6. Classification of Tissue (Review sheet) PDF

| Title | 6. Classification of Tissue (Review sheet) |
|---|---|
| Author | ekaterina burtov |
| Course | Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 |
| Institution | Miami Dade College |
| Pages | 10 |
| File Size | 610.3 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 37 |
| Total Views | 165 |
Summary
6. Classification of Tissue (Review sheet...
Description
6
E X E R C I S E
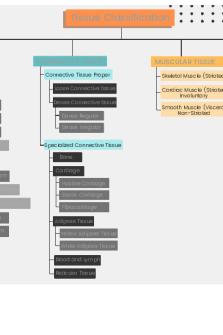
Classification of Tissues Time Allotment:2 hours.
Multimedia Resources: See Appendix B for Guide to Multimedia Resource Distributors. Eroschenko’s Interactive Histology (DE: CD-ROM) Practice Anatomy Lab™ 3.0 (PAL) (PE: DVD, website)
Laboratory Materials Ordering information is based on a lab size of 24 students, working in groups of 4. A list of supply house addresses appears in Appendix A.
24 compound microscopes, lens paper, lens cleaning solution, immersion oil 24 slides of simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, stratified squamous (nonkeratinized), stratified cuboidal, stratified columnar, pseudostratified ciliated columnar, and transitional epithelium
24 slides of mesenchyme; adipose, areolar, reticular, and dense connective tissue, regular (tendon) and irregular (dermis); hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, fibrocartilage; bone (cross section); and blood smear 24 slides of skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle (longitudinal sections)
24 slides of nervous tissue (spinal cord smear) 6 envelopes containing color images of epithelial tissues 6 envelopes containing color images of connective tissues, nervous tissue, and muscle tissues 6 envelopes containing a color image of a section of the trachea
Advance Preparation 1. Set out prepared slides of simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, stratified squamous (nonkeratinized), stratified cuboidal, stratified columnar, pseudostratified ciliated columnar, and transitional epithelium. 2. Set out prepared slides of mesenchyme; adipose tissue, areolar connective tissue, reticular connective tissue, dense connective tissue regular (tendon), and irregular (dermis) varieties; hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, and fibrocartilage; bone (cross section); and blood (smear). 3. Set out prepared slides of skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle (longitudinal sections). 4. Set out prepared slides of spinal cord smear. 5. Set out lens paper and lens cleaning solution. Have compound microscopes available. 6. For Group Challenge 1, obtain 6 medium brown envelopes. Using old histology atlases or lab manuals, cut out several color images of each of the epithelial tissues. Place various examples of the tissues in each of the 6 envelopes. You need not include all of the tissues in each envelope. Distribute 1 envelope to each group after they have studied the epithelial tissues. 7. For Group Challenge 2, obtain 6 medium brown envelopes. Using old histology atlases or lab manuals, cut out several color images of each of the connective tissues, nervous tissue, and each of the muscle tissues. Place various examples of the tissues in each of the 6 envelopes. You need not include all of the tissues in each envelope. Distribute 1 envelope to each group after they have studied the connective tissues, nervous tissue, and the muscle tissues. For the second part of this Group Challenge, obtain 6 more medium brown envelopes. Using old histology atlases or lab manuals, cut out a color image of a section of the trachea. As you proceed away from the luminal side of the tissue, you should see ciliated pseudostratifed columnar epithelium, areolar connective tissue of the lamina propria, epithelial tissue of the submucosal glands, and hyaline cartilage. Give this envelope to each group at the end of the study of tissues.
34
Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
Comments and Pitfalls 1. Slides of the lung are suggested for simple squamous epithelium, and slides of the kidney are suggested for simple cuboidal epithelium. An analogy using a quarter or pavement stone will help students visualize the three-dimensional shape of a squamous cell. 2. The dense fibrous regular connective tissue slide is sometimes labeled white fibrous tissue. 3. Students may have trouble locating the appropriate tissue on slides with multiple tissue types. Encourage them to consult lab manual Figures 6.3–6.7, available histology texts, and each other for help. 4. A television camera with a microscope adapter and monitor is very useful in this lab. By watching the monitor, students can observe the instructor locating the correct area of tissue on the slide (see item 3 in Comments and Pitfalls). It also makes it easier to answer student questions and share particularly good slides with the class. 5. Use the final envelope containing a section of the tracheal wall to help students understand how tissues are organized to form an organ. Encourage them as they look at this complicated image; tell them to start at the luminal surface and look at each tissue carefully.
Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 65) 1. c, squamous 2. c, mesenchyme 3. c, neurons 4. neurons 5. 3
Answers to Activity Questions Activity 2: Examining Connective Tissue Under the Microscope (p. 73) All connective tissues consist of cells located within a matrix. Blood is no exception, but its cells float freely in a liquid matrix. The matrix ground substance is the straw-colored fluid called plasma. Its proteins are soluble, rather than fibrous, and include albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen.
Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
Exercise 6
35
R E V I E W
6
NAME _EKATERINA BURTOV____
S H E E T
LAB TIME/DATE __9/22/21_________
EXERCISE
Classification of Tissues Tissue Structure and Function—General Review 1.
List the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, cell, tissue, and organ system
.___cell, tissue, organ, organ system 2.
Define histology. the study of microscopic structure of tissues
3.
Use the key choices to identify the major tissue types described below. Key: a. connective tissue
b. epithelium
c. muscle
B
1. lines body cavities and covers the body’s external surface
C
2.
pumps blood, flushes urine out of the body, allows one to swing a bat
B
3.
forms endocrine and exocrine glands
A
4.
anchors, packages, and supports body organs
B
5.
classified based on the shape and arrangement of the cells
C,A
6.
derived from mesenchyme
C
7.
major function is to contract
D
8.
transmits electrical signals
A
9.
consists of cells within an extracellular matrix
C
10. most widespread tissue in the body
D
11. forms nerves and the brain
Epithelial Tissue 4.
Describe five general characteristics of epithelial tissue
Polarity, cellularity, attachment, avascularity, regeneration.
36
d. nervous tissue
Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
5.
For each function listed, name one type of epithelium and an organ that provides for that function. Function 1: Protection stratified squamous epithelium, surface of skin, lining of mouth. esophagus, rectum, vagina. Stratified columnar epithelium, mammary glands, salivar gland ducts, urethra Function 2: Diffusion simple squamous epithelium. Mesothelia ( pleural, peritoneal, pericardial) endohteliua (blood vessels) alveoli, thin section of nephron loops. Function 3: Secretion simple cuboidal epithelium. Exocrine glands, ducts, kidney tubules Function 4: Filtration simple squamous epithelium. Mesothelia ( pleural, peritoneal, pericardial) , thin section of nephron loops Function 5: Absorption simple columnar epithelium. Lining of digestive tract
6.
What structural feature do epithelia that provide for protection have in common?.
7.
Describe the following cell-surface modifications using the table below. Cell-surface modification
Type(s) of epithelia with the
They are stratified
Function (include a specific organ)
modification Cilia
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Protection, secretion, move mucus with cilia. Lining of nasal cavity, trachea and bronchii
Goblet cells
Simple columnar epithelium
.synthesis and secretion of mucus. large intestine and distal ileum, respiratory tract
Microvilli
Simple columnar epithelium
.absorbtion, secretion of mucus, enzymes.. stomach, rectum, gallbladder, uterine tubus
8. Transitional epithelium is actually stratified squamous epithelium with special characteristics.
How does it differ structurally from other stratified squamous epithelia? Stratified epithelia contains more than one layer, epithelia called stratified because of shape of superficial layer . The shape of transitional between is cuboidal and squamous.Transitional epithelium is a type of stratified epithelium. ______________________________________.
How does the structural difference support its function? When the tissue stretched, its top layers are squamous, when not stretched, top layers are cuboid The surface cells have the ability to slide over one another, increasing the internal volume of the organ. 9.
How do the endocrine and exocrine glands differ in structure and function? __________________________________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
Review Sheet 6
37
exocrine glands have ducts and their secret goes to the duct. Endoc rine glands secret to extracellular fluid, they don’t have ducts._____________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___.
38
Review Sheet 6
Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
Connective Tissue 10. What are three general characteristics of connective tissues? _Support, protection, binding organs togrther____________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____
What functions are performed by connective tissue?
11.
They maintain the form of the body and its organs and provide cohesion and internal support. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________=____________________________________________________.
How are the functions of connective tissue reflected in its structure? ___
12.
There is wide variety in structure and in function as well. Living cells are soft and fragile, large amount of fibers seen provides the strength needed for the normal functions of connective tissues _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________. 13. Using the key, choose the best response to identify the connective tissues described below. a. adipose connective tissue d 1. attaches bones to bones and muscles to bones Key: b. areolar connective tissue a c. dense irregular connective 2. insulates against heat loss tissue
d
3. forms the fibrous joint capsule
g
4. makes up the intervertebral discs
d. e. f. g. h. i.
tissue dense regular connective tissue elastic cartilage elastic connective tissue fibrocartilage hyaline cartilage osseous tissue
_b_____
5. composes basement membranes; a soft packaging tissue with a jellylike matrix
___h_
6. forms the larynx, the costal cartilages of the ribs and the embryonic skeleton
_e___
7. provides a flexible framework for the external ear
___i_
8. provides levers for muscles to act on
__e__
9. forms the walls of large arteries
Nervous Tissue 14. What two physiological characteristics are highly developed in neurons? Conductivity, irritability 15. In what ways are neurons similar to other cells?. Contain nucleus and other organells How are they structurally different?. They have long processes
Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
Review Sheet 6
39
16. Describe how the unique structure of a neuron relates to its function in the body. conduct impulses on long distance
40
Review Sheet 6
Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
Muscle Tissue 17. The terms and phrases in the key relate to the muscle tissues. For each of the three muscle tissues, select the terms or phrases that characterize it, and write the corresponding letter of each term on the answer line. Key:
a. b. c. d.
striated branching cells spindle-shaped cells cylindrical cells
e. f. g. h.
voluntary involuntary one nucleus many nuclei
i. j. k. l.
attached to bones intercalated discs in wall of bladder and t h forms heart walls
Skeletal muscle: _a,d,e,h,i____________Cardiac muscle: __b,f,j,g, l_________________Smooth muscle: c,f,g,k
18. Orthopedic surgeons are fond of saying, “It is better to break a bone than it is to tear a tendon or ligament.” Based on your understanding of these two types of connective tissue, explain why that would be true. _____ tendons and ligaments heal slower because they have less blood vessels than bones _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________. 19.
A buccal swab procedure removes stratified squamous cells to obtain the DNA profile of an individual. Explain why a buccal swab shouldn’t cause bleeding.. squamous epithelia does not contain blood vessels
20.
When cardiac muscle tissue dies in adults, it is replaced with scar tissue composed of dense connective tissue. Explain howthe function of the scar tissue would differ from the function of the cardiac muscle tissue. ______Scar tissue is not able to contract
21.
Smoking impairs cilia because the toxins paralyze and can destroy the cilia. Based on this loss of function, explain whichtypes of infections smokers would be more susceptible to
______upper and lower respiratory infections, because cilia is damaged and don’t do its function (sweeping pathogens out of airways)___________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________.
Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
Review Sheet 6
41
For Review 22. Label the tissue types illustrated here and on the next page, and identify all structures provided with leaders. a: ______________________________________ b: ______________________________________ c: ______________________________________ d: ______________________________________ e: ______________________________________ f: ______________________________________
g: ________________________________ h:________________________________ i:_________________________________ j: ________________________________ k: ________________________________ l:_________________________________
Connective tissue
cilia
Columnar epithelium cell Basal membrane Basal membrane Simple columnar epitelium
Connective tissue (Lamina propria) Pseudostratified columnar epitehelium
Keratinized squamous epithelium
Basal cell layer
Basal membrane
Stratified squamous epithelium Transitional epithelium
Connective tissue (Lamina propria)
Elastin fiber Nucleus of fibroblast
Collagen fiber fibroblast
Collagen fiber
Areolar connective tissue 42
Review Sheet 6
Dense connective tissue Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
matrix osteocyte Nucleus of chondro cyte Central canal chondrocytes
Hyaline cartilage
Osseous tissue
adipocytes Nuclei of smooth muscle cell
lipids
cytoplasm
Adipose tissue
Smooth muscle
Intercalated dis
nuclei
myocyte
Cardiac muscle cell nucleus
Cardiac muscle
Skeletal muscle
Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
Review Sheet 6
43...
Similar Free PDFs

Tissue Review
- 6 Pages

Review Sheet Topic {6} Answer
- 6 Pages

Chapter 4 tissue review
- 39 Pages

HITT 1305 Chapter 6 Review Sheet
- 3 Pages

Solution of Tutorial sheet 6
- 12 Pages

Review sheet
- 42 Pages

Proliferative capacity of tissue
- 1 Pages

Histology of cardiac tissue
- 3 Pages

Histology of Nervous Tissue
- 2 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu