Haematology - Collated from sources such as Passmed, Zero to Finals, AMBOSS, BMJ best practice PDF

| Title | Haematology - Collated from sources such as Passmed, Zero to Finals, AMBOSS, BMJ best practice |
|---|---|
| Course | Medicine |
| Institution | Cardiff University |
| Pages | 12 |
| File Size | 681 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 17 |
| Total Views | 135 |
Summary
Collated from sources such as Passmed, Zero to Finals, AMBOSS, BMJ best practice...
Description
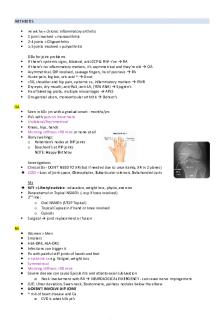
Anaemia Hb 2 osteolytic lesions Low Hb Low albumin
lesions = back ache, vertebral collapse, pathological fractures Infection
for bone lesions XR spine, skull (“punched out pepper pot skull”), pelvis Urinary BENCE JONES PROTEINS
Radiotherapy for focal disease Orthopaedic input if there’s vertebral collapse Recurrent Immunoglobulin infusions Chemotherapy
Tumour Lysis Syndrome
Triggered by Chemotherapy or steroid use Tumour breakdown releases toxic chemicals o Uric acid o Phosphate o Potassium Low Calcium PROPHYLAXIS IS KEY: o IV Allopurinol or Rasburicase before and during 1st few days o IV Fluids 2 days before o Loop diuretic
Neutropenic sepsis
Neutrophil count 38 7-14 days after chemo PROPHYLAXIS = Fluoroquinolone Mx: o IV Abx without waiting for bloods Tazocin If still unwell after 48 hrs switch to Meropenem +/- Vancomycin If not responding, consider fungal cause - CT
SVC obstruction
SOB Swelling of face, neck, arms Headache o Worse in morning Visual disturbance Jugular venous distension GET A CT WITH CONTRAST Mx: o Dexamethasone + balloon venoplasty and stenting o Lie pt on side whilst awaiting surgery (relieves pressure)
Hypercalcaemia
IV Fluids IV bisphosphonates if severe (>3.4)
Spinal cord compression Back pain o Worse when lying down or coughing Numbness
Paraesthesia Bladder/bowel dysfunction Muscle wasting T2 MRI Mx: o Immobilise pt o Dexamethasone o Urgent decompression surgery
Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Polycythaemia Vera
Essential thrombocytosis
Myelofibrosis
Cell type involved RBC
Platelets
Fibroblasts
Px
Investigation
Mx
Prognosis
JAK2 mutation >60 y/o Hyperviscosity sx e.g. headaches, dizziness, vision changes, tinnitus, pruritis (esp after hot bath), burning in fingers/toes Thrombosis Facial plethora Splenomegaly Gout (from ^ RBC turnover)
FBC: ^RBC’s (so ^Hb) ^WBC’s ^Plt’s
Venesection if low risk
--> Myelofibrosis in ~30%
FBC: Plt’s >450x109
JAK2, CALR or MPL Usually clinically well Bleeding Atypical chest pain Headache Dizziness B Symptoms Bone marrow failure sx Massive hepatosplenomegaly - causes abdo discomfort
Bone marrow shows panmyelosis Low serum EPO
WBC
--> Acute leukaemia in ~5% Monitor FBC’s every 3 months
+ Aspirin 75mg OD Aspirin 75mg OD Hydroxyurea if high risk Blood film: Tear drop RBC’s (nucleated) FBC: Low Hb ^WBC’s ^Plt’s Bone marrow biopsy is Dx
CML
Hydroxyurea if high risk: >60 y/o Previous VTE (or IFNa if child-bearing age)
JAK inhibiters - Ruxolitinib Supportive e.g. transfusions, Abx, Allopurinol Bone marrow transplant is curative
Median survival 4-5 yrs...
Similar Free PDFs

Belajar MySQL (From zero to Hero)
- 119 Pages

Synthesizing Ideas from Sources
- 2 Pages

BEST PRACTICE
- 27 Pages

Haematology notes
- 44 Pages

Uts-Finals - Prelim to Finals
- 29 Pages

MAF finals practice questions
- 10 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu