Cell transport cell membrane key 1 PDF

| Title | Cell transport cell membrane key 1 |
|---|---|
| Author | Johnathon Albato |
| Course | Cell Biology |
| Institution | Georgia Southern University |
| Pages | 2 |
| File Size | 80.8 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 24 |
| Total Views | 201 |
Summary
Key for cell membrane transport along with types of molecules...
Description
Biology 102 Chapter 7
Name _______________________ No. ___ Date _____________ Class ____
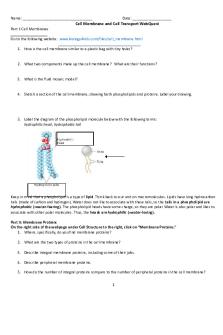
Cell Transport WebQuest - Follow the directions to the websites and answer the questions about cell membranes and cell transport. http://nhscience.lonestar.edu/biol//bio1int.htm At the top of the page, click “Cell Transport”. Then, click on Construction of the Cell Membrane. Continue through the animation, reading the information and answering the questions below. 1. What is the cell membrane mainly composed of? __lipids and proteins_______________________ 2. What are 5 types of molecules in the cell membrane? ___Phospholipids,___Fibrous Protein_____ ____Glycoprotein,_Pore Protein_and_Channel Protein_______________ 3. Name 3 lipid soluble, (fat soluble) substances that can pass through the plasma membrane. ________ ____oxygen, carbon dioxide and steroids_________________________________________ 4. What TYPE of substances need the help of proteins to pass through the plasma membrane? ________ _____water soluble substances_____________________________________________ 5. Cholesterol is only found in __animal___________ cell membranes. Click the Back button on the toolbar to return to the index page. Now Click on Passive and Active Transport. This animation is like a short movie. Watch each section FIRST, then try to answer the questions. When the navigation bar at the bottom turns yellow, it will pause and you have to press the Next button. Choose “Passive Transport” first. 1. Does passive transport require energy? __no_______ 2. The 3 types of passive transport that you will be viewing are __simple diffusion; facilitated diffusion; and osmosis_________________________________ 3. In which direction do molecules move in diffusion? from _ high_ concentration to _low_ concentration 4. When does diffusion end? __when equilibrium is reached__________ 5. What is the difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion? _facilitated diffusion uses proteins 6. What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis? _osmosis refers to the diffusion of water___ 7. If the inside of the cell membrane is hypotonic to the outside, which is hypertonic, water will travel across the cell membrane toward the ___ outside__ side until _equilibrium_ is reached. 8. This is one way in which a cell maintains __ homeostasis__. (hint: one of Mrs. Epps favorite words!) 9. What is the difference between active and passive transport? ___active transport requires energy__ 10. Why is active transport necessary? cells often require substances that are rare in theirenvironment_ 11. Describe what is happening in the ion pump animation. __ATP is used to pump H+ ion against the concentration gradient ________ 1
12. “Cell eating” is known as __phagosytosis_ and “cell drinking” is known as __pinocytosis____. These are both examples of ___endocytosis_______________. Now go to http://www.tvdsb.ca/webpages/brownt12/files/osmosis.htm Osmosis: __the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane_________________________ Because cell membranes are completely permeable to water, the environment the cell is exposed to can have a dramatic effect on the cell. Hypertonic Solutions: contain a _higher_ concentration of solute and therefore a _ lower_ concentration of solvent (water) compared to the cell's cytoplasm. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water diffuses out of the cell, causing the cell to shrivel. Play the animation. Why is water leaving the cell? _because there is more water inside than outside__ Hypotonic Solutions: contain a _lower_ concentration of solute and therefore a higher concentration of solvent (water) compared to the cell's cytoplasm. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, the water diffuses into the cell, causing the cell to swell and possibly explode. Play the animation. What are the water molecules doing? _ water is going into the cell_____ What is happening to the cell? __the cell is swelling up and bursting____________________________ Isotonic Solutions: contain the _same_ concentration of solute and therefore the _same_ concentration of water as the cell's cytoplasm. When a cell is placed in an isotonic solution, the water diffuses into and out of the cell at the same rate. The fluid that surrounds the body cells is isotonic. Play the animation. Describe what the water molecules doing _water is going into and out of the cell at the same rate_ Click the Back button on the toolbar to return to the index page. Click on Interactive Cellular Transport. Click on Diffusion/Osmosis. The concentration of solute molecules is higher on the ___ outside___ side of the cell. What do you predict will happen? __more of the solute molecules will move into the cell____________________ Activate the model. Were you correct? _yes_ Describe the exterior and interior environments of the cell after diffusion has occurred. __they are in equilibrium or they have the same concentration_________
2...
Similar Free PDFs

Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet
- 2 Pages

The Cell Membrane
- 2 Pages

4- Cell Transport Review
- 4 Pages

Cell Transport Review Worksheets
- 8 Pages

6-cell membrane web quest
- 4 Pages

Cell Transport Activity
- 3 Pages

Cell Transport Lab Report
- 2 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu