Unit 8 Monetary Policy Problem Set #8 PDF

| Title | Unit 8 Monetary Policy Problem Set #8 |
|---|---|
| Course | AP Macroeconomics |
| Institution | High School - USA |
| Pages | 3 |
| File Size | 214 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 29 |
| Total Views | 166 |
Summary
Monetary Policy Problem Set...
Description
Unit 8 Problem Set #8 1. a.
b.
4.76% 2.46% There was a stock market crash during your term.
c. 2. a. Money is defined as any asset that can easily be used to purchase goods and services. The first function of money is Medium of Exchange which means that money can easily be used to buy goods and services with no complications of barter system. The second function of money is Unit of Account which means that money measures the value of all goods and services, and it acts as a measurement of value. The third function of money is Store of Value which means that money gives you store purchasing power for the future, and it doesn’t die or spoil. Fiat money is paper money that people accept for goods and services. It is valuable because the government says it is, whereas commodity money is money that has intrinsic value or other uses, and representative money is paper money that can be traded for a fixed amount of commodity money. b. Liquidity is the ease with which an asset can be accessed and converted into cash or in other words liquidized. M0 consists of currency and coins in circulation. M1 consists of M0, checking accounts, and traveler’s checks. M2 consists of M0, M1, savings accounts, money markets, and short-term deposits. M0 is the most liquid and M2 is the least liquid type of money. c. The money multiplier measures how much the bank has to keep and lend out when someone makes a deposit. The reserve requirement is the percentage of a person’s deposit the bank has to keep. Of a $1000 deposit, the bank would have to keep $100, and they can lend out $900. There will be 10($1000)$1000 = $9000 new money.
d. The demand shifters are changes in price level, changes in income, and changes in investment taxes. The money supply is set by the Federal Reserve.
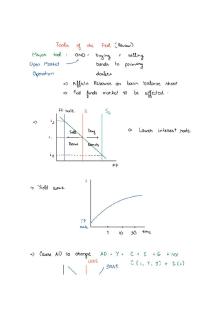
e. Loanable Funds Market is where borrowers and savers or lenders meet to buy and sell money, and Real Interest Rates are the price. It is the private sector supply and demand of loans. The demand shifters are a change in perceived business opportunities and a change in government borrowing. The supply shifters are a change in private or public savings behavior, a change in foreign investment, and a change in expected profitability. The government can “crowd out” private investors by borrowing from the private sector and spending money.
3. a. The three tools are the reserve requirement ratio, the discount rate, and the open market operations. RRR is the percent the bank can’t lend out. The Discount Rate is the interest rate that the Fed charges private banks. Open Market Operations is when the Fed buys or sells government bonds. To increase the money supply, the Fed can lower RRR, lower the discount rate, and buy bonds in the open market. To decrease the money supply, the Fed can increase RRR, increase the discount rate, and sell bonds in the open market. b. The Quantity Theory of Money is Money Supply x Velocity = Price x Quantity where velocity of money is the average times a dollar is spent and re-spent in a year. c.
d. Banks use balance sheets to keep track of all their assets and liabilities. Demand Deposit is money deposited in a checking account. Required Reserves is the deposited money the bank has to hold on to. Excess Reserves is the extra money that can be loaned out....
Similar Free PDFs

Problem Set 8 - Solutions
- 3 Pages

Chapter 8 problem set
- 5 Pages

Problem set 8 solution
- 6 Pages

Practice Problem Set 8 MRP Solutions
- 15 Pages

8-1 Problem Set Chapter 13
- 8 Pages
Chapter 16 Monetary Policy
- 3 Pages

Chapter-5 - Monetary policy
- 11 Pages

A) Monetary policy - pdf
- 4 Pages

601 UNIT 7 Problem Set
- 2 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu






