completion of contract. Completion of contract method would recognise all profits in Yr 5. This is a less ‘smooth’ earning of revenues and recognition of expenses than under the completion of contract method.
(1) What if
(2) What if
% of completion: Yrs 1 to 5 have profits recorded Yrs 1 to 5 have taxes on profits
On completion: Yrs 1 to 4 have zero profit recorded Yr 5 has all the profits of the project recorded and tax on profit.
7...
Similar Free PDFs

T03-tut Qanswers
- 7 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu