Note from PE videos - some note from the economic video given by Mr. Lo PDF
| Title | Note from PE videos - some note from the economic video given by Mr. Lo |
|---|---|
| Author | Anonymous User |
| Course | Principles of Economics |
| Institution | Trường Đại học Kinh tế Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh |
| Pages | 5 |
| File Size | 377.2 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 475 |
| Total Views | 542 |
Summary
I. Types of Profit: - Profit = Revenue – Cost (time + money) o Accounting profit = Revenue – Explicit cost o Economic profit = Revenue – (Explicit cost + Implicit cost) - Explicit cost: chi phí rõ ràng, chi phí hi n rõ = accounting costệ - Opportunity cost = time + energy + the foregone income + mon...
Description
I. -
II. -
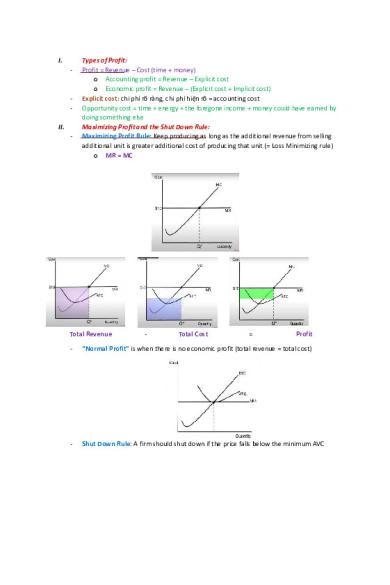
Types of Profit: Profit = Revenue – Cost (time + money) o Accounting profit = Revenue – Explicit cost o Economic profit = Revenue – (Explicit cost + Implicit cost) Explicit cost: chi phí rõ ràng, chi phí hi ện rõ = accounting cost Opportunity cost = time + energy + the foregone income + money could have earned by doing something else Maximizing Profit and the Shut Down Rule: Maximizing Profit Rule: Keep producing as long as the additional revenue from selling additional unit is greater additional cost of producing that unit (= Loss Minimizing rule) o MR = MC
Total Revenue
-
Total Cost
=
Profit
-
“Normal Profit” is when there is no economic profit (total revenue = total cost)
-
Shut Down Rule: A firm should shut down if the price falls below the minimum AVC
AFC -
III.
Total Fixed Cost
A firm’s short-run supply curve: The marginal cost curve above minimum AVC
Perfect Competition 1. Characteristic of Perfect Competition: o Many small firms o Low barriers to entry and exit o Identical products o Firms are price takers
Marginal Revenue = Demand = Average Revenue = Price (perfectly elastic) 2. Long-run equilibrium:
3. Perfect competitive firms are extremely efficient: a. Allocative efficiency: The firm is producing the amount society wants, where the price equals the marginal cost. b. Productive efficiency: The firm is producing at the lowest possible
IV.
Monopoly: 1. Characteristic of Monopoly: o High barriers to entry (other firms can’t enter) o Unique good, no close substitutes o Firms are price makers o Can’t price discriminate
cost, where the ATC is minimized.
2. Monopoly graph:
o o o
Marginal revenue is less than the demand curve MC and ATC is exactly the same as in perfect competition MR=MC: the firm produce where MR =MC, charge the price where people willing to pay.
i. ii. iii. iv. v.
Profit maximizing quantity: Q1 (MR=MC) Profit maximizing price: P2 (charge price people willing to pay) Total revenue: P2-A.-Q1-Q0 Consumer surplus: P1-A-P2 Revenue maximizing quantity (MR=0; total revenue is max): Q2
vi.
vii. viii. ix. x.
Socially optimal quantity = allocative efficiency: Q3 (MC hit D curve) Socially optimal consumer surplus: P1-C-P4 Quantity with no economic profit: Q4 (total revenue = total cost) If there is a per unit tax: 1. New quantity (MR=MC): QT 2. New price: PT Quantity goes down, Price goes up. Lump sum tax: onetime tax that affects fixed costs, MC wouldn’t change, price and quantity stay the same...
Similar Free PDFs

Note - Note
- 27 Pages

Note 40 - note
- 4 Pages

Note 3 - Note
- 4 Pages

Note 6 - note
- 5 Pages

Note 10 - note
- 5 Pages

ES Note-mid - note
- 30 Pages

Note 6 - note
- 4 Pages

Note 10 - note
- 7 Pages

Note 28 - note
- 4 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu






