Homework Chapter 02 - Production and Operations Management PDF

| Title | Homework Chapter 02 - Production and Operations Management |
|---|---|
| Author | Nguyễn Khánh Linh |
| Course | Business Administration |
| Institution | HCMC University of Technology |
| Pages | 6 |
| File Size | 154.1 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 96 |
| Total Views | 127 |
Summary
Sample Solution for Problems Chapter 02 in Production and Operations Management book...
Description
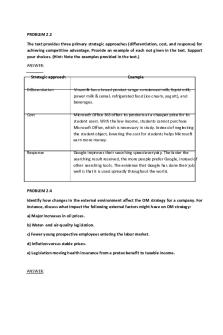
PROBLEM 2.2 The text provides three primary strategic approaches (differentiation, cost, and response) for achieving competitive advantage. Provide an example of each not given in the text. Support your choices. (Hint: Note the examples provided in the text.) ANSWER: Strategic approach
Example
Differentiation
Vinamilk has a broad product range: condensed milk, liquid milk, power milk & cereal, refrigerated food (ice cream, yogurt), and beverages.
Cost
Microsoft Office 365 offers its products at a cheaper price for its student users. With the low income, students cannot purchase Microsoft Office, which is necessary in study. Instead of neglecting the student object, lowering the cost for students helps Microsoft earn more money.
Response
Google improves their searching speed everyday. The faster the searching result received, the more people prefer Google, instead of other searching tools. The evidence that Google has done their job well is that it is used spreadly throughout the world.
PROBLEM 2.4 Identify how changes in the external environment affect the OM strategy for a company. For instance, discuss what impact the following external factors might have on OM strategy: a) Major increases in oil prices. b) Water- and air-quality legislation. c) Fewer young prospective employees entering the labor market. d) Inflation versus stable prices. e) Legislation moving health insurance from a pretax benefit to taxable income.
ANSWER:
External factors can have an impact on OM strategy for a company. For instance:
When the oil prices experience a dramatic increase, companies using oils in their value chain could be heavily affected. If oils are one of the crucial resources of the company, the Operation manager should evaluate their effectiveness on the company itself and have a critically responsive strategy. As a value-added resource to provide energy for the company’s operation, oils, or the use of oils, can be changed and even replaced with cheaper energy so as to minimize the increase in total cost. Nevertheless, if the oil is the core competency of the companies, urgent actions should be taken to ensure that it will not affect company advantages. An example can be given when companies are producers consuming a large amount of energy. The higher the prices are, the higher price the end-products have due to changes in the company’s cost structure.
When stricter water-and-air quality policies are imposed, operation managers should reevaluate their operations in that specific area and take action to ensure they don’t violate the new rules. In that case, strategies to reduce carbon footprint, as well as water consumption, should be focused on, such as reclosing current factories, adopting new technologies to facilitate wastage, replacing current-used energy with green ones, and so on. If it is too expensive and impossible to solve this phenomenon in the short-term, companies have to pay the penalties and keep seeking specific strategies/ technologies to solve the problem.
When there are fewer young prospective employees entering the labor market, the labor market is tighter, which means it is difficult to attract high-qualified candidates. Not only do the companies pay attention to employee retention strategy but they also focus on recruiting strategy to better their employment. Good quality of work-life, equitable pay, rewarding job, healthy environment, … can attract more employees but require heavy changes in strategy. It is the problem that the Operation manager has to tackle; then provide the human resources department with a thoughtful direction to execute.
OM (Operations Management) can inform a response to a change in the external environment. By identifying core competencies and key factors for success, companies can analyze their environment, determine a corporate mission, and form a strategy. (a) A major increase in oil prices can be evaluated with a manager’s resource view and value —chain analysis. Resource view would evaluate higher oil prices as a strategic disadvantage. Managers would seek a strategy that reduces oil or finds an alternative energy source. Value-chain analysis would view oil as a value-added resource but seek a
way to maximize this value with minimum cost. (b) Water- and —air quality legislation would change the OM strategies in the areas of and geography, Managers would seek to reduce water and air pollution so as to reduce or eliminate associated fines and penalties. If this is too expensive or impossible, … PROBLEM 2.5 Within the food service industry (restaurants that serve meals to customers, but not just fast food), find examples of firms that have sustained competitive advantage by competing on the basis of (1) cost leadership, (2) response, and (3) differentiation. Cite one example in each category; provide a sentence or two in support of each choice. Do not use fast-food chains for all categories. (Hint: A “99¢ menu” is very easily copied and is not a good source of sustained advantage.) ANSWER: (1) Cost Leadership: Low-cost leadership entails achieving maximum value as defined by your customer. Example: Hanuri is a restaurant that sells Korean food which applies low-cost leadership, especially in Human resources and job design and Design of goods and services (10 OM Decisions). Hanuri uses a self-serve routine that decreases the cost for Human resources. The food, in the same case, is made by average quality however, it still follows with strict discipline to meet customer expectations of value (the main target of Hanuri is mainly student with lowincome).
(2) Response: A set of values related to rapid, flexible, and reliable performance. Example: Poke Saigon founder Emmanuel Tieu was the first to introduce poke cuisine to Vietnam back in December 2016. Poke—pronounced “po-kay”—originated in Hawaii and has been an integral part of local food culture there for centuries. Historically, poke was a cheap and convenient snack for fishermen. But poke’s modern form comes in bowls of raw cubed fish on a bed of rice with vegetables dressed in sauces like soy and sesame oil. Poke Saigon became an example of our group since it meets with the Flexible response, reliability of scheduling criterias. Poke Saigon offers a wide range of add-ins for your salad bowl like salmon, tuna, fresh vegetables and so forth, which can quickly meet with any appetite of Vietnamese people. Moreover, the ingredients and the menu is made seasonal to catch up with the change in Vietnam's tropical supply market.
(3) Differentiation: Distinguishing the offerings of an organization in a way that the customer perceives as adding value. Example: From 2017, there have been more and more restaurants that apply Cantonese concepts, including Baozi. To win the market, Baozi has applied many aspects in differentiation strategy.
The Product Differentiation: So instead of selling what other Taiwanese restaurants are selling, the owner of Baozi - Chris Huynh came up with a new recipe named Baos. Traditionally, in Taiwan, Baos pork belly buns with super soft, fluffy steamed buns and full of flavor fillings. However, applying to the Vietnam market, Chris Huynh has made his restaurant more outstanding with other special flavours with crab, chicken and so forth. As a result, it became a speciality of the restaurant that if you want to eat, you can only go to Baozi. The Experience Differentiation: Baozi’s first pop up location on Tran Dinh Xu in Ho Chi Minh City was a humble spot, featuring a two-meter wide kitchen with photocopied menus. From there, Baozi has been able to stay in touch with their humble beginnings while providing customers with excellent food. When coming to Baozi, customers enjoy the friendly atmosphere of modern and warm with a high-end touch of a Taiwanese restaurant.
PROBLEM 2.8 Ranga Ramasesh is the operations manager for a firm that is trying to decide which one of four countries it should research for possible outsourcing providers. The first step is to select a country based on cultural risk factors, which are critical to eventual business success with the provider. Ranga has reviewed outsourcing provider directories and found that the four countries in the table that follows have an ample number of providers from which they can choose. To aid in the country selection step, he has enlisted the aid of a cultural expert, John Wang, who has provided ratings of the various criteria in the table. The resulting ratings are on a 1 to 10 scale, where 1 is a low risk and 10 is a high risk. John has also determined six criteria weightings: Trust, with a weight of 0.4; Quality, with 0.2; Religious, with 0.1; Individualism, with 0.1; Time, with 0.1; and Uncertainty, with 0.1. Using the factor-rating method, which country should Ranga select?
Culture selection criterion
Mexico
Panama
Costa Rica
Peru
Trust
1
2
2
1
Society value of quality work
7
10
9
10
Religious attitudes
3
3
3
5
Individualism attitudes
5
2
4
8
Time orientation attitudes
4
6
7
3
Uncertainty avoidance attitudes
3
2
4
2
Weight
Mexico
Panama
Costa Rica
Peru
Trust
0.4
1
2
2
1
Society value of quality work
0.2
7
10
9
10
Religious attitudes
0.1
3
3
3
5
Individualism attitudes
0.1
5
2
4
8
Time orientation attitudes
0.1
4
6
7
3
Uncertainty avoidance attitudes
0.1
3
2
4
2
ANSWER:
Culture selection criterion
Total Weighted Score
3.3
4.1
4.4
4.2
Using the factor-rating method, the table shows that Mexico has the lowest overall rating. Therefore, Ranga Ramasesh should select Mexico for possible outsourcing providers....
Similar Free PDFs

Production and Operations Analysis
- 535 Pages

Chapter 9 Operations Management
- 34 Pages

Chapter 3 Operations Management
- 2 Pages

Operations Management-Chapter 2
- 20 Pages

Operations Management Chapter 3
- 44 Pages

Operations Management and TQM
- 9 Pages

Operations and Management
- 80 Pages

Chapter 02 - Management Theory
- 34 Pages

Chapter 7-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 17 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu