Consumer surplus PDF
| Title | Consumer surplus |
|---|---|
| Course | Microeconomics I |
| Institution | Universitat Pompeu Fabra |
| Pages | 4 |
| File Size | 402.3 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 74 |
| Total Views | 143 |
Summary
Download Consumer surplus PDF
Description
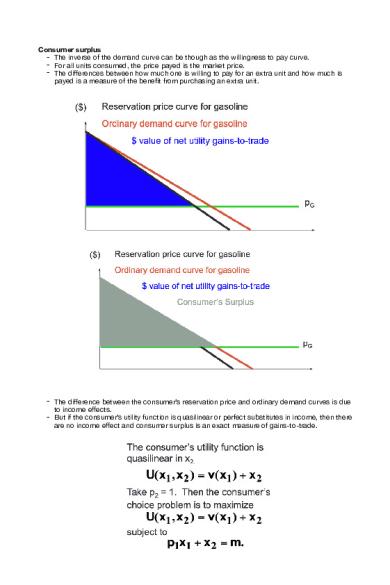
Consumer surplus - The inverse of the demand curve can be though as the willingness to pay curve.! - For all units consumed, the price payed is the market price.! - The differences between how much one is willing to pay for an extra unit and how much is payed is a measure of the benefit from purchasing an extra unit.!
!
- The difference between the consumer’s reservation price and ordinary demand curves is due to income effects.!
- But if the consumer’s utility function is quasilinear or perfect substitutes in income, then there are no income effect and consumer surplus is an exact measure of gains-to-trade.!
- We can rearrange to the following:!
!
- Consumer’s surplus is an exact dollar measure of utility gained from consuming commodity 1 when the consumer’s utility function is quasilinear in commodity 2.!
- The change of total utility due to a change in P1 is approximately the change in her consumer’s surplus.!
- Changes in consumer surplus - The numbers given from consumer surplus are just representative, what we care about is about the changes as a result from policy changes.!
- Compensating and equivalent variations - Compensating variation (CV): measures how much M.U must be paid to those affected to -
compensate their loss (ex-post perspective.) It measures the least extra income at the new prices, to restore original utility.! Equivalent variation (EV): measures how much M.U would consumers pay to avoid being worse-off (ex-ante perspective.) It measures the least extra income at the original prices, to match original utility with the new utility.! In quasilinear utility CS=EV=CV!
Example of calculating CV, EV and CS for CD!
Example for perfect complements:...
Similar Free PDFs

Consumer surplus
- 4 Pages

Consumer Surplus - Lecture notes
- 5 Pages

Le surplus du producteur
- 3 Pages

TB Ch12 Capturing Surplus
- 21 Pages

Investing Surplus Funds
- 18 Pages

Surplus UNIT - ANSWER
- 1 Pages

Surplus del consumatore
- 1 Pages

Surplus- Consumatore-E- Produttore
- 37 Pages

Le surplus du producteur
- 1 Pages

Consumer behavior
- 5 Pages

Consumer Arithmetic
- 8 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu




