50 drug curriculum - Summary MBCHB YEAR 4 PDF

| Title | 50 drug curriculum - Summary MBCHB YEAR 4 |
|---|---|
| Course | MBCHB Year 4 |
| Institution | University of Glasgow |
| Pages | 18 |
| File Size | 730.5 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 421 |
| Total Views | 477 |
Summary
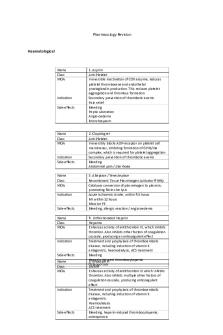
Pharmacology RevisionHaematologicalName 1. Aspirin Class Anti-Platelet MOA Irreversible inactivation of COX enzyme, reduces platelet thromboxane and endothelial prostaglandin production. This reduces platelet aggregation and thrombus formation Indication Secondary prevention of thrombotic events Pai...
Description
Pharmacology Revision
Haematological
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA Indication
Side-effects Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
1. Aspirin Anti-Platelet Irreversible inactivation of COX enzyme, reduces platelet thromboxane and endothelial prostaglandin production. This reduces platelet aggregation and thrombus formation Secondary prevention of thrombotic events Pain relief Bleeding Peptic ulceration Angio-oedema Bronchospasm
2. Clopidogrel Anti-Platelet Irreversibly blocks ADP-receptor on platelet cell membranes, inhibiting formation of GPIIb/IIIa complex, which is required for platelet aggregation Secondary prevention of thrombotic events Bleeding Abdominal pain / diarrhoea 3. Alteplase / Tenecteplase Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator (rtPA) Catalyses conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, promoting fibrin clot lysis Acute Ischaemic stroke, within 4.5 hours MI within 12 hours Massive PE Bleeding, allergic reaction / angio-oedema 4. Unfractionated Heparin Heparins Enhances activity of antithrombin III, which inhibits thrombin. Also inhibits other factors of coagulation cascade, producing an anticoagulant effect Treatment and prophylaxis of thromboembolic disease, including induction of vitamin K antagonists, haemodialysis, ACS treatment Bleeding Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia 5. Enoxaparin Osteoporosis LWMH Enhances activity of antithrombin III which inhibits thrombin. Also inhibits multiple other factors of coagulation cascade, producing anticoagulant effect Treatment and prophylaxis of thromboembolic disease, including induction of vitamin K antagonists. Haemodialysis ACS treatment Bleeding, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, osteoporosis
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects Name Class Name MOA Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects Indication
Side-effects
6. Warfarin Vitamin K antagonist Inhibits vitamin K reductase, which prevents the recycling of vitamin K to reduced form after carboxylation of coagulation factors II, VII, IX and X. This therefore prevents thrombus formation Treatment of VTE Thromboprophylaxis in AF/metallic heart valves/cardiomyopathy Bleeding Warfarin necrosis Osteoporosis 7. Dabigatran Direct thrombin inhibitor Directly inhibits conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin as inhibits action of thrombin Prophylaxis of VTE, especially post op Thromboprophylaxis in non-valvular AF Bleeding Dyspepsia 8. Rivaroxaban Factor Xa antagonist Inhibits conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, reducing concentrations of thrombin in the blood and therefore inhibits formation of fibrin clots Prophylaxis of VTE, especially post-op Thromboprophylaxis in non-valvular AF Treatment of VTE Bleeding 10. Bisoprolol / Atenolol Nausea Cardio-selective Beta-blockers 9. Apixaban These are beta-1-adrenoreceptor antagonists so Factor Xa antagonist therefore block beta-1-receptors in cardiac and renal tissue. This inhibits the sympathetic Inhibits conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, reducing concentrations in the blood and therefore stimulation of the heart and renal vasculature inhibiting formation of fibrin clots node, which in the heart, blocks Sino-atrial reducing heart ratefollowing and depresses Prophylaxis of VTE hip or cardiac knee contractility blocking receptors in myocardium. replacementby surgery Within the ident, the in release of reninAF is inhibiting, Thromboprophylaxis non-valvular preventingnausea vasoconstrictive effects of RAAS Bleeding, Hypertension / angina Rate-control in AF Support for mild/mod heart failure (bisoprolol) Bradycardia / hypotension Bronchospasm? Fatigue Cold extremities Loss of hypoglycaemic awareness
Cardiovascular
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
11. Propranolol / Carvedilol Non-cardioselective beta-blockers Propranolol is just a beta-1-adrenoreceptor antagonist, carvedilol is bete-1+2, and alph-1 antagonist. Both inhibit sympathetic stimulation in heart and vascular smooth muscle Hypertension / angina / post-MI prophylaxis Anxiety Migraine prophylaxis Support for mild/mod heart failure (Carvedilol) Bradycardia / hypotension Bronchospasm Fatigue Cold extremities Sleep disturbances Loss of hypoglycaemic awareness 12. Ramipril / Enalapril / Lisinopril / Perindopril ACE inhibitors Inhibits conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, which inhibits aldosterone release from adrenal cortex, depressing renal sodium and fluid retention, and therefore decreasing blood volume and thus blood pressure Hypertension / heart failure Nephropathy Prevention of CV events in high risk patients Dry cough (Bradykinin) Hypotension 13. Isosorbide Mononitrate / Glyceryl Trinitrate Hyperkalaemia / renal impairment Nitrates Angioedema Converted in NO, which is a potent vasodilator. Therefore, they work on coronary vessels, enhancing blood flow is ischaemic areas of myocardium. Also, reduce myocardial oxygen consumption by reducing cardiac preload and afterload Treatment of angina Severe hypertension Headache Postural hypotension / dizziness Tachycardia
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
14. Verapamil / Diltiazem Rate-limiting Calcium channel blockers Prevent cellular entry of Ca2+ by blocking L-type calcium channels. This depresses the contractility of cardiac and smooth muscles so that cardiac contractility is reduced and coronary blood vessels are dilated, reducing afterload. It also has anti-dysrhythmic actions due to prolonged AV node conduction, depressing the heart rate Supraventricular arrhythmias Treatment of angina Hypertension Verapamil – constipation, flushing/headache / dizziness / hypotension Diltiazem – GI disturbances / bradycardia / peripheral oedema / hypotension, dizziness etc. 15. amlodipine / Nifedipine / Felodipine Non Rate-limiting Calcium Channel Blockers Prevent cellular entry of calcium by blocking L-type calcium channels, depressing contractility of myocardial and smooth muscles, but mainly affecting smooth muscle. This means that coronary arteries are dilated, reducing afterload, but heart rate is not lowered Hypertension Treatment of angina Ankle oedema Abdominal pain / nausea Palpitations Flushing / headache / dizziness 16. Simvastatin / Atorvastatin / Pravastatin HMG CoA Reductase inhibitors Competitively inhibit HMG CoA reductase, the ratedetermining enzyme in mevalonate pathway synthesis of cholesterol. This causes an increase in LDL-receptor expression on the surface of hepatocytes and therefore increases hepatic uptake of cholesterol. Due to less cholesterol, reduces development of atherosclerotic plaques Familial hypercholesterolaemia Prevention of Cardiovascular events in high risk patients Myalgia Myopathy / rhabdo rare GI disturbances Deranged LFTs
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA
AntiIndication
Side-effects
17. Digoxin Cardiac Glycosides Increases vagal parasympathetic activity and inhibits Na/K pump, causing a build-up of intracellular Na. In order to remove this Na, more Ca is brought into cell by Na/Ca exchanges. The build-up of this Ca is responsible for increased for of contraction and reduced rate of conduction through AV node Heart failure Rate control in AF Nausea / vomiting Diarrhoea Confusion 18. Amiodarone Anti-arrhythmics This blocks cardiac K channels, prolonging repolarisation of cardiac action potential and therefore restoring regular sinus rhythm. Also slows AVN conduction Supraventricular / ventricular Arrhythmias Photosensitivity reaction in skin Hypersensitivity reactions Thyroid dysfunction Pulmonary fibrosis Neuro disturbance GI upset / hepatitis
19. Penicillins – Benpen, amoxicillin, flucloxacillin Beta-lactams – Penicillins Attaches to penicillin-binding-protein on forming bacterial cell walls, inhibiting transpeptidase enzyme which cross-links the bacterial wall. The bacteria therefore undergo autolysis. Fluclox covers S.aureus soft tissue infection, staphylococcal endocarditis, otitis externa Amoxicillin provides comes gram-neg in addition to gram-pos non-severe CAP Diarrhoea, vomiting Impaired liver function Hypersensitivity reaction
Infectives
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication Name Class MOA Side-effects Indication
Side-effects
20. Ceftriaxone / Cephalexin Beta lactams – Cephalosporins Work same way as penicillins, but are less susceptible to beta-lactamases than penicillins Provide both gram-positive and gram-negative cover Serious infection septicaemia / pneumonia / meningitis Hypersensitivity reactions Antibiotic-associated C.diff diarrhoea Impaired liver function 21. Vancomycin Glycopeptide Bactericidal inhibits cell-wall synthesis in gram positive bacteria Severe gram positive infections MRSA Severe C.Diff infection Fever Rash Local phlebitis as site of injection Nephrotoxicity Ototoxicity (rare) Blood disorders, including neutropenia If infusion is too fast, can get red-man syndrome 22. Gentamicin Aminoglycosides Binds to 30s ribosomal subunit – protein synthesis inhibited – prolonged post-antibiotic bacteriostatic effect. Bactericidal effect on cell wall – rapid killing early in dosing interval and is prominent at high doses. Provides synergistic effect when with other abx Severe gram-neg infections biliary tract, 23. Ciprofloxacin pyelonephritis, HAP Quinolone Some severe gram-pos soft tissue, endocarditis Interferes with bacterial DNA replication and repair Nephrotoxicity Broad-spectrum bactericidal antibiotics Ototoxicity Gram neg bacterial infection Respiratory tract infection Upper urinary tract infection Peritoneal infection Gonorrhoea Prostatitis GI toxicity QT wave prolongation C.Diff infection Tendonitis – extremely rare
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Respiratory
Indication Name Class Side-effects MOA
Indication Side-effects
24. Clarithromycin / Erythromycin Macrolide Binds to 50s ribosomal subunit, inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis Bacteriostatic AND bactericidal effects Atypical pneumonia / severe CAP Severe campylobacter infection Mild/moderate skin and soft-tissue infection Otitis media Lyme disease H.Pylori eradication therapy Diarrhoea / vomiting QT prolongation Ototoxicity with long-term use 25. Trimethoprim Inhibitor of folate synthesis Inhibits folate metabolism pathway, leading to impaired nucleotide synthesis, thus interfering with bacterial DNA replication First line antibiotic in uncomplicated UTI Acute/chronic bronchitis Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) Good range of action against gram negative and gram positive bacteria, including some MRSA cover Elevated serum creatinine Hyperkalaemia Depressed haematopoesis Rash and GI disturbances both relatively common 26. Aciclovir Anti-Virals A Guanosine derivative, it is converted to triphosphate by infected host cells. Aciclovir triphosphate then inhibits DNA polymerase, terminating the nucleotide chain and inhibiting viral DAN replication Herpes simplex infection 27. Salbutamol Varicella Zoster infection Short-acting Beta-2-adrenoreceptor agonist Nausea / vomiting Relaxes bronchial smooth muscle, inducing Local inflammation at infusion site if IV bronchodilation Inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine release from mast cells and TNF-alpha release from monocytes, reducing airway inflammation Increases mucus clearance from airways by stimulating cilia action Asthma COPD Tremor Tachycardia / cardiac dysrhythmia Headache Sleep disturbances
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA Indication
Side-effects
28. Salmeterol LABA Relaxes bronchial smooth muscle, inducing bronchodilation Inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine release from mast cells and TNF-alpha release from monocytes, reducing airway inflammation Increases mucus clearance from airways by stimulating cilia action Asthma COPD Tremor Tachycardia / cardiac dysrhythmia Headache Sleep disturbances 29. Tiotropium / Ipratropium Bromide Anti-muscarinic Bronchodilators Antagonist to muscarinic receptor M3, producing bronchodilatory effects by reducing mucus secretion and my increase clearance by cilia activation Asthma COPd Rhinits Dry mouth Cough constipation 30. Beclomethasone Inhaled corticosteroids Anti-inflammatory effect on airways, decreasing formation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulating beta-2-adrenoreceptors in airways COPD / Asthma Oral candiasis thrush Adrenal suppression Osteoporosis 31. Chloropheniramine/Desloratidine/Hydroxyzine Anti-histamines H1 receptor antagonists Inhibits Histamine-mediated contraction and vasodilation of bronchial smooth muscle Anaphylaxis Hay fever Urticaria Sedation Drowsiness Tinnitus
Neurology Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
32. Levadopa Dopamine Precursor Pro-drug, crossing BBB and converted to dopamine. Striatal dopaminergic neurotransmission is then released Parkinson’s Dyskinesia Compulsive disorders Hallucinations Nausea GI upset 33. Apomorphine / Bromocriptine / Rotigotine Dopamine agonist Stimulate post-synaptic dopamine receptors Apomorphine non-selective D1 and D2 dopamine subfamily of receptor Pramipexole Selective D3 receptor Parkinson’s Apomorphine – pain at site of injection / V&N Pramipexole – hallucinations, nausea, drowsiness, involuntary movements 34. Entacapone Catechol-O-Methyl Transferase Inhibitor Prevents peripheral breakdown of LDOPA by inhibiting COMT, an enzyme which converts LDOPA into 3-OMD, which cant cross BBB. This increases LDOPA deliverance to brain Parkinson’s, in conjunction with LDOPA and dopamine decarboxylase inhibitor Dyskinesia Neuaea Abdominal pain Vomiting Dry mouth Diziness
35. Carbamazepine Anti-Epileptic drug Voltage gated Na channel blocked on pre-synaptic membrame, blocking Na influx and there reducing neuronal excitability and decreasing action potential Epilepsy Trigeinal neuralgia Neuropathic pain Dizziness Dry mouth Ataxia Fatuigue Headache Diplopia / blurred vision Yponatraemia Rarely, Stevens-Johnson’s-Syndrome
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
36. Sodium Valproate Anti-Epileptic Drugs Weak Na channel blocker / inhibitor of GABA degrading enzymes, increasing GABA which stops action potentials Epilepsy Bipolar disease Depression Nausea Diarrhoea Gastric irritation Hyponatraemia Confusion – uncommon Behavioural disturbance – rare SJS – really rare 37. Phenytoin Anti-Epileptic drugs Acts as voltage-gated Na channel blocker on postsynaptic neuronal membrane, limiting action potential transmission and therefore limiting spread of seizure activity Epilepsy, including status epilepticus Trigeminal neuralgia Insomnia Headache Rash Constipation Vomiting Gingival hyperplasia Liver damage SJS – rare Leucopenia – rare Thrombocytopenia - rare
38. Lamotrigine Anti-Epileptic Drugs Inhibits voltage-gated Na channels and/or Ca channels. Acts on presynaptic neuronal membrane Reduces action potential and excitatory signals Epilepsy Depressive episodes associated with bipolar Nausea / vomiting Diarrhoea Tremor Insomnia Blurred vision Aggression Rarely, skin reactions such as SJS
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
39. Levetiracetam Anti-Epileptic Drugs SV2A is a synaptic vesicle protein required for neurotransmitter release but is blocked by this drug, inducing anti-epileptic effect Epilepsy Headache Fatigue Anxiety / irritability Drowsiness constipation 40. Citalopram / Fluoxetine / Sertraline Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Inhibition of reuptake of serotonin of synaptic cleft in CNS, increasing serotonin stimulation of somatodendritic 5-HT1Aa and terminal autoreceptors Depression Buiia OCD Dry mouth Nausea Insomnia Anxiety Decreased libido 41. Amitriptyline / Imipramine / Doxepin Tricyclic Antidepressants Stops reuptake of monoamines by binding to monoamine pump at pre-synaptic cleft. This combats depression Depression Panic disorders Neuropathic pain Sedation Postural hypotension / tachycardia Urinary retention Dry mouth Blurred vision / diplopia 42. Haloperidol /Chlorpromazine / Clozapine Anti-psychotics Blocks dopamine receptors, having an action on mesolimbic and nigrostriatal parts of the brain, as well as anti-histaminergic and anti-cholinergic effects. These effects therefore reduce positive symptoms of schizophrenia and can cause sedation and provide anti-emetic activity Schizophrenia Mania Delusions / hallucinations Behavioural problems Anti-emetic (haloperidol) Sedation Postural hypotension / tachycadia Urinary retention Dry mouth Blurred vision
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
43. Diazepam / Lorazepam / Midazolam Benzodiazepines Increases GABA affinity for GABA receptor, increasing chloride flow through chloride channels. Hyperpolarisation occurs, reducing activity of limbic, thalamic, hypothalamic areas of the brain Axiety Epilepsy Muscle Spasm Alcohol withdrawal Sedation Ataxia Altered mental status Insomnia 44. Prednisolone / betamethasone / Methylpred Corticosteroids Binds to glucocorticoids, causing up-regulation of a variety of anti-inflammatory mediators and down regulation of pro-inflammatory, providing immunosuppression Replacement therapy in adrenal insufficiency Post-transplant immunosupression Treatment of exacerbations of variety of inflammatory conditions Treatment of acute asthma Sleep disturbance Mood disturbance / psychosis Hyperglycaemia Immunodeficiency Easy bruising Moon-faced / increased abdominal fat Gluacoma Striae HTN Gastric irritation 45. Etanercept / Infliximab / Adalimumab Anti-TNF agents Block interactions with TNF and TNF cell receptors. TNF are produced from macrophages and stimulate cytokines (IL1, IL8, IL6). So inhibition reduces inflammation Rheumatoid Arthritis Psoriatic arthritis Ankylosing spondylitis JIA Injection site reactions Flu-like symptoms fever, headache, runny nose Immune deficiency esp. legionells and listeria and reactivation of TB
Name Class MOA
Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA Indication
Side-effects
Name Class MOA
Indication Side-effects Name Class MOA
Indication Name Side-effects Class MOA
Similar Free PDFs

Meropenem (Merem) - drug summary
- 1 Pages

BNF Drug Summary
- 7 Pages

THE DRUG Tariff - Summary
- 6 Pages

Drug Calculations Summary
- 2 Pages

Summary of drug calculations
- 4 Pages

4 Year Plan - my 4 year plan
- 2 Pages

Summary CFA curriculum book pdf
- 11 Pages

Calc summary year 2021
- 2 Pages

4. anticoagulants drug table
- 5 Pages

Entire Law Year 1 Summary
- 191 Pages

Biology-Curriculum - Curriculum
- 18 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu