Government:-Reviewing Public Policy PDF

| Title | Government:-Reviewing Public Policy |
|---|---|
| Author | Sophia Burke |
| Course | American Government |
| Institution | University of Georgia |
| Pages | 9 |
| File Size | 121.2 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 56 |
| Total Views | 172 |
Summary
Public Policy Notes...
Description
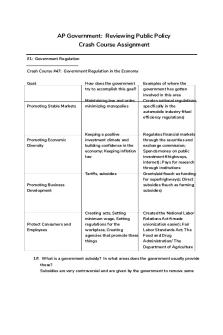
AP Government: Reviewing Public Policy Crash Course Assignment #1: Government Regulation Crash Course #47: Government Regulation in the Economy Goal:
How does the government try to accomplish this goal?
Promoting Stable Markets
Promoting Economic Diversity
Maintaining law and order, minimizing monopolies
Keeping a positive investment climate and building confidence in the economy; Keeping inflation low
Tariffs, subsidies Promoting Business Development
Protect Consumers and Employees
Creating acts, Setting minimum wage, Setting regulations for the workplace, Creating agencies that promote these things
Examples of where the government has gotten involved in this area Creates national regulations, specifically in the automobile industry (fuel efficiency regulations)
Regulates financial markets through the securities and exchange commission; Spends money on public investment (highways, internet); Pays for research through institutions Grants/aid (such as funding for superhighways); Direct subsidies (such as farming subsidies)
Created the National Labor Relations Act (made unionization easier); Fair Labor Standards Act; The Food and Drug Administration/ The Department of Agriculture
1. What is a government subsidy? In what areas does the government usually provide these? Subsidies are very controversial and are given by the government to remove some
type of burden; they are typically used to promote a social good or an economic policy. The government usually provides these through grants/aid and direct subsidies.
2. How has government regulation of the economy changed over time? Before the twentieth century, the federal government didn’t really do that much when it came to regulation of the economy due to policy, taxation, and the supreme court’s interpretation of the commerce clause. The government became involved because of the creation of railroads; they became involved in order to prevent discriminatory pricing (Interstate Commerce Act). Different events such as the Gilded Age, World War I and The Great Depression demanded government involvement.
3. What rationale does the government give for interfering in economic regulation? The government rationalizes interfering in economic relation with the fact that they are trying to achieve their goals in making the economy prosper.
Application Question: Why is the idea of government involvement in the economy so controversial? What role does this idea play in the modern day debate between the two major parties? The idea of government involvement in the economy is so controversial because many people believe that these laws and regulations are created in order to benefit the government and not the public or the economy. In the modern day debate between the two major parties, this idea plays a significant role on policies and regulations that each party wants to create involving the economy.
#2: Monetary and Fiscal Policy Crash Course #48: Monetary and Fiscal Policy
1. What is monetary policy? The way the government regulates the amount of money in circulation in the nation’s economy. 2. Who controls monetary policy in the United States? The United States Federal Reserve System 3. What are the two primary tasks of the FED? To control inflation and to encourage full employment
4. What are the four functions of the FED? (Which is the most important?) ● Responsible for clearing checks and supplying actual currency ● Sets up rules for banks ● Loan money to other banks and set interest rates (MOST IMPORTANT) ● Controls how much money is circulated in the economy
5. What impact does a change in interest rates have? A change in interest rates can cause inflation 6. Who selects the leaders of the FED? Why? They are an independent body and are not elected but appointed by the government. In doing so, they are able to focus on broader interests rather than their own reelection.
7. What is fiscal policy? Fiscal policy refers to the government’s ability to raise taxes and spend the money it raises.
8. What is supply side economics? Whose idea? Created by President Ronald Reagan, supply side economics is the idea that if you lower taxes on businesses and individuals then the individuals will be able to spend more and the businesses will be able to invest more and the economy as a whole will
grow.
9. What has happened to the tax rate (overall) in the last 30 years? Over the past 30 years, the trend is for there to be lower federal taxes, but the percentage of revenue that the federal government receives from taxes has held steady.
10. What are uncontrollable (or mandatory spending)? Examples? Uncontrollable or mandatory spending are items that the government cannot cut because they are written into law by Congress (ex. interest payments on the federal debt and farm subsidies). 11. What are the two biggest examples of mandatory spending? The two biggest examples of mandatory spending are on social security and Medicare, paid for by dedicated federal tax dollars; they provide income and health insurance for the elderly. 12. What is discretionary spending? Discretionary spending is government spending that the government makes by choice (at their discretion); however, there are only a select few programs on which the federal government can choose to spend or not spend.
13. How can the government balance the budget? Other than by cutting spending, the government can balance the budget by raising taxes.
Application Question: Which type of economic policy has the most POLITICAL impact? (Consider things like campaigns and elections, branches of government, etc.) Explain your answer. The type of economic policy that has the most political impact would be fiscal policy because it is probably the point of most debate between democrats and republicans. The ability to levy taxes on citizens has been controversial throughout American history and many people believe that the government is too involved. Fiscal policy is always a point of debate between presidential candidates and candidates often use this to try and get ahead
in the election. False promises, namely candidates promising to maintain or lower taxes, are often made to get elected. This is unlike monetary policy, which is controlled by the FED and led by an appointed official. Therefore, there is less incentive to do or promise things to ensure reelection. One of the powers of the legislative branch is to set federal tax rates. In addition, bills originate in the House and are then approved by the Senate; so, in opposition to monetary policy, which is controlled by the Federal Reserve, fiscal policy is controlled by the actual government and therefore has greater political impact.
#3: Social and Domestic Policy Crash Course #49: Social Policy 1. What are the goals of social policy? To protect against risk and insecurity and promote equal opportunity; others aim to assist the poor. 2. Historically, how have Americans viewed these goals? Historically, Americans are generally skeptical of these social policy goals because of strong faith in individualism and suspicion of government action (distrust). 3. When does government involvement in social policy start? Government involvement in social policy largely started with the Great Depression, when people’s views of the government and poverty shifted significantly. Poverty increased greatly and became so widespread that many people began to feel that the government had a responsibility to do something about it. FDR responded to this with the New Deal, implementing social security and AFDC. 4. What is Social Security? How does it work? Social security provides monthly payments to people over the age of 65. When you work on a payroll, taxes are deducted from your wages and the amount is matched by your employers. 7.65% gets taken from your paycheck; 6.2% goes towards social security, and 1.45% goes towards Medicare. The money that is collected is used to pay for elderly Americans; the program redistributes wealth from younger working people to older retired people.
5. What is the potential problem with Social Security? The number of people receiving benefits is increasing as baby boomers get older,
and the number of people paying into social security is falling. Eventually, there may not be enough money to pay out benefits to those who qualify.
6. What are some potential solutions? Some potential solutions include congressional legislation that could potentially raise the payroll tax or the benefit age above 65.
7. What is the potential problem for Medicare? The potential problem for medicare is that less people are paying into Medicare, and medical costs are rising.
8. What is the Aid to Families with Dependent Children (AFDC) program? The AFDC was a welfare system that paid benefits to women and children (amount of the payments depended on the number of children dependents). 9. What happened to AFDC? The AFDC was repealed and replaced by Temporary Aid to Needy Families.
10. What are some examples of non-contributory programs? Programs include: free school lunches, federal housing assistance programs, and supplemental nutrition assistance programs.
11. Why do many people dislike these types of programs? Conservatives argued that the AFDC created dependency, or an incentive not to work; meaning that people who did not deserve these benefits were receiving them.
12. What is the 1996 Welfare Reform Act? How did it change things? The Personal Responsibility and Opportunity Reconciliation Act was passed in 1996 and got rid of AFDC and replaced it with TANF, which emphasized that aid was temporary. There were work and time restrictions put in place as well.
13. What is the one area of social policy that almost everyone agrees on in the US? Almost all Americans agree that education is essential to finding good, highpaying jobs that will enable people to achieve greater economic stability.
Application Question: How are social policies reflected in political views? (In other words, in what areas of social policy do the two major parties disagree and how?) How do interest groups influence social policies? There are various subjects that the two political parties disagree on, however, how to help and care for the elderly is probably the most discussed today. Conservative
Republicans believe that welfare creates dependency, and people should have personal responsibility to work hard and provide for themselves; in other words, they believe that dependency on these programs will become so great that people will use this as an excuse not to work which will hurt the economy significantly. On the other hand, liberal democrats believe that government action is necessary to achieve equal opportunity for all and should step in to help redistribute wealth and provide for the needy. In addition, interest groups attempt to influence social policy through lobbying and hiring representatives to advocate for increased or decreased government involvement.
#4: Foreign and Military Policy
Crash Course #50: Foreign Policy 1. What are the five elements of foreign policy? ● Diplomacy ● ● ● ●
Military and Security Policy International Human Rights Policies Economic Policies Environmental Policy
2. What are the goals of foreign policy? The overarching goal of foreign policy is to provide security; however the goal of American foreign policy is to create prosperity and work toward making the world a
better place. 3. What is the current largest focus of foreign policy? Terrorism 4. Until what event did the US remain isolationist (for the most part)? World War I (threats seemed detrimental to American security) 5. What is deterrence? Building up enough military strength to discourage potential enemies from attacking the United States.
6. What is the danger in using military action in foreign policy? It is dangerous because while Americans are usually on board with short, decisive, and victorious military action, the longer a war drags on, the less support it tends to have and the more costly it becomes (both in lives and money).
7. How does the US participate in economic foreign policy? They maintain an active role in international organizations, such as The World Trade Organization that make and uphold trade rules.
8. How does the US try to “make the world a better place?” Through international human rights initiatives and international peacekeeping missions.
9. How is environmental policy involved in foreign policy? It is involved in foreign policy because we are all living on one planet in the same environment.
10. How is foreign policy made? Most of the day to day foreign policy decisions are left to bureaucrats, such as the president or other heads of state in other countries (only one person).
11. Who is responsible for creating foreign policy?
The State Department, but they receive aid from the Department of Defense and other agencies such as the CIA and NSA.
12. How does Congress influence foreign policy? The Senate has the constitutional power to ratify treaties, but since a ⅔ vote is required, the president will often try to create foreign policy with executive agreements that only require a majority vote in both houses, which is usually easy to secure.
13. How do interest groups influence foreign policy?
They can influence policy by shaping the agenda but they don’t do much work when it comes to crafting the policies themselves; regarding domestic policy, interest groups are most effective when focusing on one issue.
Application Question: What are the current biggest issues within foreign policy and how does each party intend to tackle them?
In his acceptance speech at the Republican convention, President Trump claimed that many U.S. allies take the United States’ support for granted, and foreign countries should contribute more financially for U.S. security guarantees in order to ensure that American troops will come to their aid. For example, President Trump wants Mexico to finance the wall he wants to build between the United States and Mexico in order to prevent the influx of illegal immigrants, but Mexico refuses to do so. The Democrat philosophy revolves around the idea that military strength and soft power can shape global affairs....
Similar Free PDFs

Public Policy Essay
- 3 Pages

Public Policy Analysis paper
- 15 Pages

Public Policy Assignment
- 4 Pages

Public Policy - Elarba Badih
- 3 Pages

Reading Article - Public Policy
- 2 Pages

Agreements Against Public Policy
- 6 Pages

Public Policy final study guide
- 7 Pages

Marxist theory of Public Policy
- 8 Pages

Public Policy Decision Making Models
- 18 Pages

Interest Groups and public policy
- 10 Pages

Official Actors IN Public Policy
- 14 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu