Drugs Used in Optometry Australia PDF

| Title | Drugs Used in Optometry Australia |
|---|---|
| Author | Ai Lam |
| Course | Knowledge Of Health And Illness For Optometrists 2 |
| Institution | Flinders University |
| Pages | 6 |
| File Size | 409.2 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 10 |
| Total Views | 198 |
Summary
A table breaking down the drugs used in optometry Australia including mechanism of action, indications, dosage and contraindications. ...
Description
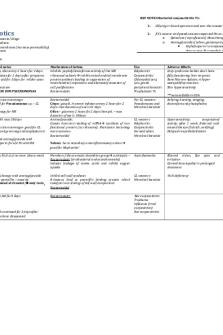
KEY NOTES Bacterial conjunctivitis Tx:
Ocular Antibiotics Mechanism of Action of Antibacterial Drugs 1. Inhibit cell wall synthesis 2. Affect cytoplasmic membrane (increase permeability) 3. Affect protein synthesis 4. Affect folic acid 5. Affect DNA synthesis Drug Chloramphenicol 0.5% drops 1% ointment
Dose and notes Every qih, then every 2 hours for 2 days. Q.i.d. continue for 2 days after symptoms cleared – qid for 5 days for milder cases
(chlorsig)
Broad spectrum NOT GOOD FOR PSEUDOMONAS
Quinolones Ciprofloxacin Ofloxacin
Broadspectrum coverage Still good for Pseudomonas sp. – CL wearers Monotherapy for MK
Aminoglycosides
1-2 gtt q4h max 10 days
Gentamycin 0.3% (Genoptic)
Broadspectrum coverage- good for CL wearers and gram neg and staphylococci
Tobramycin 0.3% (tobrex)
Use fortied aminoglycoside with Cephalosporin for old Px with MK
Brolene Propamidine 0.1% drops 0.15% ointment
1-2 drops B.i.d-t.i.d no more than a week
Cephalosporin (cefazolin) 5% drops
1.
Chlorsig is broad spectrum and over the counter
2.
If CL wearer and pseudomonas suspected Mx as MK: o Quinolone (ciprofloxacin) Monotherapy o Aminoglycosides (tobrex, gentamycin)+ Cephalosporin Cephalosporin is compound @ chemist and only lasts 4 days so new Rx is needed- too troublesome!!!
Mechanism of Action Inhibits peptidyltransferase activity of the 50S ribosomal subunit inhibit mitochondrial membrane protein synthesis leading to suppression of mitochondrial respiration and ultimately cessation of cell proliferation Bacteriostatic
Use Blepharitis Conjunctivitis Chlamydial conj. Low grade peripheral keratitis Prophylactic Tx
Bacteriocidal Cirpo- gtt qid. In severe infetions every 2 hours for 2 days- max duration of use is 21 days Oflox – gtt every 2 hours for 2 days then qid. – max duration of use is 10 days Aminoclycoside: Causes incorrect reading of mRNA synthesis of non functional protein (at ribosome). Resistance becoming more common Bacteriocidal
For CL wearersPseudomonas and Microbial keratitis
Adverse Effects Gray syndrome: babies don’t have fully functioning liver enzymes Bone Marrow Aplasia: A hypersusceptibility reaction. Skin hypersensitivity ***not available in USA Itchying, burning, stinging, discomfort and photophobia
Contraindications Infants Pregnancy Lactation CYP450: can be interfered by due to inhibiting microsomal enzymes Oral Anti-coagulants pregnancy
CL wearers Blepharitis Conjunctivitis Corneal ulcers Microbial keratitis
Hypersensitivity, conjunctival toxicity after 1 week. External rash around the eye (lid itch, swelling) Delayed re-epithelialisation
Member of the aromatic diamidine group antiseptic – Bacteriostatic (antibacterial and acanthamoeba) Induces leakage of amino acids and inhibit oxygen uptake
Acanthameoba
Blurred vision, Eye pain and irritation Corneal keratopahty in prolonged treatment
Hypersensitivity CL’s use
Q1h Duotherapy with aminoglycoside Synthetic penicillin – must be compounded at chemist only lasts 4 days
Inihbit cell wall synthesis B-lactam: bind to penicillin binding protein which catalyse cross-linking of cell wall components Bacteriocidal
CL wearersMicrobial keratitis
Vit K deficiency
Known allergy Haemophillia
Macrolides Azithromycin
1-2 drops bid for 3 days
Bacteriostatic
Tetracyclines ointment
Bid or qid continued for 2 days after symptoms have disapeared
Bac conjunctivitis Trachoma Influenza (viral conjuntivitis) Bac conjunctivitis
Tobrex has a secondary anti-inflammatory action good for blepharitis!
< 8 years old
Ocular Antivirals Drug Acyclovir 3% (Zovirax) ointment
Use Topical: HSV epithelial and stromal keratitis Oral: reduce severity of acute symptoms and reduce recurrence of epithelial/ stromal HSV by 30/50%
Dose and Notes Ointment: 1cm 5x/day for 14 days then 3 days after recovered Oral: 800mg 5x/day for 7 days then 3 days after
Mechanism of Action Acyclovir triphosphate competitively inhibits viral DNA polymerase. When incorporated into viral DNA acts as chain terminator since it lacks deoxyribose 3’-OH end no DNA synthesis
Side Effects Mild stinging Superficial punctate keratopathy
Contradictions Avoid CL use
MK Review peroid: Next day Day 3 Every 1-2 days until lesion gets better Once a week for 2-3 weeks after recovery If by day 7 lesion has not altered, Px should be referred to an opthalmologist MK Antibiotic Tx Empirical: Quinolone monotherapy (Ciprofloxacin 0.3%) OR Cephalosporin + Aminoglycoside Cefazolin 5%+ Gentamicin 1.5%
Ocular Steroids Drug
Use
Penetration
Mechanism of Action
Side Effects
Contradictions
Prednisolone acetate 1% (PredForte)
Fluorometholone with acetate 1% (Flarex) Fluorometholone with alcohol 0.25% (FML Forte) Fluorometholone SUSPENSION 0.1% FML Dexamethasone sodium 0.1% (Maxidex) Hydrocortisone 0.5% or 1% ointment
Acute anterior uveitis Qih for 1 hr, then every one for 1 day. Qid for 1-2 days and taper gradually. Reduce by one drop every week (4 week taper) Post LASIK Sx to reduce graft rejection Iritis Inflammation and infection
Allergic conjunctivitis GPC, sterile infiltrates Episcleritis Dry eye Qid for 1 week then taper Treat short-term inflammatory eye conditions, conjunctivitis, iritis, uveitis, keratitis Tid for temporary relief of anterior blepharitis, seborrheic dermatitis
Best penetration into AC
Glucocorticoid inhibit the edema, fibrin deposition, capillary dilation, and phagocytic migration of the acute inflammatory response, as well as capillary proliferation, deposition of collagen, and scar formation.
Use for 18months Posterior Subcapsular Cataract
Surface acting, 2.5x stronger potency then prednisolone
Corticosteroids inhibit inflammatory response oedema, capillary dilation and proliferation, leukocyte migration and scar formation associated with inflammation
4 months PSC
Surface acting
Work by induction of phosolipase A2 inhibitory proteins, these proteins control biosynthesis of mediators or inflammation such as prostaglins and leukotrienes by inhibiting the reliase of their precursor – arachionic acid.
Surface acting, low penetrance
High potency, good penetration Rapid acting- short duration
Corticosteroid decrease inflammation 1. Decrease lymphocytes, monocytes ect 2. Inhibit synthesis of interleukins, cytokines 3. Stablise lysomal membranes
Viral Fungal Mycobacterium infectious Purulent conditions of the eye After FB removal Undiagnosed red eye Glaucoma – corticosteroids increase IOP Herpetic Keratitis Tuberculosis
Discomfort in eye, FB sensation
Ocular Penetrance (most to least): 1. Acetate 2. Alcohol 3. Phosphate
Anti Glaucoma Drug
Mechanism of Action
Dose and Notes
Side Effects
Contraindications
1 drop once a day in the evening
Prostagaladin Analogue:
Increase uveoscleral outflow (upregulation production of various metaloprotinases →
Stinging, burning Periorbital pigmentation
Inflammatory disease Hx of CMO HSV keratitis
Anti Glaucoma Drug
Mechanism of Action
Dorzolamide 2% (Trusopt)
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor: Brinzolamide 1% (Azopt)
decrease aqueous production Decrease IOP 10 -20%
Acetazolamide 250mg (Diamox) tablet
Decrease IOP 20-30%
Dose and Notes
Side Effects
Contraindications
Monotherapy: gtt t.i.d Adjunctive therapy: bid (good adjunctive therapy to B-blocker) gtt t.i.d Better tolerance than dorzolamide due to more physiological pH
Ocular: Stinging/burning Hypersensitivity Irreversible corneal decompensation Corneal oedema, haze (children)
Ocular: Corneal endothelium compromise
Common: Paraesthesia of hands & feet Nausea vomiting, fatigue & weight loss Depression Uncommon: Bone marrow depression aplastic anaemia Ocular: Browache Stinging/ irritation Ciliary spasm (myopia) Miosis Papillary block - advanced cataract Retinal detachment - high myopia Cataract –long term use Systemic (uncommon): Headache Dyspnea Bradycardia/arrhythmia Salivation, sweating Diarrhoea/vomiting GI disturbance
Hypersensitivity to sulfonamides Marked renal or hepatic problem Pregnancy
250mg Tablet: 1-4 times a day 500mg Capsule 1-2 times a day
Pilocarpine 1% (Pilopt)
Direct acting muscarinic agonist: act on mACh receptors contaction ciliary muscle and sphincter papillae open up spaces in TM and causes miosis further opens up angle
Carbachol 1.5% (Isopto Crbachol)
Decrease IOP 20-25%
Cholinergic Agonist
gtt q.i.d for open angle 3 drops over 30 minutes for closed angle It has been shown to decrease uveoscleral outflow, which may have a significant clinical effect in the eye with compromised TM outflow Tid More potent than pilocarpine - may be used to control IOP where pilocarpine is ineffective or in cases of pilocarpine sensitivity
Systemic: Hypersensitivity to sulfonamides
Ocular: High myopia Cataracts Inflammation Infection Previous Hx of RD Neovascular & uveitic glaucoma – vasodilation & increase inflammation Px...
Similar Free PDFs

Drugs USED IN Parkinson Disease
- 10 Pages

Drugs used for Constipation
- 3 Pages

Health Priorities in Australia
- 30 Pages

Social Darwinism in Australia
- 3 Pages

Italian Hospitality in Australia
- 3 Pages

Drugs in solution
- 10 Pages

plastic used in concrete
- 29 Pages

Fixatives used in Histopathology
- 9 Pages

Abbreviations used in histology
- 2 Pages

Optometry basics
- 72 Pages

Racism in australia, essay plan
- 20 Pages

Pdhpe- Health priorties in Australia
- 21 Pages

SLOW WAGE Growth IN Australia
- 1 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu