Muscles Tables (Upper Extremity and Lower Extremity) PDF
| Title | Muscles Tables (Upper Extremity and Lower Extremity) |
|---|---|
| Course | Physical therapy |
| Institution | Our Lady of Fatima University |
| Pages | 29 |
| File Size | 934.1 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 228 |
| Total Views | 631 |
Summary
Download Muscles Tables (Upper Extremity and Lower Extremity) PDF
Description
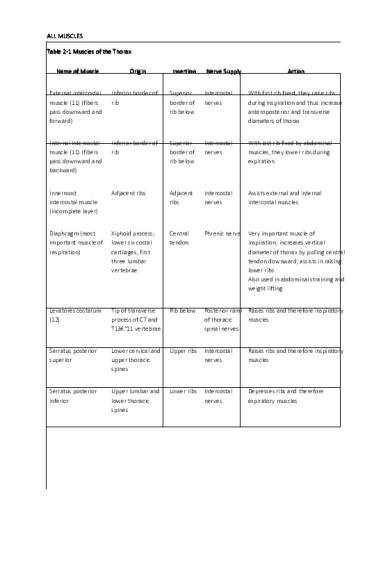
ALL MUSCLE MUSCLESS Table 2-1 Mu Muscles scles of the TThorax horax Name of M Muscle uscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Action
External intercostal muscle (11) (fibers pass downward and forward)
Inferior border of rib
Superior border of rib below
Intercostal nerves
With first rib fixed, they raise ribs during inspiration and thus increase anteroposterior and transverse diameters of thorax
Internal intercostal muscle (11) (fibers pass downward and backward)
Inferior border of rib
Superior border of rib below
Intercostal nerves
With last rib fixed by abdominal muscles, they lower ribs during expiration
Innermost intercostal muscle (incomplete layer)
Adjacent ribs
Adjacent ribs
Intercostal nerves
Assists external and internal intercostal muscles
Diaphragm (most important muscle of respiration)
Xiphoid process; lower six costal cartilages, first three lumbar vertebrae
Central tendon
Phrenic nerve
Very important muscle of inspiration; increases vertical diameter of thorax by pulling central tendon downward; assists in raising lower ribs Also used in abdominal straining and weight lifting
Levatores costarum (12)
Tip of transverse process of C7 and T1–11 vertebrae
Rib below
Posterior rami Raises ribs and therefore inspiratory of thoracic muscles spinal nerves
Serratus posterior superior
Lower cervical and upper thoracic spines
Upper ribs
Intercostal nerves
Raises ribs and therefore inspiratory muscles
Serratus posterior inferior
Upper lumbar and lower thoracic spines
Lower ribs
Intercostal nerves
Depresses ribs and therefore expiratory muscles
Table 4-1 Mu Muscles scles of the An Anterior terior Abdomin Abdominal al Wall
Name of Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Action
External oblique
Lower eight ribs
Xiphoid process, linea alba, pubic crest, pubic tubercle, iliac crest
Lower six thoracic nerves and iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves (L1)
Supports abdominal contents; compresses abdominalcontents; assists in flexing and rotation of trunk; assists inforced expiration, micturition, defecation, parturition, and vomiting
Internal oblique
Lumbar fascia, iliac crest, lateral two thirds of inguinal ligament
Lower three ribs and costal cartilages, xiphoid process, linea alba, symphysis pubis
Lower six thoracic nerves and iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves (L1)
As above
Transversus
Lower six costal cartilages, lumbar fascia, iliac crest, lateral third of inguinal ligament
Xiphoid process linea alba, symphysis pubis
Lower six thoracic nerves and iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves (L1)
Compresses abdominal contents
Rectus abdominis
Symphysis pubis and pubic crest
Fifth, sixth, and seventh costal cartilages and xiphoid process
Lower six thoracic nerves
Compresses abdominal contents and flexes vertebral column; accessory muscle of expiration
Pyramidalis (if present)
Anterior surface of pubis
Linea alba
12th thoracic nerve
Tenses the linea alba
Table 4-2 Mu Muscles scles of the PPosterior osterior Abd Abdominal ominal Wall Name of Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Action
Psoas
Transverse processes, bodies, and intervertebral discs of 12th thoracic and five lumbar vertebrae
With iliacus into lesser trochanter of femur
Lumbar plexus
Flexes thigh on trunk; if thigh is fixed, it flexes trunk on thigh, as in sitting up from lying position
Quadratus lumborum
Iliolumbar ligament, iliac crest, tips of transverse processes of lower lumbar vertebrae
12th rib
Lumbar plexus
Fixes 12th rib during inspiration; depresses 12th rib during forced expiration; laterally flexes vertebral column same side
Iliacus
Iliac fossa
With psoas into lesser trochanter of femur
Femoral Flexes thigh on trunk; if thigh is nerve fixed, it flexes the trunk on the thigh, as in sitting up from lying position
Table 6-1 Mu Muscles scles of the PPelvic elvic Walls and FFloor loor Name of Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Action
Piriformis
Front of sacrum
Greater trochanter of femur
Sacral plexus
Lateral rotator of femur at hip joint
Obturator internus
Obturator membrane and adjoining part of hip bone
Greater trochanter of femur
Nerve to obturator internus from sacral plexus
Lateral rotator of femur at hip joint
Levator ani
Body of pubis, fascia of obturator internus, spine of ischium
Perineal body; anococcygeal body; walls of prostate, vagina, rectum, and anal canal
Fourth sacral nerve, pudendal nerve
Supports pelvic viscera; sphincter to anorectal junction and vagina
Coccygeus
Spine of ischium
Lower end of sacrum; coccyx
Fourth and fifth sacral nerve
Assists levator ani to support pelvic viscera; flexes coccyx
Table 8-1 Mu Muscles scles of Perine Perineum um Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Action
External anal ssphincter phincter
Subcutaneous part
Encircles anal canal, no bony attachments
Inferior rectal nerve and perineal branch of fourth sacral nerve
Together with puborectalis muscle forms voluntary sphincter of anal canal
Superficial part
Perineal body
Deep part
Encircles anal canal, no bony attachments
Puborectalis (part of levator ani)
Pubic bones
Sling around junction of rectum and anal canal
Perineal branch of fourth sacral nerve and from perineal branch of pudendal nerve
Together with external anal sphincter forms voluntary sphincter for anal canal
Perineal branch of pudendal nerve
Compresses urethra and assists in erection of penis
Coccyx
Male Ur Urogenital ogenital Muscles
Bulbospongiosus
Perineal body
Fascia of bulb of penis and corpus spongiosum and cavernosum
Ischiocavernosus
Ischial tuberosity
Fascia covering corpus Perineal branch of cavernosum pudendal nerve
Assists in erection of penis
Sphincter urethrae
Pubic arch
Surrounds urethra
Perineal branch of pudendal nerve
Voluntary sphincter of urethra
Superficial transverse perineal muscle
Ischial tuberosity
Perineal body
Perineal branch of pudendal nerve
Fixes perineal body
Ischial ramus
Deep transverse perineal muscle
Perineal body
Perineal branch of pudendal nerve
Fixes perineal body
Perineal branch of pudendal nerve
Sphincter of vagina and assists in erection of clitoris
Female Ur Urogenital ogenital Muscles
Bulbospongiosus
Perineal body
Fascia of corpus cavernosum
Ischiocavernosus
Ischial tuberosity
Fascia covering corpus Perineal branch of cavernosum pudendal nerve
Sphincter urethrae
Same as in male
Superficial transverse perineal muscle
Same as in male
Deep transverse perineal muscle
Same as in male
Causes erection of clitoris
Table 9-1 Mu Muscles scles Connec Connecting ting the Up Upper per Limb to the Thorac Thoracic ic Wall Muscle
Origin
Pectoralis major
Clavicle, sternum, and upper six costal cartilages
Lateral lip of bicipital groove of humerus
Medial and lateral C5, 6, Adducts arm and rotates it medially; 7, 8; T1 clavicular fibers also flex arm pectoral nerves from brachial plexus
Pectoralis minor
Third, fourth, and fifth ribs
Coracoid process of scapula
Medial pectoral nerve from brachial plexus
C6, 7, 8 Depresses point of shoulder; if the scapula is fixed, it elevates the ribs of origin
Clavicle
Nerve to subclavius from upper trunk of brachial plexus
C5, 6
Subclavius First costal cartilage
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Nerve Roots
Action
Depresses the clavicle and steadies this bone during movements of the shoulder girdle
Serratus anterior
a
Upper eight ribs
C5, 6, 7 Draws the scapula forward around the thoracic wall; rotates scapula
Medial border Long thoracic and inferior nerve angle of scapula
The predominant nerve root supply is indicated by boldface type.
P.442 Table 9-2 Mu Muscles scles Connec Connecting ting the Up Upper per Limb to the Ver Vertebral tebral Colum Column n Muscle
Trapezius
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Nerve Roo Roots ts
Action
Spinal part of accessory nerve
XI cranial nerve (spinal part)
Upper fibers elevate the
Thoracodorsal nerve
C6, 7, 8,
Extends, adducts,
Occipital bone, ligamentum nuchae,
Upper fibers into lateral third of
spine of seventh cervical vertebra, spines of all thoracic vertebrae
clavicle; middle (motor) and C3 and 4 (sensory) and lower fibers into acromion and spine of scapula
Latissimus dorsi
Iliac crest, lumbar
Floor of bicipital
fascia, spines of lower six thoracic vertebrae, lower three or four ribs, and inferior angle of scapula
groove of humerus
Levator scapulae
Transverse processes of first four cervical vertebrae
Medial border of scapula
C3 and 4 and dorsal scapular nerve
C3, 4, 5
Raises medial border of scapula
Rhomboid minor
Ligamentum nuchae and spines of seventh cervical and first thoracic vertebrae
Medial border of scapula
Dorsal scapular nerve
C4 C4, 5
Raises medial border of scapula upward and medially
Rhomboid major
Second to fifth thoracic Medial border of spines scapula
Dorsal scapular nerve
C4 C4, 5
Raises medial border of scapula upward and medially
scapula; middle fibers pull scapula medially; lower fibers pull medial border of scapula downward
and medially rotates the arm
a
The predominant nerve root supply is indicated by boldface type.
Table 9-3 Mu Muscles scles Connec Connecting ting the Sca Scapula pula to the Humer Humerus us Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Deltoid
Lateral third of clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula
Middle of lateral surface of shaft of humerus
Axillary nerve
C5 C5, 6
Abducts arm; anterior fibers flex and medially rotate arm; posterior fibers extend and laterally rotate arm
Supraspinatus
Supraspinous fossa of scapula
Greater
Suprascapular nerve
C4, 5, 6
Abducts arm and
Infraspinous fossa of scapula
Greater
Suprascapular nerve
(C4), 5, 6
Teres major
Lower third of lateral border of scapula
Medial lip of bicipital groove of humerus
Lower subscapular nerve
C6 C6, 7
Medially rotates and adducts arm and stabilizes shoulder joint
Teres minor
Upper two thirds of lateral border of scapula
Greater tuberosity of humerus; capsule of shoulder joint
Axillary nerve
(C4), C5 C5, 6
Laterally rotates arm and stabilizes shoulder joint
Subscapularis
Subscapular fossa
Lesser tuberosity of humerus
Upper and lower subscapular nerves
C5, 6, 7
Medially rotates arm and stabilizes shoulder joint
Infraspinatus
a
tuberosity of humerus; capsule of shoulder joint
tuberosity of humerus; capsule of shoulder joint
Nerve Supply
The predominant nerve root supply is indicated by boldface type.
Nerve Roots
Action
stabilizes shoulder joint
Laterally rotates arm and stabilizes shoulder joint
Table 9-5 Mu Muscles scles of the Ar Arm m Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Nerve Roots
Action
Anterior Com Compartment partment Biceps bra brachii chii
Long head
Supraglenoid tubercle of scapula
Tuberosity of radius and bicipital aponeurosis into deep fascia of forearm
Short head
Coracoid process of scapula
Musculocutaneous C5, 6 nerve
Supinator of forearm and flexor of elbow joint; weak flexor of shoulder joint
Coracobrachialis Coracoid process of scapula
Medial aspect of shaft of humerus
Musculocutaneous C5, 6, 7 Flexes arm and also nerve process of weak adductor
Brachialis
Coronoid process of ulna
Musculocutaneous C5, 6 nerve
Front of lower half of humerus
Flexor of elbow joint
Posterior Compartment Tri Triceps ceps
Long head
Infraglenoid tubercle of scapula
Lateral head
Upper half of posterior surface of shaft of humerus
Medial head
Lower half of posterior surface of shaft of humerus
a
Olecranon process of ulna
Radial nerve
The predominant nerve root supply is indicated by boldface type.
C6, 7, 8 Extensor of elbow joint
Table 9-6 Mu Muscles scles of the An Anterior terior Fascial C Compartment ompartment of th the e Forearm Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Nerve Roots
Action
Pronator Teres
Median nerve
C6, 7
Pronation and flexion of forearm
Bases of second and third metacarpal bones
Median nerve
C6, 7
Flexes and abducts hand at wrist joint
Flexor retinaculum and palmar aponeurosis
Median nerve
C7, 8
Flexes hand
Pisiform bone, hook of the hamate, base at fifth metacarpal bone
Ulnar nerve
C8; T1
Flexes and adducts hand at wrist joint
C7, 8; T1
Flexes middle phalanx of fingers and assists in flexing proximal phalanx and hand
C8; T1
Flexes distal phalanx of thumb
Humeral head
Medial epicondyle of humerus
Lateral aspect of shaft of radius
Ulnar head
Medial border of coronoid process of ulna
Flexor carpi radialis
Medial epicondyle of humerus
Palmaris longus
Medial epicondyle of humerus
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Humeral head
Medial epicondyle of humerus
Ulnar head
Medial aspect of olecranon process and posterior border of ulna
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
Humeroulnar head
Medial epicondyle of humerus; medial border of coronoid process of ulna
Middle phalanx of medial four fingers
Radial head
Oblique line on anterior surface of shaft of radius
Flexor pollicis longus
Anterior surface of shaft of radius
Distal phalanx of thumb
Median nerve
Anterior interosseous branch of median nerve
Flexor digitorum profundus
Anteromedial surface of shaft of ulna
Distal phalanges of medial four fingers
Ulnar (medial half) and median (lateral half) nerves
C8; T1
Flexes distal phalanx of fingers; then assists in flexion of middle and proximal phalanges and wrist
Pronator quadratus
Anterior surface of shaft of ulna
Anterior surface of shaft of radius
Anterior interosseous branch of median nerve
C8; T1
Pronates forearm
a
The predominant nerve root supply is indicated by boldface type.
Table 9-7 Mu Muscles scles of the La Lateral teral Fascial Compartment of tthe he Forearm Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Nerve Roots
Action
Brachioradialis
Lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus
Base of styloid process of radius
Radial nerve
C5, 6, 7
Flexes forearm atridge of humerus elbow joint; rotates forearm to the midprone position
Extensor carpi radialis longus
Lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus
Posterior surface of base of second metacarpal bone
Radial nerve
C6, 7
Extends and abducts hand at wrist joint
Table 9-8 Mu Muscles scles of the PPosterior osterior Fas Fascial cial Compartmen Compartmentt of the Forearm Muscle
Origin
Insertion
Nerve Supply
Nerve Roots
Action
Extensor carpi radialis brevis
Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Posterior surface of base of third metacarpal bone
Deep C7, 8 branch of radial nerve
Extends and abducts hand at wrist joint
Extensor digitorum
Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Middle and distal phalanges of medial four fingers
Deep C7, 8 branch of radial nerve
Extends fingers and hand (see text for details)
Extensor digiti minimi
Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Extensor expansion of little finger
Deep C7, 8 branch of radial nerve
Extends metacarpal phalangeal joint of little finger
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Base of fifth metacarpal bone
Deep C7, 8 branch of radial nerve
Extends and adducts hand at wrist joint
Anconeus
Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Lateral surface of olecranon process of ulna
Radial nerve
Extends elbow joint
Supinator
Lateral epicondyle of humerus, anular liga...
Similar Free PDFs

Lower-Extremity-Orthosis
- 7 Pages

Lower Extremity lecture
- 10 Pages

Upper Extremity Muscle Cheat Sheet
- 18 Pages

Lab Week 3 Lower Extremity Bones
- 4 Pages

Hip Muscles and lower body
- 2 Pages

Muscles of Upper Limb
- 11 Pages

Muscles of Lower Limb - musclee
- 7 Pages

Muscles of the lower limb2013
- 46 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu







