Intro. to Inorganic Qualitative Analysis Post-Lab (Part I) PDF

| Title | Intro. to Inorganic Qualitative Analysis Post-Lab (Part I) |
|---|---|
| Course | General Chemistry |
| Institution | University of California Davis |
| Pages | 3 |
| File Size | 75.1 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 92 |
| Total Views | 150 |
Summary
CHE 2C post-lab: Introduction to Inorganic Qualitative Analysis Part II for Prof. J. Chamberlain...
Description
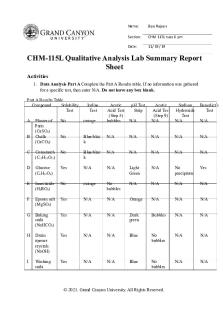
Intro. to Inorganic Qualitative Analysis Post-Lab (Part I) Question 1a) A 1 mL portion of the unknown is treated with 2 mL of 6 M NaOH, added a few drops at a time with shaking. Immediately thereafter, 10 drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide are added dropwise with shaking, and the test tube is then heated for a few minutes in a water bath until bubbling ceases. The resulting conglomerate is then centrifuged and the supernatant liquid is decanted off and saved. (Although you have not demonstrated these facts for yourself, Ca2+ will be precipitated as the hydroxide at this stage and K+ will remain in the decanted liquid.) At this stage of the experiment which elements could be found in the DECANTED LIQUID? Answer: K, Cr, Zn Question 1b) A 1 mL portion of the unknown is treated with 2 mL of 6 M NaOH, added a few drops at a time with shaking. Immediately thereafter, 10 drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide are added dropwise with shaking, and the test tube is then heated for a few minutes in a water bath until bubbling ceases. The resulting conglomerate is then centrifuged and the supernatant liquid is decanted off and saved. (Although you have not demonstrated these facts for yourself, Ca2+ will be precipitated as the hydroxide at this stage and K+ will remain in the decanted liquid.) At this stage of the experiment which elements could be found in the PRECIPITATE? Answer: Ca, Mn, Fe, Co Question 2a) The precipitate from Question 1 that possibly contains Ca, Mn, Fe, or Co, is washed twice, first with a 1 mL portion of 1 M NaOH and then with 1 mL of deionized water. The tube is centrifuged after each washing and the two supernatant liquids are discarded. Now the precipitate is treated with 1 mL of 6 M HNO3 and the test tube is heated briefly in a water bath. The test tube is then centrifuged, and the supernatant liquid is decanted and saved. (The Ca(OH)2 produced in Question 1 is acid soluble.) At this stage of the experiment, which elements could be found in the DECANTED LIQUID? Answer: Ca, Fe Question 2b) The precipitate from Question 1 that possibly contains Ca, Mn, Fe, or Co, is washed twice, first with a 1 mL portion of 1 M NaOH and then with 1 mL of deionized water. The tube is centrifuged after each washing and the two supernatant liquids are discarded. Now the precipitate is treated with 1 mL of 6 M HNO3 and the test tube is heated briefly in a water bath. The test tube is then centrifuged, and the supernatant liquid is decanted and saved. (The Ca(OH)2 produced in Question 1 is acid soluble.) At this stage of the experiment, which elements could be found in the REMAINING PRECIPITATE? Answer: Mn, Co
Question 3a) The precipitate from Question 2 that possibly contains Mn or Co is treated with 1 mL of 6 M
HNO3 followed immediately by the drop-wise addition of 3% hydrogen peroxide until the precipitate fully dissolves. The test tube is then heated in a water bath until bubbling ceases. At this stage of the experiment, which elements could be found in the resulting LIQUID? Answer: Mn, Co Question 4a) The decantate from Question 1 that possibly contains K, Zn, or Cr, is neutralized with acetic acid and divided into the appropriate number of portions. You will be running a confirmatory test for K using the original unknown solution rather than this decantate. Ignoring the portion allotted for K, into how many portions should the decantate be divided? Answer: 2 Question 4b) The decantate from Question 1 that possibly contains K, Zn, or Cr, is neutralized with acetic acid and divided into the two portions. The confirmatory test for Zn should be carried out on one of these portions in a spot plate well. Which of the following is the appropriate confirmatory test for Zn? Answer: Add dithizone in chloroform and look for a red complex formation. Question 4c) The decantate from Question 1 that possibly contains K, Zn, or Cr, is neutralized with acetic acid and divided into the two portions. The confirmatory test for Cr should be carried out on one of these portions in a spot plate well. Which of the following is the appropriate confirmatory test for Cr? Answer: Add lead(II) nitrate and look for a yellow precipitate. Question 5a) The decantate from Question 2 that possibly contains Ca and Fe, is neutralized with 6 M NaOH and one drop of 6 M HNO3, and is divided into the appropriate number of portions. You will be running a confirmatory test for Ca using the original unknown solution rather than this decantate. Ignoring the portion allotted for Ca, into how many portions should the decantate be divided? Answer: 2 Question 5b) The decantate from Question 2 that possibly contains Ca and Fe, is neutralized with 6 M NaOH and one drop of 6 M HNO3, and is then divided into the two portions. The confirmatory test for Fe should be carried out on one of these portions in a spot plate well. Which of the following is the appropriate confirmatory test for Fe? Answer: Add KSCN and look for the solution to turn red.
Question 6a) The decantate from Question 3 that possibly contains Mn or Co is divided into two portions. The confirmatory test for Mn should be carried out on one of these portions in a spot plate well. Which of the following is the appropriate confirmatory test for Mn?
Answer: Add NaBiO3 and look for a dark purple precipitate. Question 6b) The decantate from Question 3 that possibly contains Mn or Co is divided into two portions. The confirmatory test for Co should be carried out on one of these portions in a spot plate well. Which of the following is the appropriate confirmatory test for Co? Answer: Add potassium acetate and then potassium nitrite, and look for a yellow precipitate accompanied by the release of a slight amount of a brown odorous gas Question 7a) The original unknown solution is tested separately for the presence of potassium and calcium. What is the confirmatory test for K? Answer: Add Na[(C6H5)4B] and look for a yellow precipitate. Question 7b) The original unknown solution is tested separately for the presence of potassium and calcium. What is the confirmatory test for Ca? Answer: Add potassium oxalate solution and look for a white precipitate....
Similar Free PDFs

Qualitative Analysis of Anions
- 11 Pages

Exam Qualitative analysis sample
- 4 Pages

Qualitative Analysis of Carbohydrate
- 13 Pages

Task 1 - Qualitative analysis
- 4 Pages

Qualitative Structural Analysis
- 18 Pages

Qualitative Analysis - Beams
- 15 Pages

Qualitative Analysis of Cations
- 27 Pages

Qualitative Analysis-Sp21
- 6 Pages

5. Qualitative Movement Analysis
- 1 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu