Lab- Brain & Cranial nerves week12 PDF

| Title | Lab- Brain & Cranial nerves week12 |
|---|---|
| Course | Anatomy & Physiology I |
| Institution | Fleming College |
| Pages | 4 |
| File Size | 169.5 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 74 |
| Total Views | 166 |
Summary
assigned lab work...
Description
Anatomy & Physiology I The Brain & Cranial Nerves week 12 1. a) Identify the meningeal layers covering the brain. A Periosteal laer B Meningeal layer D arachniod E Pia mater
C
Dura mater
b) What is the difference between the layer of dura around the brain compared that around the spinal cord? In the carinal cavity, the dura consists of two layers the outer periosteal layer and the inner meningeal layer
2. Differentiate between a gyrus and a sulcus. The gyri are the folds the sulci are the shallow grooves 3. a) What is cerebrospinal fluid? is a clear, colorless liquid composed primarily of water that protects the brain and spinal cord from chemical and physical injuries. b) Where is CSF produced? It is produced by the ependymal cell lining the ventricles of the vain and by the choroid plexus
c) Where does CSF circulate? Circulates through cavities in the brain and spinal cord.
4. a) Identify the 4 major parts of the brain. Brain stem cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon
b) Name the 3 regions of the brain stem. Midbrain, pons, medulla oblonagata
c) Name the 3 major regions of the diencephalon. Thalamus hypothamus, epithalamus (pineal gland d) Name the 4 lobes of the brain found in each cerebral hemisphere Frontal (2) parietal (2) temporal (2) occipital (2)
Please give a brief description of the physiology for each structure. Cerebrum
Basal Nuclei
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Epithalamus
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla oblongata
Cerebellum
Limbic system
Reticular formation
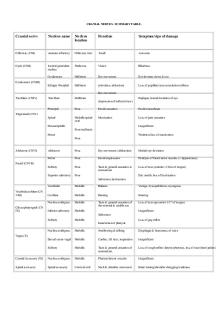
5. a) Complete the following chart for the cranial nerves using very brief descriptions. Cranial Nerve
Name
Function
Olfactory
Sense of smell
Optic
Sense of vision
Oculomotor
Eye movement, opening eyelid
trochlear
Eye movement
trigeminal
Sensory to face motor for mastication (chewing) 3 branches largest CN
Abducens
Eye movement
Facial
Facial expression: sensory (taste) parasympathetic motor (tear, nasal and salivary glands
Vestibulocochlear
Sense of hearing and equilibrium
I
II
III
IV
V
VI
VII
VIII
IX
Glossopharyngeal Sensory tongue and pharynx taste, pain, swallowing thorax and abdomen, parasympathetic (heart, lungs abdominal vicera)
vagus
Sensory (taste) motor (swallowing) thorax and abdomen parasympathetic (heart, lungs, abdominal viscera)
Accessory
Supply larynx, pharynx and soft palate motor to trapezius and sternocleidomastoid
Hypopglossal
Tongue (movement for food mixing and speech)
X
XI
XII
b) Discuss how are the various nerve functions might be tested? (Note: We will test the cranial nerves associated with the special senses in another lab.)...
Similar Free PDFs

Cranial Nerves
- 2 Pages

Cranial Nerves
- 2 Pages

Cranial Nerves Worksheet
- 2 Pages
Cranial Nerves Summary
- 4 Pages

20. Cranial Nerves
- 1 Pages

Drawing of cranial nerves
- 2 Pages

Cranial nerves QUIZ - QUIZ
- 2 Pages

Cranial Nerves examination osce
- 3 Pages

Neuro: Cranial Nerves Assessment
- 3 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu






