Combining Voltage Sources PDF
| Title | Combining Voltage Sources |
|---|---|
| Course | Advanced Circuit Analysis |
| Institution | Old Dominion University |
| Pages | 5 |
| File Size | 317.1 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 114 |
| Total Views | 160 |
Summary
Teacher: Jones
Notes about Combining Voltage Sources...
Description
EET 300 || Chapter 1(D) Lesson Notes
Combining Sources
1 OF 5
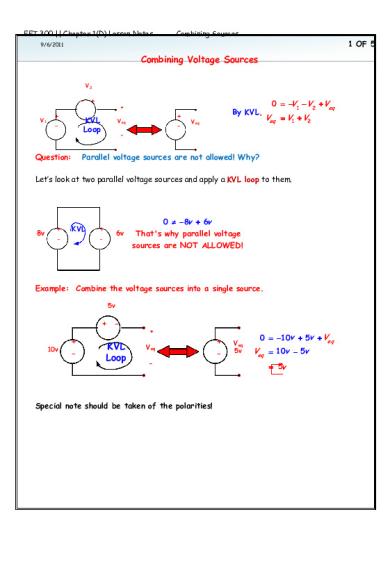
9/6/2011
Combining Voltage Sources V2
- + V1
+ -
+
KVL Loop
Question:
+ -
Veq
By KVL, Veq
0 V1 V2 Veq
Veq V1 V2
-
Parallel voltage sources are not allowed! Why?
Let’s look at two parallel voltage sources and apply a KVL loop to them.
8v
+ ‐
KVL
+ ‐
6v
0 8v 6v That's why parallel voltage sources are NOT ALLOWED!
Example: Combine the voltage sources into a single source. 5v
+ 10v
+ -
KVL Loop
+ Veq -
Special note should be taken of the polarities!
+ -
Veq 5v
0 10v 5v Veq
Veq 10v 5v 5v
EET 300 || Chapter 1(D) Lesson Notes
Combining Sources
2 OF 5
9/6/2011
Combining Current Sources I eq
I1
By KCL, Ieq
I2
0 I 1 I 2 Ieq
Ieq I1 I2
Current Sources in series are not allowed! This should be especially obvious. Consider the fact that current in a series circuit is the same everywhere. However, if you had two current sources of different values in the series circuit then that would cause the all the same rule to be broken. Thus, it “DOES NOT WORK!” and “IS NOT ALLOWED”. Example: Combine the two current sources in the circuit shown into a single source.
Ieq
I1 3 mA
0 I1 I2 Ieq
I2 5mA
I eq
8mA
By KCL
Ieq 3mA 5mA 8mA
EET 300 || Chapter 1(D) Lesson Notes
Combining Sources
3 OF 5
9/6/2011
Dependent Source Models A dependent source has an output which depends on some other voltage or current in the circuit. The dependent source is denoted by a diamond as can be seen in the four models from EET 210 below.
VCVS + Vi -
+ -
VCIS + Vi -
A vi
Basic amp model EET 210,220,330 A = voltage gain (Unitless)
gm vi
FET and Vaccum tube model g m = transconductance (1/ )
R m ii
R m = transresistance
ICVS ii
+ -
ICIS ii
ii
BJT Model
= Current gain
EET 300 || Chapter 1(D) Lesson Notes
Combining Sources
4 OF 5
9/6/2011
Dependent Source Example: Determine: The voltage across the A: dependent source. The Voltage, Vo B: 3A C: The power absorbed/supplied by the dependent source. The power absorbed/supplied by D: the independent source. Check the power balance equation. E:
8 + VR + Vo -
+ -
KVL
2VR
Solution:
KVL :
0 -Vo VR 2VR
Vo 3VR But
VR 3A(8 ) 24 v
so,
Vo 72v
B
The Voltage across the Dependent Source Vdep 2VR
8 + 72v -
KVL
48v A
PInd 3A (72v ) 216W PR 3A (24v ) 72W Pdep 3(48) 144W
+ 24v -
3A
2(24)
+ -
2VR
(Delivered ) D (Absorbed ) (Absorbed ) C
Power Balance Equation Power Delivered = Pow er Absorbed ? PInd PR Pdep 216W 72W 144W 216W 216W
The Multisim Proof of this work follows:
BALANCE D!
E
EET 300 || Chapter 1(D) Lesson Notes
Combining Sources
5 OF 5
9/6/2011
Let’s take a moment and consider the meaning of voltage and current polarity signs in a circuit. Current Arrows: A current arrow in a circuit represents an imaginary ammeter in the circuit. The direction that the arrow is pointing indicates the manner in which the imaginary ammeter is hooked up. It has NOTHING to do with actual direction of the current. For instance, observe the arrow in the figure shown below (I T ). The observed current in the circuit is 3A going in a clockwise direction due to the current source in a series circuit. However, the drawn current arrow indicates that the ammeter is hooked up in such a way that it will read -3A. Therefore, the current reading you would document from your CALCULATIONS would be IT = -3A.
IT The same thing applies to voltage polarities shown on + 3A 72v circuit. The VR variable shown to the right represents a voltmeter hooked up with the positive terminal connected to the left of the resistor and the negative terminal connected to the right of the resistor. It will read +24V.
8 + VR -
KVL
+ -
2VR...
Similar Free PDFs

Combining Voltage Sources
- 5 Pages

Voltage regulators
- 26 Pages

Dynamic Voltage Restoration
- 5 Pages

High Voltage Engineering
- 213 Pages

Stator Voltage Control
- 4 Pages

Voltage Bandgap Reference
- 19 Pages

High-Voltage Engineering
- 547 Pages

Archaeological Sources
- 6 Pages

Combining Forms - Lecture notes All
- 12 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu






