The Cell Membrane PDF

| Title | The Cell Membrane |
|---|---|
| Course | AP Biology |
| Institution | High School - USA |
| Pages | 2 |
| File Size | 44.8 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 21 |
| Total Views | 215 |
Summary
How cell membrane was discovered, fluid mosaic model, and proteins in the cell membane....
Description
The Cell Membrane Wednesday, October 9, 2019
8:50 AM
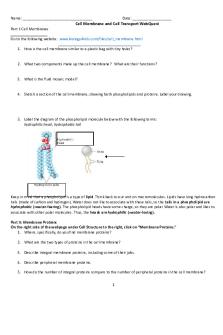
I. Timeline a. Charles Overton (1895) i. Said membranes are made of lipids b. Langmuir (1917) i. Placed them in benzene to study structure of lipids c. Gorter and Grendel (1925) i. Establish structure as lipid bilayer d. Davson & Danielli (1935) i. "Sandwich Model" e. Electron Microscope (1950's) i. Showed more details in higher resolution of cell membrane f. Problems with "Sandwich model" (1960's) g. Singer & Nicolson- Fluid Mosaic Model "1972" i. Movement between membranes ii. There's multiple parts of proteins, carbs, cholesterol, etc. II. Fluid Mosaic Model a. Lipids i. Phosolipids 1) Hydrophilic phosphate head and hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails 2) Saturated a) Tails become more close with each other 3) Unsaturated a) Tails are fluid w/ space b) Prevent packing 4) Movement a) Lateral movement is common, b) Don't often flipflop (once a month) because tails are exposed to water ii. Cholesterol 1) Helps to maintain fluidity at body temperature 2) Adaptive characteristic for different environmental temperatures b. Proteins i. Integral Proteins 1) Embedded in the membrane 2) Transport Proteins a) Movement of Large hydrophilic substances across membrane b) Active or passive transport 3) Enzymes a) Bind substrates and lower amount of energy it takes for reaction ii. Peripheral Proteins 1) Attach to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix (ECM) noncovalently 2) Maintain cell shape and stabilize certain membrane proteins 3) Cell to cell recognition- identification that are specifically recognized by membrane proteins of other cells iii. Both can function as intercellular junctions 1) Hook together various junctions, such as gap junctions or tight junctions iv. Signal Transduction
1) Binding of certain chemicals can alter shape to relay messages inside cell 2) Signal molecule and receptor c. Carbohydrates i. Carbohydrate chains, glycolipid, glycoprotein ii. Cell-to-cell recognition III. Synthesis and Sidedness of Membranes a. Membranes have distinct inside and outside faces...
Similar Free PDFs

The Cell Membrane
- 2 Pages

Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet
- 2 Pages

6-cell membrane web quest
- 4 Pages

Ecampa lab report - cell membrane
- 14 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu