J. ARPILLEDA-BMLS3B UIC HEMATOLOGY RBC Anomalies PDF

| Title | J. ARPILLEDA-BMLS3B UIC HEMATOLOGY RBC Anomalies |
|---|---|
| Author | Jenny Frazier |
| Course | Medical Laboratory Science |
| Institution | University of the Immaculate Conception |
| Pages | 5 |
| File Size | 118.4 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 247 |
| Total Views | 822 |
Summary
Download J. ARPILLEDA-BMLS3B UIC HEMATOLOGY RBC Anomalies PDF
Description
Jenny H. Arpilleda BMLS 3B POIKILOCYTES (RESULTS OF MEMBRANE DEFECT) RBC ANOMALIES ACANTHOCYTES ➔ Also known as Spur cell, Thorny Cell (resembles spurs on cowboy boots) ➔ Cell with multiple thorny or knobly spikely projections that are irregularly distributed around the cellular membrane and may vary in size. ➔ Spheroid with 3-12 irregularly spikes/ spicules; fewer than echinocytes ➔ Microcytic; lacks of central pallor (differentiates them from echniocytes) ➔ Disease Associations: Predominant in Abetalipoproteinemia and Spur cell anemia • Abetalipoproteinemia: Increased ratio between RBC to plasma lipids resulting from the inability to absorb lipids in the small intestine. The decrease in plasma lipids produce membrane defect resulting to the increase in sensitivity of the cell to the external and internal forces. • Liver Disease • Hereditary Acanthocytosis • Mcleod Syndrome ECHINOCYTES ➔ Burr cell, Crenated RBC, Sea urchin Cell ➔ Regular 10-30 scalloped short projections; evenly distributed ➔ Less spherical than the acanthocytes ➔ The deformability depends on a variety of factors such as the relationship of the surface area of the cell to its volume, the type of hemoglobin present, or the lipid characteristics. ➔ Crenation can occur as the result of the physical loss of intracorpuscular water. ➔ Rigid cell which leads to premature destruction. ➔ May also be artifactual: Exposure to hypertonic solution; ➔ Improper anticoagulant-to-blood ratio; prolonged storage • Uremia →Results from osmotic
➔ Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency → Deficiency in ATP CODOCYTE ➔ Target Cell,Mexican Hat Cell, Bull’s Eye Appearance ➔ Cells with central area of Hgb surrounded by a relatively colorless ring and a peripheral ring of Hgb ➔ Resembles a shooting target ➔ Disease Association: o Thalassemia→ → Caused by maldistribution of hemoglobin o Hemoglobinopathies SS, CC, DD, EE o Liver Disease→ Due to the deficiency in the phospholipids and cholesterol content in the RBC membrane o In certain enzyme defects, cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine are abnormally increased within the RBC and become incorporated into the membrane lipid. o Hemolytic Anemia o LCAT Deficiency Disease LEPTOCYTE ➔ Thinner variant of target cell ELLIPTOCYTE ➔ Generally narrower and more elongated than megalocytes ➔ Elliptical (rod, sausage or cigarshaped) RBC ➔ Have normal cell-size volume Hereditary Elliptocytosis or Ovalocytosis ➔ Defect is considered to be in the cytoskeleton, with a decreased in the membrane protein band 4.1 ➔ Abnormality in the spectrin component of the RBC Membrane o Iron Deficiency Anemia o Thalassemia Major o Myelophthisic Anemia OVAL MACROCYTES (Megalocytes) ➔ oval (egg-shaped) ➔ Although these cells are similar in
• •
imbalance Kidney Disorder Liver Disease → Abnormality in the lipid content of the membrane
appearance to elliptocytes, megalocytes are macrocytic and have a fuller and rounder appearance. ➔ Bipolar aggregation of Hgb
➔ Reduction in membrane cholesterol ➔ Disease Association: o Myeloblastic anemia o Myelodysplasia o Vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies
o
Pencil cell or Oat cell ➔ thinner variant of elliptocyte o Hereditary elliptocytosis o Hereditary ovalocytosis Spherocyte ➔ Cells that have lost their normal biconcave shape. ➔ Microcytic, round, dense, extremely compact RBC with no central pallor ➔ Disease Association: o Hereditary spherocytosis→ → Cells occur as the ratio of the surface area of the erythrocyte to the volume of the cell contents decreases because of the loss of cell membrane o Inherited structural defect of the RBC membrane o Immune Hemolytic Anemia o Extensive Burns (along with Schistocytes)→ → Caused by direct physical trauma such as heat or chemical injury o *Banked blood stored for time Stomatocyte ➔ Mouth or slit like pallor area/ bowl shaped (Gr. Stoma=mouth) ➔ Disease Association: o Hereditary Stomatocytosis→ → Results from increased sodium ion and decreased potassium ion concentration within the cytoplasm of the erythrocyte. o Rh Null Disease→ → Lacks the Rh antigen complex o Acquired Stomatocytosis (Liver Disease, Alcoholism) o *Artifact Drepanocyte ➔ Other Name: Sickle Cell, Menisocyte ➔ Thin, dense, elongated RBC pointed at least one of the ends; may be curved ➔ The membrane is smooth and the cell stains uniformly throughout ➔ This is due to abnormal hemoglobin caused by glutamic acid substitution
o
Sickle Cell Anemia →Result from the gelation of polymerized deoxygenated hemoglobin S. Polymerization of hemoglobin S is influenced by both lowered oxygen levels and decreased blood pH. Sickle Cell-β-Thalassemia
Schistocyte ➔ Other Name: Schizocyte,Fragmentocyte ➔ Fragmentation produced by damage of RBC by fibrin, altered vessel walls, prosthetic heart valves ➔ May also be produced from the ruptured vacuole of the blister cell ➔ Disease Association: o DIC o TTP o Hemolysis o Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia (MAHA) Keratocyte ➔ Other Name: Helmet Cell ➔ RBC fragment in shape of a helmet, a half-moon or a spindle ➔ Partially deformed but not cut ➔ Have spicules, resembling two horns, result from a ruptured vacuole ➔ Disease Association: o DIC o TTP o Hemolysis o Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia (MAHA) Blister cell ➔ This cell containing one or more eccentric vacuoles which may rupture; resembles a blister on the skin ➔ It has a significantly thinned area at the periphery or outer border of the cell membrane. ➔ Disease Association: o Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia (MAHA) o Pulmonary Emboli in sickle cell anemia→ → Result from the traumatic interaction of blood vessels and circulating blood such as fibrin deposits. Knizocyte ➔ RBC with triangular shape
for valine at the 6th position on the beta chain. ➔ Disease Association:
➔ Resembles a pinched bottle Folded Cell
➔ RBC with membrane folded over ➔ Disease Association: o Hemolytic anemia o Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia (MAHA) o Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Dacryocyte ➔ Other Name: Teardrop Cell, Dacrocyte ➔ Usually smaller than normal RBCs ➔ RBC with a single pointed extension resembling a teardrop or pear ➔ Disease Association: o Hemolytic Anemia o Myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia (MMM), o Myeloproliferative disorders including leukemia→ → Cells unable to pass through small openings of splenic sinuses Pyropoikilocyte ➔ Other Name: Microspherocyte ➔ damaged erythrocyte due to sensitivity to warm temperature ➔ Disease Associations: o Extensive burns o Hereditary Microspherocytosis, o Hereditary Pyropoikilocytosis
o o o
Infections Cancers Diabetes mellitus
Red blood cell agglutination ➔ Red blood cells stick together in clumps due to protein called agglutinins. Poikilocytes (Presence of Inclusion bodies) Siderocyte ➔ MATURE ERYTHROCYTE with IRON containing granules ➔ Disease Association: Anemia of abnormal iron metabolism (i.e. Sideroblastic Anemia) Sideroblast ➔ IMMATURE ERYTHROCYTES with IRON containing granules ➔ Disease Association: Anemia of abnormal iron metabolism (i.e. Sideroblastic Anemia) Hemosiderin ➔ stained with Perl’s Prussian Blue ➔ Disease Associations: o Anemia of abnormal iron metabolism (i.e. Sideroblastic Anemia)
Semilunar bodies Howell Jolly Bodies ➔ Other Name: half moon/crescent cell ➔ fragments of RBC membrane which looks like crescent bodies ➔ Disease Associations: Malarial Infection Bite cell ➔ Other Name: Degmacyte ➔ contain one or more “bites” caused by the removal of cellular inclusions by the splenic macrophages through the process called pitting ➔ Glucose-6-phophate dehydrogenase (G6PD) Deficiency o Hemoglobin breaks down and Heinz bodies are formed. Bite cells are formed when splenic macrophages engulf the Heinz bodies in the cell. Rouleaux Formation ➔ Red blood cells that are arranged in rows like “stacked coins” due to an increase in proteins.
➔ Round, solid-staining, dark-blue to purple inclusions, 1 to 2 micrometers in size. ➔ If present, cells contain only one or two Howell-jolly bodies single or double dotted bodies inside the RBC which are REMNANTS OF DNA ➔ Disease Associations: o Megaloblastic Anemia o Post-splenectomy o Hyposplenism o Hemolytic Anemia Pappenheimer Bodies ➔ Or Siderotic granules → which are dark-staining particles of iron that are visible with the use of Prussian blue stain. ➔ erythrocytes with cluster of IRON granules often near the periphery (since iron are deposited in the mitochondria of the cell) can be stained with Wright’s stain...
Similar Free PDFs

RBC Anomalies - - Hematology 1
- 21 Pages

HEMATOLOGY 1 - WBC Anomalies
- 8 Pages

MTAP-3-Hematology - hematology
- 13 Pages

KONotes On RBC - Notes on RBC
- 20 Pages

Antropología 1º Medicina UIC
- 69 Pages
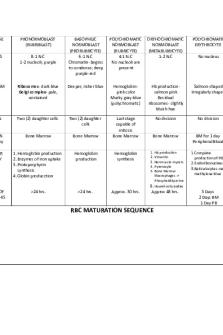
RBC Maturation Sequence
- 1 Pages

Leadership Development- RBC
- 5 Pages

Hematology Reviewer
- 15 Pages

Hematology exam
- 7 Pages

Hematology Reviewer
- 9 Pages

Hematology exam
- 6 Pages

RBC-Advantages & Disadvantages
- 1 Pages

UIC Lab 3 report
- 13 Pages

Hematology Analyzer
- 3 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu

