The Tibial Nerve - Course - Motor - Sensory - Teach Me Anatomy PDF

| Title | The Tibial Nerve - Course - Motor - Sensory - Teach Me Anatomy |
|---|---|
| Author | Venice Marie Cordeta |
| Course | Physical Therapy |
| Institution | St. Paul University Iloilo |
| Pages | 3 |
| File Size | 309.8 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 95 |
| Total Views | 159 |
Summary
Download The Tibial Nerve - Course - Motor - Sensory - Teach Me Anatomy PDF
Description
10/19/2020
The Tibial Nerve - Course - Motor - Sensory - TeachMeAnatomy
Tibial Nerve Home / The Lower Limb / Nerves of the Lower Limb / Tibial Nerve
Original Author(s): Matt Archer Last updated: April 21, 2020 Revisions: 42
The tibial nerve is a major peripheral nerve of the lower limb. It has several cutaneous and motor functions in the le In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the tibial nerve – its anatomical course, functions and clinical correla
Overview Nerve roots: L4-S3 Sensory: Innervates the skin of the posterolateral leg, lateral foot and the sole of the foot. Motor: Innervates the posterior compartment of the leg and the majority of the intrinsic foot muscles.
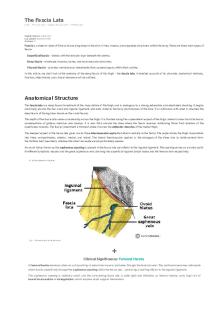
Anatomical Course The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve, and arises at the apex of the popliteal fossa. It travels through the muscles in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg. Here, the tibial nerve also gives rise to branches that which innervates the posterolateral aspect of the leg. The tibial nerve continues its course down the leg, posterior to the tibia. During its descent, it supplies the deep mu At the foot, the nerve passes posteriorly and inferiorly to the medial malleolus, through a structure known as the superiorly by the flexor retinaculum. Within this tunnel, branches arise from the tibial nerve to supply cutaneous inne Immediately distal to the tarsal tunnel, the tibial nerve terminates by dividing into sensory branches, which innerva
10/19/2020
The Tibial Nerve - Course - Motor - Sensory - TeachMeAnatomy
Patients complain of paraesthesia in the ankle and sole of the foot, which can radiate up the leg slightly. It is a by rest. Tarsal tunnel symptoms can be treated conservatively by anti-inflammatory drugs and changes in footwe successful, the flexor retinaculum can be cut surgically, which releases the pressure.
Motor Functions The tibial nerve innervates all the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg. They are divided into a deep and Deep Popliteus – Laterally rotates the femur on the tibia to unlock the knee. Flexor hallucis longus – Flexes the big toe and plantar flexes the ankle. Flexor digitorum Longus – Flexes the other digits and plantar flexes the ankle. Tibialis posterior – Inverts the foot and plantar flexes the ankle. Superficial Plantaris – Plantar flexes the ankle. Soleus – Plantar flexes the ankle. Gastrocnemius – Plantar flexes the ankle and flexes the knee.
Sensory Functions In the popliteal fossa, the tibial nerve gives o cutaneous branches. These combine with branches from the com nerve. This sensory nerve innervates the skin of the posterolateral side of the leg and the lateral side of the foot. The tibial nerve also supplies all the sole of the foot via three branches: Medial calcaneal branches: These arise within the tarsal tunnel, and innervate the skin over the heel. Medial plantar nerve: Innervates the plantar surface of the medial three and a half digits, and the associated sol Lateral plantar nerve: Innervates the plantar surface of the lateral one and a half digits, and the associated sole
10/19/2020
The Tibial Nerve - Course - Motor - Sensory - TeachMeAnatomy
Fig 3 – Cutaneous innervation to the sole of the foot.
+ Clinical Relevance: Damage to the Tibial N Damage to the tibial nerve is rare, and is often a result of direct trauma, entrapment through narrow space or co Damage results in loss of plantar flexion, loss of flexion of toes and weakened inversion (The tibialis anterior can...
Similar Free PDFs

7. sensory motor intergration
- 6 Pages

The Glossopharyngeal Nerve
- 2 Pages

Cranial Nerve Assessment Tests
- 2 Pages

Teach documentary
- 1 Pages

Introduction to Sensory Systems
- 4 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu