lab1 Report- Reflexes PDF

| Title | lab1 Report- Reflexes |
|---|---|
| Author | Ayşe KILIÇ |
| Course | Anatomy And Physiology II With Lab |
| Institution | Southern Maine Community College |
| Pages | 5 |
| File Size | 80.6 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 86 |
| Total Views | 125 |
Summary
Anatomy lab report about somatic and autonomic reflexes....
Description
1
Ayse Kilic Christopher Easton 09/07/2021 Bio 128 05- Lab1
Somatic and Autonomic Reflexes Lab Report
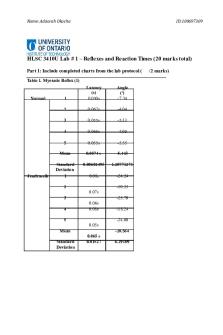
Activity 1 - Testing the Patellar Reflex and Calcaneal Tendon Reflex Procedure The patient was seated on a chair with legs hanging free.Subject’ right knee supported so that subject's muscles are relaxed and then taped the patellar ligament sharply with the reflex hammer just below the knee between the patella and the tibial tuberosity. Same procedure applied for the left leg. After that, the patient adds a column of three digit numbers while the reflex is tested simultaneously. To see the effect of fatigue on the subject' reflex, the subject runs until they feel really fatigued and the procedure repeated. Lastly, patients’ shoes were taken off and the foot dorsiflexed slightly to increase the tension of the gastrocnemius muscle and then sharply tapped patients' calcaneal tendon with the broad side reflex hammer. Result Tapping the patellar ligament contracted muscle spindles in the quadriceps and the patient's right lower leg automatically kicked outward. The same reaction was observed in the left leg. It has been observed that changing the focus point does not provide a change on the patellar reflex. After testing the effect of exercise on patellar reflex, the result was less vigorous. The end of the calcaneal tendon reflex testing, It was observed that the foot tended to plantar flexion. Conclusion It was seen that the reflexes here are working correctly. If it didn't happen or happens excessively that can be an indication of disorder or damage to the nervous system. It was observed that the patient's distraction did not have an effect on the patient's patellar reflex. It is because The normal knee-jerk reflex involves no input to or from the brain. Sensors that detect stretching of the tendon of this area send electrical impulses back to the spinal cord. As
2
a result the brain gets the info after reflex is done. After testing the effect of exercise on patellar reflex, the result was less vigorous.It because muscle function exercise is what caused the changes that were observed because, after exercise the muscles are tired or worn out. This caused the patellar reflex to be less vigorous immediately following exercise.
Activity 2- Initiating the Superficial Cord reflexes Procedure The subject sat with eyes closed and with the dorsum of one hand resting on the laboratory bench.Obtained a sharp pencil, and suddenly pricked the subject’s index finger. Result As a result the subject moved the hand away. Conclusions Extensor part of this reflex occurs simultaneously. When sensory neurons respond the stimuli biceps muscles contract and move the arm away. It's because the signal did not send to the brain, and action time shortened.
Activity 3- Initiating the Plantar Reflex Procedure Subject removed a shoe and lay on the laboratory bench with knees slightly bent and thighs rotated so that the posterolateral side of the foot rested on the cot. Draw the handle of the reflex hammer firmly along the lateral side of the exposed sole from the heel to the base of the great toe. Result The patient’s toes flexed and moved closer together. No other movement was observed. Conclusions In humans, stimulation of these receptors causes the toes to flex and move together. The result was normal. Damage to the corticospinal tract, however, produces Babinski’ sign of an
3
abnormal response in which the toes flare and the great toes move in an upward direction. In newborn infants, it is normal to see Babinski’ sign due to incomplete myelination of the nervous system.
Activity 4- Initiating the corneal Reflex Procedure The patient was seated in a chair. While the patient was facing the opposite wall, the patient's cornea was touched quickly and softly with a cotton ball. Result The patient blinked involuntarily with both eyes. Conclusion Corneal reflex is a protective reflex that occurs when the cornea is touched. Causes both eyes to blink when one cornea is touched. Ensures both eyes protected from foreing object or irritant in the environment Healthy respond to touching one cornea is that both eyes blink.The result was normal on the experiment. The absence of this reflex is an ominous sign because It's often indicates damage to the brain stem resulting from compression of the brain or other trauma.
Activity 6- Initiating Pupillary reflexes Procedure The lights were dimmed to measure the light effect on the pupil. A ruler and flashlight were used for this process. The patient was asked to look at a fixed point and the size of the patient's right and left pupils were measured as best as possible. Then, the patient's hand was asked to be placed vertically to the right of his nose. Again, the patient's left eye was illuminated and what happened to the pupil was observed. The right eye was examined without moving the light and the pupil was measured again.
4
Result In the first measurement, the right pupil was 7 mm and the left pupil was 7 mm. After the vertical closure of the right side of the patient's face, it was determined that the pupil narrowed and measured as 5 mm with the effect of light on the left eye. Without changing the position of the light (on the right eye), the left pupil was examined and it was found that it shrunk at the same rate as the right eye. Conclusion The purpose of the pupillary response would be to protect the eye from too much sunlight and to aid vision in very light or dark situations.The pathways are connected contralaterally.Parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system active during the testing of these reflexes.
Activity 7- Initiating the Ciliospinal Reflex Procedure While the patient looked straight ahead, the left side of the neck of the patient was touched with the help of a pencil. Changes in left and right pupils were examined. Result It was observed that while the left pupil was expanding, the right pupil did not give any reaction. Conclusion Sympathetic stimulation in both irises is not closely integrated because as we see in the reflex, both irises work individually( ipsilateral stimulation). Each iris is innervated by a nerve on the same side of the body
5...
Similar Free PDFs

lab1 Report- Reflexes
- 5 Pages

Lab1 - Lab Report
- 1 Pages

Lab1 - Lab Report
- 27 Pages

Lab1
- 1 Pages

Lab1
- 5 Pages

Lab1
- 8 Pages

Neonatal Reflexes
- 3 Pages

LAB1 - Matlab
- 5 Pages

Matlab Lab1
- 17 Pages

Lab1 - Lab
- 9 Pages

Infant Reflexes Chart
- 1 Pages

Primitive Reflexes Chart
- 1 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu