Lab 5 Reflex and Reaction times Assignment PDF

| Title | Lab 5 Reflex and Reaction times Assignment |
|---|---|
| Course | Human Physiology |
| Institution | University of West Georgia |
| Pages | 4 |
| File Size | 455.2 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 108 |
| Total Views | 154 |
Summary
Download Lab 5 Reflex and Reaction times Assignment PDF
Description
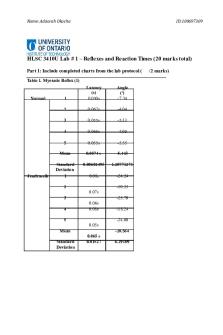
Ruby Iyamu Name:__________________________ BIOL 3513/6513 Human Physiology Reflexes and Reaction Times Post-Lab Questions 1. In the knee-jerk reflex arc, the synapse between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron occurs where? a. Within the spinal cord b. In the brain c. Within the muscle of the leg d. Between the receptor and the spinal cord 2. A voluntary reaction differs from a reflex because a. It is performed from choice b. It involves more complex pathways c. It is under the control of higher brain functions d. All of the above 3. Which of the following statements about the knee-jerk reflex is false? a. It is a monosynaptic reflex. b. The leg extends in response to a hammer tap. c. Visual receptors sense the hammer tap. d. The afferent nerve travels from the receptor to the spinal cord. 4. Select the correct sensory pathway in a reflex arc. a. Sensory neuron, spinal cord, interneuron, motor neuron, muscle b. Sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, muscle, spinal cord c. Interneuron, motor neuron, muscle, sensory neuron, spinal cord d. Interneuron, motor neuron, sensory neuron, spinal cord, muscle 5. Which of the following factors should decrease an individual’s reaction time? a. Fatigue b. Distractions c. Practice d. Errors 6. What portion of the reflex arc is responsible for detecting the change in the environment? a. Effector b. Receptor c. Sensory neuron d. Motor neuron
7. What is another name for the knee-jerk reflex? a. Myostatic b. Myotatic c. Papillary d. Kicking 8. Both the knee-jerk and the papillary reflexes are examples of simple spinal reflexes. a. True b. False 9. Complex reflexes have a longer latency between the stimulus reception and the reflex response. a. True b. False 10. What is another name that describes pain stimulation? a. Flexion b. Myotatic c. Papillary d. Nociceptive Use the table of data from an experiment measuring knee-jerk reflex responses below for questions 11-15.
Normal
Mean Jendrassik
Mean
Latency (s) 0.02 0.025 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.021
Angle (°) 9.44 6.2 7.43 7.51 6.36 7.388
0.035 0.025 0.025 0.035 0.035 0.031
9.1 10 9.53 10.15 11.53 10.062
11. How did the Jendrassik maneuver change the latency for the knee-jerk reflex? The typical latency is 0.021 seconds, while the jendrassiks move has a latency of 0.031 seconds. As a result of Jendrassik's maneuver, the knee jerk reaction has a longer latency period.
12. Is the reaction time affected by using additional nervous pathways at the same time as the reflex response (e.g. Jendrassik maneuver)? By engaging additional motor units and removing descending inhibition, the Jendrassiks maneuver improves knee jerk reflex response. As a result, the use of additional neural routes has little effect on reaction time. 13. Which condition (Normal or Jendrassik) has the greatest variability in the latency measurements? The jendrassiks move has the most delay variability. 14. Which condition (Normal of Jendrassik) causes the smallest deflection of the knee in response to the stimulus? The normal jerk reflex has the smallest deflection. 15. If a balloon was popped at the exact moment that the tendon hammer struck the knee, would you expect to see a delay in the knee-jerk response? Because optic pathways are not implicated, the same speed and amplitude will be obtained Use the following table of reaction time data below to answer questions 16-21.
Mean
With With Auditory Random Warning Regular Distraction Cue 0.13 0.13 0.1 0.39 0.15 0.13 0.1 0.58 0.13 0.1 0.22 0.07 0.2 0.2 0.14 0.09 0.49 0.2 0.18 0.26 0.19 0.09 0.34 0.13 0.17 0.16 0.14 0.23 0.13 0 0.3 0.21 0.2 0.11 0 0.4 0.14 0.12 0 0.14 0.16 0.15 0.06 0.36 0.18
16. How do distractions affect reaction time? Distraction lengthens reaction time. 17. How does being able to predict when the stimulus is administered (e.g. Regular) affect reaction time? The ability to forecast sensory timing (regular) reduces reaction time. 18. Which condition has the greatest amount of variability in terms of reaction time? With distraction, the most variation in reaction time is observed.
19. Is it plausible to assume that fewer distractions would decrease the latency of initiating the response to the cue? If there are less distractions, the subject's reaction time will shorten and he or she will react faster. 20. Is it plausible to assume that the longer reaction time for auditory cues is due to a longer processing pathway in comparison to visual cues (e.g. Warning)? The visual route transmits information faster than the auditory pathway. As a result, auditory stimuli require a longer reaction time. 21. What was the control condition for the reaction time data collected above? Random data served as the control condition. 22. Would we likely see an increase in the variability of our data measurements if we increased the number of data points? Yes, there will be a noticible increase. 23. Would we be able to make meaningful comparisons between Normal knee-jerk response latency data from one individual and latency data measured utilizing the Jendrassik maneuver from a second individual? Yes, the knee jerk in the first person shows a proper response arc. Due to the lack of inhibitions in the second individual with jendrassik maneuer, the knee jerk takes on an exacerbated form.
24. When collecting data points for a single experimental condition (e.g. Normal knee-jerk response), how would changing the position of the hammer strike affect your data set? In tests like Tendon reflex, the location of the hammer hit is crucial for data collection since reflexes produce in different ways. 25. If a student wanted to conduct a similar experiment to the one illustrated in the second table above (reaction time data) comparing data collected from two students, should data be collected for all conditions for both students in order to be able to meaningfully evaluate the results? If the experiment was carried out in the same way, the findings would be comparable. 26. Is it good practice to collect the same number of data points for each experimental condition? No, in order to determine the difference between the changes of experimental data, we must conduct an experiment in which we increase the number of data points. 27. If we didn’t collect the data for the Auditory Cue in the reaction time experiment, would we still be able to evaluate the remaining data? We will be able to identify something only when the stimulus is auditory. 28. If we didn’t collect the data for the Normal knee-jerk response, would we be able to evaluate the Jendrassik maneuver data? No, if we performed a knee jerk in normal settings and did not receive a reaction, we must now perform a jendrassik maneuver to obtain a decent knee jerk response Patellar reflex is increased using the Jendrassik maneuver. As a result, it's critical to have knee jerk access....
Similar Free PDFs

reflex physiology and anatomy
- 4 Pages

Lab 5 Post-Lab Assignment
- 3 Pages

Lab Assignment 5
- 1 Pages

Lab Report Reaction Rate Lab
- 3 Pages

Reaction Energy SE - Lab
- 7 Pages

Grignard Reaction Lab Report
- 11 Pages

Lab 10 Wittig Reaction
- 9 Pages

Reaction Time Lab
- 4 Pages

Single Replacement Reaction lab
- 2 Pages

Reaction 1c - assignment
- 2 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu