Lab Report Questions - Lab #1 Reflexes and Reaction Times PDF

| Title | Lab Report Questions - Lab #1 Reflexes and Reaction Times |
|---|---|
| Author | Sydeny Rye |
| Course | Human Motor Control & Learning |
| Institution | University of Ontario Institute of Technology |
| Pages | 6 |
| File Size | 209.8 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 11 |
| Total Views | 133 |
Summary
Lab...
Description
Name: Adaorah Okocha
ID:100697309
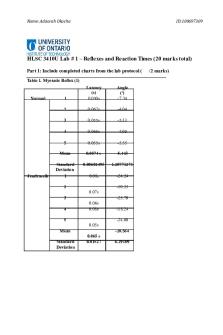
HLSC 3410U Lab # 1 – Reflexes and Reaction Times (20 marks total) Part 1: Include completed charts from the lab protocol ( Table 1. Myotatic Reflex (1)
Normal
Jendrassik
1
Latency (s) 0.050s
Angle ( o) -7.34
2
0.062s
-4.04
3
0.055s
-5.33
4
0.065s
-4.95
5
0.055s
-5.55
Mean
0.0574 s
-5.443
Standard Deviation 1
0.00602495
1.20771271
0.08s
-24.24 -10.55
2 0.07s
-25.79
3 4
0.06s 0.08s
-18.24 -24.00
5 0.05s Mean Standard Deviation
-20.564 0.065 s 0.01527
6.29109
/2 marks)
Name: Adaorah Okocha
ID:100697309
Table 2. Reaction Times (1) Condition Visual Cue 1
With Warning 0.14
Predictable 0.016
With Distraction 0.015
Auditory Cue 0.177
0.05
0.221
0.176
0.173
0.075
0.105
0.373
0.135
0.117
0.075
0.323
0.192
0.116
0.052
0.213
0.161
0.076
0.116
0.212
0.14
0.101
0.109
0.181
0.002
0.022
0.105
0.300
0.147
0.125
0.109
0.364
0.145
0.118 2 0.132 3 0.136 4 0.129 5 0.135 6 0.114 7 0.079 8 0.096 9 0.131 10 Mean Standar d deviation
0.072
0.072
0.282
0.06
0.181 0.123875
0.089875
0.099875
0.2575
0.135
0.01374708
0.03663502
0.03330996
0.072291
0.05585952
Name: Adaorah Okocha
ID:100697309
Part 2: Complete the following questions based on your analysis ( /18 marks) 1.What is the Jendrassik maneuver? What effect does it have on the myotatic reflex? (3) The Jendrassik Maneuver is a medical maneuver, in which the patient needs to clench his teeth flex all sets of fingers into a hook-like formation, and interlock those sets of fingers together. The effect of the Jendrassik maneuver on the myotical reflex is that it makes the reaction time marginally quicker. This occurs because an inhibitory signal is transmitted to the hands instead of a quadriceps signal, which results in quicker reaction to the stimulus that is hitting the knee. 2.Briefly explain the pathway of a “simple” reflex. Given your results, how did the Jendrassik Maneuver alter your reflex? (3) The receptor registers a certain stimulus and converts it into an electrical response. The input is then processed into the sensory neuron. The neuron transmits electrical reactions from the receptor to the central nervous system, the brain or spinal cord, through the dorsal root, into the dorsal horn. Arriving sensory input from the sensory neuron is processed by interneurons and transmitted by electrical impulses to the lower motor neuron. The motor (efferent) neuron helps to transmit an electrical signal from the central nervous system to the periphery. The effector (muscle or gland) refers to the electrical signal of the motor neuron. The Jendrassik Maneuver improved the reaction by increasing the speed of the myotical reflex. 3.on your data, are the means and standard deviations for reaction time the same under all conditions? Why do you think this is? (3) In the data means and standard deviations for reaction times are different under both circumstances, this can be because since some of the conditions require slower production. For eg, the 'with distraction' state had the greatest mean and standard deviation since it took
Name: Adaorah Okocha
ID:100697309
longer for the information to be analysed because you’re counting backwards from 100 by 7s. The brain is interrupted by counting, which creates a longer response time for the reaction under this condition. 4.Which conditions increase the reaction time, and which decrease it? Why? (3) The 'with alert' and 'predictable' situations improve the response time, and the 'with distraction' reduces the response time. The 'with alert' and 'predictable' increase because the information can be handled more easily because you know it's going to happen. The distracted state shortened the response time when the brain was dealing with another stimulus, thereby requiring a longer time to absorb all the information at once. 5.Do you think the difference in reaction time between auditory and visual cues is due to different processing times in the brain? Please include reference(s). (3) Yes, I do a study showed that the duration of the auditory reaction is quicker than the time of the visual reaction (Shelton,2010). And males also have shorter response times relative to females for both auditory and visual stimuli. Another research study has found that the response to sound is quicker than the reaction to light. The auditory stimulus enters the brain earlier than the visual stimulus, resulting in a faster response time (Ghuntla e tal, 2014). The findings of the tests indicate that, in this case, the visual stimulus had a shorter response time than the auditory cue. This may be attributed to the fact that there were other participants in the experiment who made it loud, making the visual stimulus quicker than the auditory cue
Name: Adaorah Okocha
ID:100697309
6. Could the difference in reaction time between the exercises only be due to inherent variability in the experimental method? (3) I would say yes, implicit variation is present when people respond differently to different stimuli and process information in different ways. The test was also performed in a lab with other people about making it slightly loud, which may have influenced the findings as well. So intrinsic uncertainty is there, but this is not the only explanation that there are variations in reaction speeds.
Name: Adaorah Okocha
ID:100697309 References
Ghuntla TP, Mehta HB, Gokhale PA, Shah CJ. A comparison and importance of auditory and visual reaction time in basketball players. Saudi J Sports Med 2014;14:35-8 J. Shelton and G. Kumar, "Comparison between Auditory and Visual Simple Reaction Times," Neuroscience and Medicine, Vol. 1 No. 1, 2010, pp. 30-32. doi: 10.4236/nm.2010.11004....
Similar Free PDFs

Lab Report Reaction Rate Lab
- 3 Pages

Grignard Reaction Lab Report
- 11 Pages

Lab questions - lab report
- 2 Pages

Green wittig reaction lab report
- 5 Pages

Iodine Clock Reaction Lab Report
- 4 Pages

Lab 1 - lab report
- 3 Pages

Lab report 1 - lab
- 6 Pages

Lab 1 - Lab 1 Report
- 6 Pages

Lab Report 1 - Lab 1
- 3 Pages

LAB 1 - Lab Report Template
- 2 Pages

Measurement Lab #1 - Lab report
- 6 Pages

Biochem lab 1 - Lab report
- 6 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu