Problems on EOQ with answers PDF

| Title | Problems on EOQ with answers |
|---|---|
| Course | Operations management production & service |
| Institution | Centennial College |
| Pages | 5 |
| File Size | 196 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 41 |
| Total Views | 178 |
Summary
Economic Order Quantity Problems and SOlutions....
Description
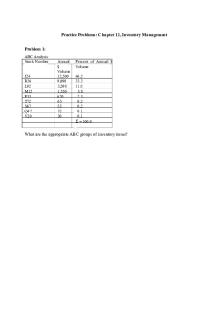
Problems on EOQ and Re-Order Point
1) A certain type of computer costs $1,000, and the annual holding cost is 25%. Annual demand is 10,000 units, and the order cost is $150 per order. What is the approximate economic order quantity? A) 16 B) 70 C) 110 D) 183 E) 600 Solution: Under Square root (2*10,000*150) ÷ 250 = 109.5 Answer: C 2) In the basic EOQ model, if D = 6000 per year, S = $100, H = $5 per unit per month, the economic order quantity is approximately A) 24. B) 100. C) 141. D) 490. E) 600. Solution: Under Square root (2*6000*100) ÷ 5*12 = 141 Answer: C
4 )A firm that makes electronic circuits has been ordering a certain raw material 250 ounces at a
time. The firm estimates that carrying cost is 30% per year, and that ordering cost is about $20 per order. The current price of the ingredient is $200 per ounce. The assumptions of the basic EOQ model are thought to apply. For what value of annual demand is their action optimal? Answer: This problem reverses the unknown of a standard EOQ problem.
250 =
; solving for D results in D =
= 93,750
5 )Given the following data: D = 65,000 units per year, S = $120 per setup, P = $5 per unit, and H
= 25% per year, calculate the EOQ and calculate annual costs following EOQ behaviour. Answer: EOQ is 3533 units, for a total cost of $4,415.88
Q∗ =
TC =
= 3532.7
∙S+
∙H=
∙ 120 +
∙ .25 ∙ 5 = 2207.94 + 2207.94 = 4415.88
6 )Holding costs are $35 per unit per year, the ordering cost is $120 per order, and sales are
relatively constant at 300 per month. What is the optimal order quantity? What are the annual inventory management costs? Answer: Order size is Q∗ =
= 157.12
Annual inventory costs are ∙ 120 + ∙ 35 + 2749.55 + 2749.55 = $5,499.10. 7. Holding costs are $35 per unit per year, the ordering cost is $120 per order, and sales are relatively constant at 300 per month. What is the optimal order quantity? What are the annual inventory management costs? Solution: Demand= 300*12 = 3600 Ordering cost = 120 Holding cost = 35 EOQ = √(2 * 3600 * 120) / 35 = 157.12 Total cost = (3600*120)/157.12 + (157.12 * 35)/2 = 2749.49 + 2749.6 = $ 5499.09
8. A company makes bicycles. It produces 450 bicycles a month. It buys the tires for bicycles from a supplier at a cost of $20 per tire. The company’s inventory carrying cost is estimated to be 15% of cost and the ordering is $50 per order. a. Calculate the EOQ Demand, D = (2 tires per bicycle) * (450 bicycles per month) * (12 months in a year) = 10,800 tires Ordering cost. S = $120 per order Holding cost, H = (15% of $20 per tire) = $3.00 per tire per year EOQ = √(2*10800*50)/3 = √ 400,000 = 600 tires
b.What is the number of orders per year? N = D / Q = 10800 / 600 = 18 orders per year
c. Compute the average annual ordering cost.
18 orders per year * $50 per order = $900 per year
d. Compute the average inventory. (In EOQ model)
Q / 2 + Safety Stock Q/ 2 + 0 600 / 2 = 300 tires e .What is the average annual carrying cost? (Average inventory) * Holding cost = 300 tires * 3 = $900 per year f .Compute the total cost. Average annual ordering cost + Average annual carrying cost $ 900 + $ 900 = $1800
9. Given the following information for an important purchased part, compute the (a) EOQ, (b) total purchase cost, (c) annual holding cost, (d) annual order cost, (e) annual total cost, (f) reorder point, (g) number of orders placed per year and (h) time between orders.
Annual requirements (R) = 5,000 units Order cost (S) = $100 per order Holding rate (k) = 20% Unit cost (C) = $20 per unit Lead time (LT) = 6 days Number of days per year = 360 days Ans.:
a) 𝐸𝐸 𝐸=√2𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸= √2×5,000 𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸 ×$1000.20×$20=500 𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸 b) Total purchase cost = R ´ C = 5,000 units ´ $20 = $100,000 c) Annual holding cost = Q/2 ´ k ´ C = 500 units / 2 ´ 20% ´ $20 = $1,000 d) Annual ordering cost= R/Q ´ S = 5,000 units / 500 units ´ $100 = $1,000 e) Annual total cost = $1,000 + $1,000 = $2,000 f) Reorder point (ROP) = 5,000 / 360 ´ 6 = 83.33 units g) Number of orders placed per year = 5,000 / 500 = 10 orders h) Time between orders = 360 / 10 = 36 days 10. Given the following information for a purchased part, compute the (a) EOQ, (b) total purchase cost, (c) annual holding cost, (d) annual order cost, (e) annual total cost, (f) reorder point, (g) number of orders placed per year and (h) time between orders. Monthly demand = 3,500 units Order cost (S) = $250 per order Holding cost (kC) = $8.65 per unit per year Unit cost (C) = $85 per unit Lead time (LT) = 12 days Number of days per year = 365 days Ans.: (a) 𝐸𝐸𝐸=√2𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸= √2×3,500 𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸×12×$250$8.65=1,558.12 𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸 (b) Total purchase cost = R ´ C = 42,000 units ´ $85 = $3,570,000 (c) Annual holding cost = Q/2 ´ k ´ C = $6,738.88 (d) Annual ordering cost= R/Q ´ S = $6,738.88 (e) Annual total cost = $6,738.88 + $6,738.88 = $13,477.76 (f) Reorder point (ROP) = (3,500*12) / 365 ´ 12 = 1,380.82 units (g) Number of orders placed per year = (3,500*12)/1,558.12 = 26.96 orders
(h) Time between orders = 365/26.96 = 13.54 days...
Similar Free PDFs

Problems on EOQ with answers
- 5 Pages

EOQ Practice Problems
- 1 Pages
EOQ Problems - Mandatory
- 7 Pages

Density Problems with Answers
- 2 Pages

Auditing Problems with Answers
- 12 Pages

Modelo EOQ Básico Inventado
- 1 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu









