1 Introduction to Bioinorganic chemistry Unit 1 PDF

| Title | 1 Introduction to Bioinorganic chemistry Unit 1 |
|---|---|
| Course | Essential and trace leiments |
| Institution | Aligarh Muslim University |
| Pages | 12 |
| File Size | 1.1 MB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 37 |
| Total Views | 163 |
Summary
Introduction of Bio-inorganic Chemistry...
Description
31-08-2018
Lecture Course Title Date
:1 :Bioinorganic chemistry and metalloenzymes. :2nd August 2018
Course code
:CHM 413
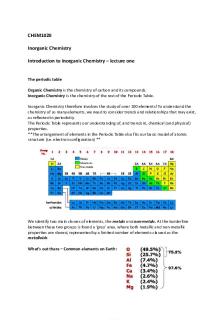
Introduction to Bioinorganic chemistry
Instructor :Dr. Pankaj Kumar Koli
Detailed Syllabus Unit-I Essential and trace metal ions in biological system. Deficiency/excess of Mn, Co, and Zn metal ions. Structure of chlorophyll, Photosynthesis, Photo system I and Photo system II. Unit-II Metalloenzymes; cytochromes and iron-sulphur proteins, nitrogen fixation, Zinc enzymes; carboxypeptidase, carbonic anhydrase. Iron enzymes-catalase and peroxidase. Unit-III General aspects of chemistry of dioxygen, Fe, Cu and Co. Nature of M-O2 linkage, heme proteins, molecular mechanism of oxygenases, Copper enzyme–superoxide dismutase. Cobalt enzyme; Cyanocobalamin. Biochemical bases of essential metal deficiency with special reference to Cu, Zn. Unit-IV Complexes of transition metal (Pt) as anticancer agent, mechanism of action. Toxic effect of Pt complexes to human body. Carbonic anhydrase and its mechanism of action super oxide dismutase. Mechanism of dismulation of super oxide ion.
1
31-08-2018
Books Recommended And Study Materials 1. Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry, S.J. Lippard and J.M. Berg, University Science Books. 2. Bioinorganic Chemistry, I. Bertini, H.B. Gray, S.J. Lippard and J.S. Valentine, University Science Books. 3. Inorganic Biochemistry, vols I and II. ed., G.L. Eichhorn, Elsevier. 4. Progress in Inorganic Chemistry, Vols. 18 and 38 ed. J.J. Lippard, Eiley. 5. Inorg. Chemistry by Shriver Alkem Oxford University Press. 6. Modern Inorg. Chemistry by W. Jolly, 2nd Edition Mc Graw Hill Inc. 7. Bioinorganic Chemistry by A.K. Das CBS Publication & distribution.
Bioinorganic Chemistry: A New field
2
31-08-2018
Periodic table of Life
BioInorganic chemistry Study of Inorganic elements in the living systems
Sodium potassium pump (1/5th of all the ATP used)
Hemoglobin Myoglobin Cytochromes Ferredoxin
Vit B12
Hemocyanin
Carbonic anhydrase Carboxypeptidase
Xanthine Oxidase Aldehyde Oxidase
3
31-08-2018
Important roles metals play in biochemistry 1. Regulatory Action
Sodium potassium channels and pump
Na, K
Nerve signals and impulses, action potential, muscle contraction
2. Structural Role
Calcium in bones, teeth
Ca, Mg
provide strength and rigidity
3. Electron transfer agents
Cytochromes: redox intermediates
Fe2+/Fe3+
membrane-bound proteins that contain heme groups and carry out electron transport in Oxidative phosphorylation
4. Metalloenzymes
Carbonic anhydrase, Carboxypeptidase
Zn
biocatalysts, CO2 to HCO3 −, protein digestion
5. Oxygen carriers and storage Fe, Cu
Hemoglobin, Myoglobin, Hemocyanin 18 times more energy from glucose in presence of O2
6. Metallo coenzymes Co
Vitamin B 12 biomethylation
● Mammals are believed to use only 25 of the known elements ● 96% of our body is made up of C,H,N,O ● Even Though some elements are present in very small quantities in body, they maintains essential functions.
4
31-08-2018
Transition Metals in Biomolecules Iron Most abundant metal in biology, used by all plants and animals including bacteria. Some roles duplicated by other metals, while others are unique to Fe. Iron use has survived the evolution of the O2 atmosphere on earth and the instability of Fe(II) with respect to oxidation to Fe(III). Zinc Relatively abundant metal. Major concentration in metallothionein (which also serves as a reservoir for other metals, e.g. Cd, Cu, Hg). Many well characterized Zn proteins, including redox proteins, hydrolases and nucleic acid binding proteins. Copper Often participatse together with Fe in proteins or has equivalent redox roles in same biological reactions. Reversible O2 binding, O2 activation, electron transfer, O2- dismutation (SOD), NO biosynthesis. Cobalt Unique biological role in cobalamin (B12-coenzymes) isomerization reactions. Manganese Critical role in photosynthetic reaction centers, and SOD enzymes. Molybdenum Central role in nitrogenase enzymes catalyzing N2 NH3, NO3 NH3 Chromium, Vanadium and Nickel Small quantities, uncertain biological roles. Sugar metabolism (Cr); Ni only in plants and bacteria (role in CH4 production) and SOD enzymes.
Structure of a metallo-protein : A metal complex perspective Spiral - α helix form of protein
Tape - β Pleated sheet form of protein
Prosthetic groups – A metal complex positioned in a crevice. Some of the ligands for this complex or some times all f the ligands are provided by the side groups of the amino acid units. The geometry around the metal and bond distances and angles are decided by the protein unit
Myoglobin
Carbonic anhydrase
5
31-08-2018
Metalloenzymes and Oxygen carriers = Protein + Cofactor A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes. Cofactors are either organic or inorganic. They can also be classified depending on how tightly they bind to an enzyme, with loosely-bound or protein-free cofactors termed coenzymes and tightly-bound cofactors termed prosthetic groups. Porphyrins with different are a metals at its centre common prosthetic group in bioinorganic chemistry
Cytochrome C
Coenzyme B12
Hemocyanin
Myoglobin
Chlorophyll
ProtoporphyrinIXandHeme
15 different ways to arrange the substituents around the porphyrin. Only one isomer, protopophyrin IX is found in the living system. Porphyrins are planar and aromatic
6
31-08-2018
Proteins–consistsofdifferentaminoacidsinaspecificsequenceconnectedbythepeptidebond–
A few important amino acids relevant to the present course
HISTDINE This amino acid has a pKa of 6.5. This means that, at physiologically relevant pH values, relatively small shifts in pH will change its average charge. Below a pH of 6, the imidazole ring is mostly protonated.
GLUTAMIC ACID has carboxylic acid functional group which is hydrophilic, has pKa of 4.1 and exists in its negatively charged deprotonated carboxylate form at physiological pH ranging from 7.35 to 7.45.
VALINE is a branched-chain amino acid having a hydrophobic isopropyl R group. In sickle-cell disease, valine substitutes for the hydrophilic amino acid, glutamic acid, in hemoglobin. Valine is hydrophobic
SERINE is an amino acid having a CH2OH side group. By virtue of the hydroxyl group, serine is classified as a polar amino acid. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865.
7
31-08-2018
Theprimarystructureofaprotein
Thefourlevelsofproteinstructure
Hbondbetweensidechains, hydrophobicinteractions, disulfurlinkages,electrostatic interactions
Seeyoutube video“proteinstructure”Univ ofSurrey’
8
31-08-2018
Hemoglobin‐ aquaternarystructureofaprotein
4 units, Each unit has a prosthetic group (heme) embedded in a crevice and partly coordinated by histidine units
Inorganic Active site / Prosthetic group
In molecular biology, the active site (prosthetic group) is part of an enzyme where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction. It can perform its function only when it is associated with the protein unit Heme in Myoglobin (O2 storage)
Ferredoxin (e transfer)
Nitrogen Fixation Carbonic anhydrase Enzyme
9
31-08-2018
Inorganic Prosthetic group of three well known oxygen carriers
Presentin Vertebrates
Presentin molluscs
Presentinsomesea worms
Hemoglobin S (Sickle Cell Anaemia)
Sickle-cell anaemia is caused by a mutation in the β-globin chain of haemoglobin, causing a hydrophilic amino acid glutamic acid to be replaced with the hydrophobic amino acid valine. In areas where malaria is a problem, people's chances of survival actually increase if they carry sickle-cell trait (Carrier). The malaria parasite has a complex life cycle and spends part of it in red blood cells. In a carrier, the presence of the malaria parasite causes the red blood cells with defective haemoglobin to rupture prematurely, making the plasmodium unable to reproduce. The polymerization of Hb S affects the ability of the parasite to digest Hb.
10
31-08-2018
Role in Medicine and diagnosis Some very toxic metals (e.g. Hg and As) were used to treat syphilis and other infections in the past. Hg is still used today: amalgam, skin lightening cream, eye drops, nasal sprays. Nowadays, inorganic pharmaceuticals are becoming more and more important in medicine
Cardiolyte is a radioactive imaging agent to assess blood flow through heart. It is an Isonitrile complex which uses of 99mTc (generated from 98Mo by irradiation with neutrons; t1/2 = 6 h). Cardiolyte’s advantages: Readily taken up by blood and tissues. Rapid clearance without evidence of metabolism
Chemistry at active site of Hemerythrin (Hr)
Hemerythrin
proton-coupled electron transfer evidence for proton transfer comes from resonance Raman work
11
31-08-2018
Early Structural Models for Deoxy-hemerythrin
None does the chemistry of the protein!
Functionally relevant model of Hemerythrin
O-Ligand
Product matches protein Mössbauer, resonance Raman, UV-vis spectra Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 4662-4673
10.1021/ic010076b
12...
Similar Free PDFs

UNIT 1 Introduction TO ICT
- 7 Pages

Unit 1: Introduction to MedSurge
- 10 Pages

1. Introduction to Hematology
- 1 Pages

Chemistry Unit 1 exam Questions
- 22 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu