Biology Gizmo - Cell Division PDF

| Title | Biology Gizmo - Cell Division |
|---|---|
| Course | Psychology 104 |
| Institution | University of Alberta |
| Pages | 5 |
| File Size | 175.9 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 80 |
| Total Views | 175 |
Summary
gizmo...
Description
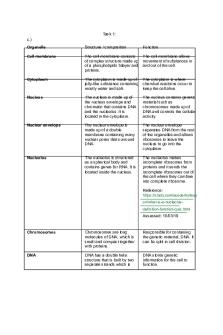
Biology Gizmo - Cell Division Prior Knowledge Questions: 1. Cells reproduce by splitting in half, a process called cell division. What do cells need to do between divisions to make sure that they don’t just get smaller and smaller? They need to grow between divisions to ensure that they don’t get smaller. 2. The genetic information of a cell is carried in its DNA (short for deoxyribonucleic acid). What do cells need to do between divisions to make sure that a full set of DNA gets passed on to each daughter cell? The DNA must be copied so there is a full set of DNA to pass on to each daughter cell. Gizmo Warm-up: 1. Look at the cells. Do they all look the same? Yes they all look the same 2. Cells that are in the process of dividing are said to be in mitosis or cytokinesis. Cells that are not dividing are in interphases. a. Of the 100 cells shown, how many are in the process of dividing? 20 b. How many cells are in the interphase stage of their life cycle? 80 c. Based on these two observations, would you say that a cell spends most of its life cycle in interphase or in mitosis/cytokinesis? I would say that a cell spends most of its life cycle in interphase. Activity A: Phases of the cell cycle Question: What are the stages of the cell cycle? 1. Observe: Click Play and hold the cursor over the cell. Observe the cell as it divides several times. (This happens quickly!) What do you notice happening during this process? You can see the chromosomes line up then separate and then you see two nucleuses then the cell splits.
2.Summarize: On the DESCRIPTION pane, read about each phase in the cell cycle. In the spaces below, sketch the cell in each phase and summarize what occurs in your own words.
Phase
Interphase
Prophase
Sketch
Summary The cell grows and develops by forming organelles and replicating its DNA.
The nuclear membrane disappears, and the chromatin condenses into chromosomes. Spindle fibres develop between centrioles that travel to opposing ends of the cell.
Metaphase
The spindle fibres bring the chromosomes together to align them on the equator.
Anaphase
The fibres separate the chromosomes, and the chromatids travel to different ends of the cell.
Telophase
A nucleus develops around each chromosome, and the chromosomes unravel into chromatin.
Cytokinesis
The cell membrane pinches the cell and splits it into two daughter cells.
1. Analyze: Use your summaries and the Gizmo to answer the following questions: a. What are the four phases of mitosis? Anaphase, telophase, interphase, and metaphase. b. During which phase is the DNA duplicated? DNA is duplicated in interphase.
c. What is the relationship between chromatin and chromosomes? Chromatin is a substance within chromosomes consisting of DNA and protein. d. In which phase are chromatids pulled apart? Chromosomes are pulled apart in anaphase.
e. What is the role of the centrioles? They gave spindle fibers around them and they help determine the location of the nucleus. f.
In which phase does a new nuclear membrane develop? A new nuclear membrane develops in telophase.
g. A cell has a single line of chromosomes. What is the phase? The phase is Metaphase. h. During which three phases are individual chromosomes no longer visible? Cytokinesis, telophase, and interphase. 4. Think and discuss: Why is it important that the cell’s DNA is duplicated before cell division? Before the cell splits, the DNA must be reproduced so that both new daughter cells have the same amount of DNA. 5. Challenge: Human cells have 46 chromosomes. Each chromosome consists of a pair of identical chromatids attached together by a structure called a centromere. Once the chromosome has split, each chromatid is called a daughter chromosome. At the end of cytokinesis, how many daughter chromosomes will be found in each cell? Explain. There will be 0 since the chromatids disintegrate into chromatin during telophase before cytokinesis.
Activity B - Duration of phases: Question: What is the relative duration of each phase of the cell cycle? 1. Collect data: Set the Cycle Length to 10 hours and click Play. Click Pause when the maximum number of cells has been reached. On the TABLE tab, click Record data.
Record the number of cells in each phase of the cell cycle in the table below. Then click Play, wait for a while, and click Record data again. Repeat this process until you have recorded four sets of results, and then find the average number of cells in each phase.
Trial
Interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
1
78
10
3
2
3
4
2
80
10
3
3
3
1
3
82
10
3
1
2
2
4
80
11
3
1
3
2
Avg.
80
10.25
3
1.75
2.75
2.25
2. Analyze: Which phase of the cell cycle is the longest? Shortest? The longest phase is interphase and the shortest is anaphase.
Explain your answers: The more cells in a cycle the longer it takes and the less cells in a cycle the shorter it takes 1. Calculate: You can use your data to estimate the duration of each phase of the cell cycle. For example, if 8% of the cells were in prophase and the cell cycle was 10 hours long, then prophase would last 8% of 10 hours, or 0.8 hours (48 minutes). Use percentages to estimate the duration of each phase of the cell cycle. Show your work. Interphase: 0.845×10=8.45 8hr27 min Prophase: 0.077×10=0.77 46.2 min Metaphase: 0.01×10= 0.1 6 min Anaphase: 0.025×10=0.25 15 min Telophase: 0.02×10=0.2 12 min Cytokinesis: 0.03×10=0.3 18 mi Extension - Cell populations Question: How quickly do cells multiply? 1. Collect data: Click Play to start a new simulation. Click Pause when the maximum number of cells is reached. View the total number of cells on the GRAPH tab. What is the general shape of the graph? Parabola 2. Analyze: Look closely at the graph. a. About how long did it take to grow the first 20 cells? 25 hours
a. About how long did it take to grow the last 20 cells? 2 hours b. Would you say the rate of cell growth is increasing or decreasing? Explain. It is rising since producing 20 cells takes less time. Furthermore, the grown graph’s slope steadily increases
3. Extend your thinking: In living organisms, the cell cycle is closely regulated. What do you think will happen if cell division is not controlled? If it is not managed, cells can either create too many cells too rapidly, resulting in abscesses and masses in the body, or generate too few cells, putting pressure on and harming other regions and blocking functioning. If they produce insufficiently, the body will be deprived of cells that perform a certain role, threatening balance....
Similar Free PDFs

Biology Gizmo - Cell Division
- 5 Pages

Gizmo CELL Division - Lab
- 3 Pages

Cell Division Gizmo 2021 Part 2
- 4 Pages

2 - Cell & Cell Division & Epithelia
- 30 Pages

Cell Division SE - bio
- 5 Pages

Cell Division SE 1241241
- 5 Pages

Cell+division - Lab
- 3 Pages

Cell Division Lab Worksheet
- 6 Pages

DAT Bootcamp - Cell Division
- 11 Pages

CELL Cycle Gizmo - Lab
- 2 Pages
Cell biology
- 3 Pages

Cell Energy Gizmo
- 6 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu



