Intro slides physics 15 a harvard PDF

| Title | Intro slides physics 15 a harvard |
|---|---|
| Author | Antobio Teixeira |
| Course | Physics 15a |
| Institution | Harvard University |
| Pages | 11 |
| File Size | 836.9 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 22 |
| Total Views | 132 |
Summary
Intro slides physics 15 a harvard bla bla...
Description
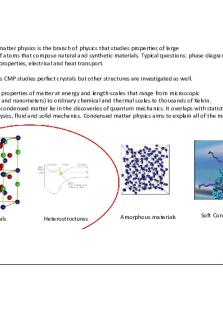
Condensed matter physics is the branch of physics that studies properties of large collections of atoms that compose natural and synthetic materials. Typical questions: phase diagrams, mechanical properties, electrical and heat transport. In most cases CMP studies perfect crystals but other structures are investigated as well. It deals with properties of matter at energy and length-scales that range from microscopic (microKelvin and nanometers) to ordinary chemical and thermal scales to thousands of Kelvin. The roots of condensed matter lie in the discoveries of quantum mechanics. It overlaps with statistical physics, materials physics, fluid and solid mechanics. Condensed matter physics aims to explain all of the material world.
Crystals
Heterostructures
Amorphous materials
Soft Condensed Matter
Condensed Matter Physics provided intellectual advances that had major impact on science as a whole. The idea of spontaneous symmetry breaking came first in CMP in understanding magnetism. It was then applied for superconductivity and finally to high energy physics, where it is now the basis of the standard model. Fractional quantum Hall effect gave rise to understanding topological field theories.
Antiferromagnetism
Ferromagnetism
Superconductivity
Quantum Hall Effect
Universality of physical phenomena Universality of thermodynamic properties, phase transitions
Universality of collective excitations Goldstone modes: spin waves, Bogoliubov modes Amplitude Mode: Anderson-Higgs excitation
Universality of physical phenomena: Higgs mode feV
pK
peV
nK
Cold atoms experiments 10-11 - 10-10 K
neV
µK
µeV
mK
meV
eV
keV
MeV GeV
TeV
K
room temperature
LHC
Higgs mode of the standard model, 2012 Higgs mode in ultracold atoms, 2012
Condensed matter physics plays a central role in many technological and scientific advances of the last decades. Condensed Matter Physics gave birth to the transistor, the first integrated circuit, the laser, the low-loss optical fibers. This made it possible to create a modern computer and communication industries.
First solid state transistor created at Bell labs
Intellectually condensed matter physics is very vital now. Recent studies find overlaps with string theory, topology, computer science (new field of quantum information), atomic physics, quantum optics, …
Experiments play a crucial role in Condensed Matter Physics. Nature brings surprises Prior to discovery of high temperature superconductors, theorists suggested fundamental bounds on Tc
Matthias’ rules for discovery of new superconductors
We are dealing with complicated systems and there is no hope to solve them exactly. Ideas of symmetry are crucial
We often use simplified models that capture the essential aspects of the phenomena
Emphasis of this course: models of non-interacting quasiparticles...
Similar Free PDFs
Intro slides physics 15 a harvard
- 11 Pages

Intro to computational physics
- 3 Pages

Unit 15 - Medical Physics
- 11 Pages

382600267 Intro to Mastering Physics
- 25 Pages

Harvard Referencing - Grade: A
- 28 Pages

Os1a-slides - slides
- 168 Pages

Epithelial Slides Practice Quiz A
- 22 Pages

Nr435-slides 1 - slides
- 15 Pages

Advanced Physics 2 Lab Manual Intro
- 30 Pages

Demenze fino a 42 slides
- 3 Pages

Intro - Grade: A
- 1 Pages

254436541-Physics 3-A
- 10 Pages

Intro to Ad - Lecture notes 1-15
- 6 Pages

Physics IA - Grade: A+
- 12 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu

