P2 - 11111111111 PDF

| Title | P2 - 11111111111 |
|---|---|
| Author | Jerry Ren |
| Course | Physiotherapy IV |
| Institution | University of Newcastle (Australia) |
| Pages | 6 |
| File Size | 566.2 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 3 |
| Total Views | 144 |
Summary
11111111111...
Description
1. Arteries, Veins and Lymphatics: Using wet specimens, images and models Ø Describe the structures that make up the boundaries of the axilla
Apex – also known as the axillary inlet, it is formed by lateral border of the first rib, superior border of scapula, and the posterior border of the clavicle. Lateral wall – formed by intertubercular groove of the humerus.
Medial wall – consists of the serratus anterior and the thoracic wall (ribs and intercostal muscles).
Anterior wall – contains the pectoralis major and the underlying pectoralis minor and the subclavius muscles.
Posterior wall – formed by the subscapularis, teres major and latissimus dorsi.
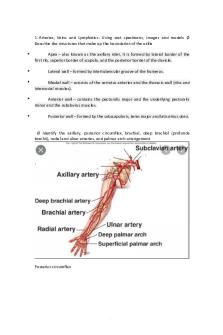
Ø Identify the axillary, posterior circumflex, brachial, deep brachial (profunda brachii), radial and ulnar arteries, and palmar arch arrangement
Posterior circumflex
Ø View deep veins that lie in close proximity to the arteries – be able to differentiate between a large artery and a large vein (consider wall thickness and inherent structure of these two types of vessels)
静脉里面有 valve Ø Identify sites of main arterial pulses in the upper limb
Ø Look at the arrangement of the main superficial veins in the cubital fossa region of the elbow. Identify the median cubital vein (common site for taking blood) and describe general location of the basilic and cephalic veins (lymphatic flow is closely aligned)
Location of basilic vein:The basilic vein usually lies in the deep subcutaneous tissue at the antecubital crease and pierces the brachial fascia in the distal third of the upper arm; however, occasionally it lies beneath the fascia at the antecubital crease. Location of cephalic veins: located in the superficial fascia along the anterolateral surface of the biceps. Ø Identify the deep veins of the upper limb and consider the naming of these veins
Because the deep veins always lie nearby a artery, the name of the veins are the same with the nearby artery. Ø Look for examples of lymph nodes in the axillary region and describe a role of the lymphatic system
managing the fluid levels in the body The blood in our blood vessels is under constant pressure. We need that to push nutrients (food the cells need), fluids and some cells into the body’s tissues to supply those tissues with food, oxygen and defence. All of the fluids and its contents that leak out into the tissues (as well as waste products formed in the tissues, and bacteria that enter them through our skin) are removed from them by the lymphatic system. When the lymphatic system does not drain fluids from the tissues properly, the tissues swell, appearing puffy and uncomfortable. If the swelling only lasts for a short period it is called oedema. If it lasts longer (more than about three months) it is called lymphoedema....
Similar Free PDFs
P2 - 11111111111
- 6 Pages

Insight P2
- 11 Pages

P2 notes
- 198 Pages

Assessment p2
- 3 Pages

Líquidos corporais - Resumo P2
- 11 Pages

P2 M1D1 - Unit 10,13,19
- 7 Pages

DLR P2 - Mécanismes endogènes
- 18 Pages

P2 Solman - Guerrero
- 35 Pages

P2 L1 Malicious Code
- 240 Pages

P2 Sangre II. Hemolisis
- 4 Pages

P2: Turbina Pelton
- 9 Pages

P2 spk akuntansi modifikasi
- 1 Pages

Resumo P2 EDO
- 3 Pages

Anatomia II P2- Carol
- 16 Pages

P2. Imprimer. La compensation
- 5 Pages

P2 Eco - practica 2
- 7 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu