Activity COST AND COST Analysis PDF

| Title | Activity COST AND COST Analysis |
|---|---|
| Author | Leizel Ruiz |
| Course | Cost Accounting |
| Institution | Cagayan State University |
| Pages | 5 |
| File Size | 104.2 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 173 |
| Total Views | 367 |
Summary
ACTIVITY COST AND COST ANALYSISNite Corporation has developed the following flexible budget formula for annual indirect labor costs:Total Cost = P480,000 + P5 per machine hourOperating budgets for the current month are based upon 20, machine hours of planned machine time. Indirect labor costs includ...
Description
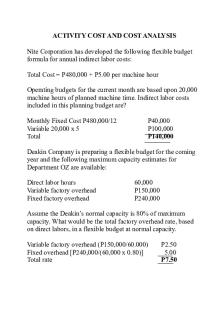
ACTIVITY COST AND COST ANALYSIS Nite Corporation has developed the following flexible budget formula for annual indirect labor costs: Total Cost = P480,000 + P5.00 per machine hour Operating budgets for the current month are based upon 20,000 machine hours of planned machine time. Indirect labor costs included in this planning budget are? Monthly Fixed Cost P480,000/12 Variable 20,000 x 5 Total
P40,000 P100,000 P140,000
Deakin Company is preparing a flexible budget for the coming year and the following maximum capacity estimates for Department OZ are available: Direct labor hours Variable factory overhead Fixed factory overhead
60,000 P150,000 P240,000
Assume the Deakin’s normal capacity is 80% of maximum capacity. What would be the total factory overhead rate, based on direct labors, in a flexible budget at normal capacity. Variable factory overhead (P150,000/60.000) Fixed overhead [P240,000/(60,000 x 0.80)] Total rate
P2.50 5.00 P7.50
At a sales level of P300,000, Jamaica Company’s gross margin is P15,000 less than its contribution margin, its net income is P50,000, and its selling and administrative expenses total P120,000. At this sales level, its contribution margin would be: Net Income Add: selling and admin expense Gross Margin Add: excess of contribution margin over gross margin Contribution margin
P50,000 P120,000 P170,000 P15,000 P185,000
During the month of June, Behold Corporation produced 12,000 units and sold them for P20 per unit. Total fixed costs for the period were P154,000, and the operating profit was P26,000. Based on the foregoing information, the variable cost per unit for the month of June was: Contribution margin per unit: (P154,000 + P26,000) / 12,000 units Variable cost per unit: P20.00 – P15.00
P15.00 P5.00
Data to be used in applying the high-low method shows the highest cost of P69,000 and the lowest cost of P52,000. The data show P148,000 as the highest level of sales and P97,000 as the lowest level. What is the variable cost per peso sale? Change in cost / Change in sales = Variable cost per peso sale (P69,000 – P52,000) / (P148,000 – P97,000) P17,000 / P51,000 = P0.33
Given the following information, choose the cost and activity that would be used as the high data point in high-low cost estimation: Costs Activity (hours) P51,000 40,000 P50,000 41,000 P58,000 42,000 P56,000 43,000 P56,000 43,000 Use the following simple regression results based on the data from the Madrigal Corporation to answer Question Nos. 1 and 2 Dependent Variable – Machine maintenance costs Independent Variable – Machine hours Computed Values Intercept P3,500 Coefficient on independent variable P3.50 Coefficient of correlation 0.856 2 R 0.733 1. What percentage of the variation in maintenance costs is explained by the independent variable? 73.3% 2. What is the total maintenance cost for an estimated activity level of 20,000 machine hours? Variable Cost 20,000 x 3.5 Fixed Cost Total
P70,000 P3,500 P73,500
Cherokee Company applies factory overhead on the basis of direct labor hours. Budget and actual data for direct labor and overhead for the year are as follows: Budget Actual Direct labor hours 600,000 650,000 Factory overhead costs $720,000 $760,000 The factory overhead for Cherokee for the year is: A. overapplied by $20,000 B. overapplied by $40,000 C. underapplied by $20,000 D. underapplied by $40,000 E. neither underapplied nor overapplied
At the end of the year, Paola Company had the following account balances after applied factory overhead had been closed to Factory Overhead Control: Factory Overhead Control Cost of Goods Sold Work in Process Finished Goods
$ 1,000 CR 980,000 DR 38,000 DR 82,000 DR
The most common treatment of the balance in Factory Overhead Control would be to: A. carry it as a deferred credit on the balance sheet B. report it as miscellaneous operating revenue on the income statement C. credit it to Cost of Goods Sold
D.
prorate it between Work in Process and Finished
Goods E. prorate it among Work in Process, Finished Goods, and Cost of Goods Sold...
Similar Free PDFs
Activity COST AND COST Analysis
- 5 Pages

Cost Accounting Basic Activity
- 11 Pages

Cost volume profit analysis
- 11 Pages

Tb ch03-cost-analysis
- 11 Pages

Cost control analysis
- 2 Pages

FULL COST :: Direct COST
- 1 Pages

Cost Behavior - Cost Accounting
- 78 Pages

COST Acctg 2 - cost
- 1 Pages

Cost Analysis Template for PDF
- 5 Pages

M7 Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
- 2 Pages

Cost hw - Cost accounting homework
- 18 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu




