SM 131 Midterm Review PDF

| Title | SM 131 Midterm Review |
|---|---|
| Author | Isha Zhang |
| Course | Business, Society, and Ethics |
| Institution | Boston University |
| Pages | 22 |
| File Size | 735 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 93 |
| Total Views | 163 |
Summary
SM 131 Midterm Review...
Description
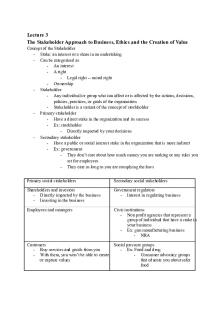
Lecture 3 The Stakeholder Approach to Business, Ethics and the Creation of Value Concept of the Stakeholder - Stake: an interest or a share in an undertaking - Can be categorized as - An interest - A right - Legal right -- moral right - Ownership - Stakeholder - Any individual or group who can affect or is affected by the actions, decisions, policies, practices, or goals of the organization - Stakeholder is a variant of the concept of stockholder - Primary stakeholder - Have a direct stake in the organization and its success - Ex: stockholder - Directly impacted by your decisions - Secondary stakeholder - Have a public or social interest stake in the organization that is more indirect - Ex: government - They don’t care about how much money you are making or any rules you set for employees - They care as long as you are complying the laws Primary social stakeholders
Secondary social stakeholders
Shareholders and investors - Directly impacted by the business - Investing in the business
Government regulators - Interest in regulating business
Employees and managers
Civic institutions - Non profit agencies that represent a group of individual that have a stake in your business - Ex: gun manufacturing business - NRA
Customers Social pressure groups - Buy services and goods from you - Ex: Food and drug - With them, you won’t be able to create - Consumer advocacy groups or capture values that educate you about safer food
Local communities - Ex: New Balance needs people from Boston -- build platforms
Media and academic commentators - Break developing of what is going on in a company - good/bad press
Suppliers and other business partners - If you are not doing well, you won’t be able to pay them - If they are not doing well, they can’t get you what you need in time
Trade bodies - help/hinder business - Non profit organizations - Lobby - Like civic institutions - Bigger organizations that help w/ one initiative or another Competitors - Companies have to react what their competitors are doing - How they are paying their employees - Don’t want to lose employees
Nonsocial Stakeholders - Social: helping humans - Nonsocial: helping non human species such as environment
Primary nonsocial stakeholders
Secondary nonsocial stakeholders
Natural environment - Sustainability - Environment is important to people and business - We don’t business to take too much resources that we don’t have enough for future
Environmental interest groups - Representing natural environment - Speak for it
Future generations - Haven’t existed
Animal welfare organizations - Speak for animals because they can’t speak for themselves - PETA
Nonhuman species Stakeholder management: 5 key questions - Who are our organization’s stakeholders? - Social - Nonsocial - Primary - Secondary - What are our stakeholders’ stakes? - What are they looking for? - Employees: more money? Shareholders: greater return? - Could be the same, depends - Legitimacy, power, urgency - What opportunities and challenges do our stakeholders present to the firm? - Threats: e.g. GM workers - They are on strike, asking for more money, more coverage for their health insurance, and temporary workers get the same benefit as their full-time workers - Company min the benefit give to their workers by call them Independent contacts or temporary workers - Workers stop working when they strike - sales are down, revenue is done - Opportunities: e.g. Vertex pharmaceuticals - FDA is on their side - Shareholder is so excited because their value is going up - Customers are happy because there's finally a cure - Benefiting so many stakeholders
-
-
What responsibilities (economic, legal, ethical and philanthropic) does the firm have to its stakeholders? - Carroll 4-part test for each stakeholders - What's my economic obligation? Legal obligation? Ethical obligation? Philanthropic obligation? - Decide what is going to be the strategy - Collaborate w/ workers? Depends, Vertex is, but GM is not ( GM's employees need negotiate because they are not happy) - Defend for themselves but seems like cannot go that far - For some instance, defend is the only way - E.g. PETA - against use animal for testing even though gov allowed - Law allowed to do even though PETA is not happy about this - Cost but necessary What strategies or actions should the firm take to best address stakeholder challenges and opportunities?
Example: GM -- a car manufacture - CEO of GM is making tons of money, but workers aren’t getting paid a lot - Went on a strike until agreement has been reached - Employees are not showing up to work - Urgency these employees are making - Company is losing huge amount of money - Set a legitimate claim - Opportunities & threat - Posing a huge threat - It is imperative for GM to reach the agreement to get workers back to work - Cost a lot - Responsibilities
-
- Pay them well - Ethical Strategies - Not threat: monitor - Threat: corporate and negotiate with them
Four stakeholder types
-
-
-
-
Supportive - High potential for cooperation, low for threat - Strategy is involvement - Happy as could be - Ex: shareholders (if you are making them a lot of money) Marginal - Low potential for cooperation and threat - Strategy is to monitor - Don’t have enough power to make a difference to your business - You don’t have to keep them in your direct sight - Ex: baristas of starbucks - Nobody is going on strike - Doing their job - Not so involved in daily management Unsupportive - High potential for threat, low for cooperation - Strategy is to defend - Don’t like you no matter what you do - Ex: activist groups - PETA - Create headlines oppose you - Put blood on fur Mixed - Blessing
-
Sometimes like you sometimes hate you High on potential for threat and cooperation Strategy is to collaborate Ex: GM - Was once happy - Not happy now -- strike - If GM does the right thing -- pay them enough money -- happy - If not -- unhappy
The stakeholder responsibility matrix
What strategies/actions should management take? ● Do we deal directly or indirectly with stakeholders ● Do we take the offense or defense in dealing w/ stakeholders? ● Do we accommodate, negotiate, manipulate, or resist stakeholder overtures? ● Do we employ a combination of the above strategies or pursue a singular course of action? ○ Depends what you up against Strategic steps toward global stakeholder management - Governing philosophy - Integrate stakeholder management into the firm’s governing philosophy - Values statement - Create a stakeholder inclusive values statement - Measurement system - Implement a stakeholder performances measurement system
Legitimacy refers to the perceived validity or appropriateness of a stakeholder’s claim to a stake - PETA don't have legitimacy claim, response so they might go a little too far - Interest of PETA is not legitimate if the drug can cure cancer - Perceived Power refers to the ability or capacity of the stakeholder(s) to produce an effect - To get something done that otherwise may not be done - Can they affect your company Urgency refers to the degree to which the stakeholder’s claim demands immediate attention or response. - Urgency may imply that something is critical—it really needs to get done
Lecture 4 Corporate Governance Corporate governance ● Refers to the method by which a firm is being governed, directed, administered, or
●
controlled, and to the goals for which it is being governed In concerned w/ the relative roles, rights, and accountability of such stakeholder groups as owners, boards of directors, managers, employees, and other stakeholders
How a firm is organized: Roles of four major groups 1. Shareholders: own stock in the firm, giving them ultimate control (the shareholderprimacy model) a. With shares, they have voting rights to select the board of directors b. The candidates to be on the board are already chosen, if they need to be reelected on the annual meeting, each of them only needs one vote to get reelected in c. Elect & vote for the directors 2. Board of directors: govern and oversee management of the business a. Hire/appoint CEO or other C-executives 3. Managers: the individuals hired by the Board to manage the business on the daily basis a. C-executives --> hire middle-level managers --> hire employees 4. Employees: hired to perform actual operational work a. Entry-level employee, the salary * 300 = CEO salary i. In bigger companies, the ratio is huge that create an issue
The corporation's hierarchy of authority
Every co has to be incorporated in a state State has body of laws govern the co ● Files the paperwork to the state ● State has rules & regulations
Vote for the board, board hire managers, managers hire employees
Also shareholders (part of their compensation, they also issued share of the company)
●
Roles of the shareholders ● Represent own interests as investors ○ Have the right to have info for their investments ○ Care about how the co is doing, want it to do well otherwise sell the shares and buy another company's share ○ A lot power Attend annual meetings and elect board of directors and terms of compensation ○ As long as have enough shares to voting right ○ Some hold voting online - virtual meeting ○ Get to vote however # of shares you own ● Vote on the board, proposals (mange proposal abt what they want to do later), significant transactions (acquiring another co), end the company
Approve executive compensation plans Approve external auditing firm ○ Board of directors find one, shareholders approve ● Approved significant transactions involving issuance of stock ● Exert pressure to make companies more responsible through activism ○ If not happy abt decision mangers, can let know: email, talk, voice need to be heard ● Sue management for violations of a duty of care and duty of loyalty ○ If their voice is not being heard nicely, they can sue ● Why does the company pays the executives & board so much ● Not involved in the day to day managements nor working there Role of the board of directors ● Governance and oversight ○ Identify risk & oversee risk management ● Making sure the co is not taking too much risk ○ Hire and fire the executives ○ Ensure the integrity of published financial statements ○ Plan and set executive compensation ● Shareholder need to approve and vote for that, but board set & determine ● Give favorable compensation package to executives -problem made ● Why give so much when the company is not doing well ○ Protect the interests of shareholders ○ Protect the company's assets and reputation ○ Ensure compliance w/ all laws, regulations & code of conduct policies ● E.g. anti-discrimination policy, ethic policy ● Make sure employees are trained and adhered Fiduciary duties of the board - in a position of trust ● Duty of loyalty - represent interest of owners & act w/o a conflict of interest ○ Put the interest of the corporation ahead of yourself ● Want the company to succeed, not just yourself as a corporate manager ○ Violation does lead to criminal conduct (but not always) ● Violate when put self interest ahead of the corporation ○ E.g. Elizabeth Holmes - she knew her invention had issues as it doesn't give accurate results for the blood test but she is telling the public that this invention works accurate, do this for enrich herself - reputation ● Duty of care - understand the company: act in good faith; make informed decisions and observe business formalities ○ You need to do your hw, work hard, attend to meeting and take notes, ● ●
make sure everything is transparent and make sure there's paper trial behind big decisions, make informed decisions (do the research behind all the decisions you made) ○ Violate when (e.g. ) the board decides to increase the salary for the executives because they have done this for the past five yrs. ● This is easy, requires no effort on their part ● Duty of care says you need to have a benchmark, measuring their performance or outcomes that's objective ● Fare increase? Pay the CEO 5% or not? (Hire a audit company to decide) ○ Transparency, file to show ● The business judgment rule: a court of law will not hold a director personally liable for a business decision so long as the director is following a duty of loyalty and a duty of care Board committees ● Audit committee: ensures the integrity of financial statements & assesses the adequacy of internal controls ○ Financially literary ( high-level financial ) ● Nominating committee: ensures that competent and objective board members are selected ○ Selecting future executives ○ Have company in mind when selecting executives ○ Step down or promote executives ● The compensation committee: evaluates executive performance & recommends terms and conditions of employment ○ Fairly paid [ not over/under ○ Not earn much enough to pay for the employees ● Corporate responsibility/Sustainability committee: address issues of diversity, equal employment opportunity, environmental affairs, consumer affairs ○ Social mission, diversity initiatives of employee ○ Look for this committee when search for companies ● Could have more committees depends on the company’s mission ○ The first 3 are standards The role of the CEO ● Serve as role model ● The Chief Executive Officer runs and manages the company day to day ○ Establishes the strategy of the company ○ Serves as a role model for all employees ○ Sets financial and non-financial goals ● Achieves results ○ Triple-bottom line: social & environmental results? ● Develops leadership talent ○ As much as possible
○ CEO mostly stay for a period rather than founders ○ Future potential CEO, develop leadership even after they left ○ E.g. Mary Barra in GM ■ Work from the bottom to CEO ■ Successful under her leadership: went out from the past storm and be profitable The board's relationship w/ the CEO ● Boards are responsible for monitoring CEO performance and dismissing poorly performing CEOs ● If a CEO also serves as Chairman of the Board, this duality can affect their independence. It is best to separate these roles ○ E.g. Facebook ● Board are also responsible for determining executive compensation Issues surrounding compensation ● CEO pay-firm performance relationship ○ Inverse (increased pay while decreasing profit) ○ Any relationship possible, no requirement for a measurement in place ● But try to linking CEO pay w/ performance to avoid scandals ● Excessive CEO pay ○ No ban or limit on pay, but some are paid really unreasonably high ○ E.g. McKesson's CEO in place over 10 yrs, his salary added it up is close to $1 billion, ethically a problem? Shouldn't that take away some? ● Executive retirement plans & exit packages ○ Promised even though entering scandals ● Ford's CEO walked away with million of money as the exit packages ● Outside director compensation ○ Only meet few times annually ○ Part-time workers [make a lot money from it] ● E.g. Facebook ○ Historically not paid as a volunteer base, but for the past few decades they are paid ○ Want to be get voted in, to get a lot money with doing not very much ● Transparency; SEC Rules ○ If not transparent, we cannot know what these executives made or how much are paid ● Although it is transparent now, they still got a lot compensation package Excessive CEO pay ● Ratio of CEO pay to that of average worker ○ 1950, 20 to1 ○ 2014, 216 to 1 ● Say on pay
●
○ Evolved from concerns over excessive executive compensation ○ Shareholders can take a vote on approving increase the compensation or not ○ Not binding, the board can ignore this Clawback provisions ○ Compensation recovery mechanisms that enable a company to recoup CEO pay, typically in the event of financial restatement or executives' misbehavior ○ 补偿恢复机制,使公司能够补偿首席执行官的薪酬,特别是在财务重述或
高管的不当行为 Executive retirement plans & exit packages ● Golden parachutes ○ 黄金降落伞(按照聘用合同中公司控制权变动条款对高层管理人员进行补 偿的规定) Retirement packages ○ $210 million to Robert Nardelli when he was ousted from Home Depot ● Did sth bad, but still take away much - why incentive CEO when they did things bad ○ $125 million to outgoing Bank of America CEO Kevin Lewis ○ In contrast, many of today's workers do not have retirement plan Outside director compensation ○ Pay board members is a recent idea ○ From 2003-2015, their median pay rose abt a third, from $175,800 to $258,000 ●
Improving corporate governance ● Legislative efforts: ○ Sarbanes–Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX) ● Amends (修改) securities laws to protect investors in public companies ● Enhances public disclosure to require reporting of off-balance sheet transactions & personal loans to executives ● Limits the non-auditing services an auditor can provide to a firm it audits ● Make it unlawful for accounting firms to provide services where conflicts of interest exist ● CEOs and CFOs must certify financials ands are held responsible for financial representations ○ The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act ● Established the Financial Stability Oversight Council to identify risks affecting the entire financial industry ● Regulates risky derivatives like credit default swaps ● Requires hedge funds to register w/ the SEC
● ● ●
Oversees credit rating agencies & regulate credit cars, loans, and mortgages Requires certain capital reserves for banks so that they do not become too leveraged Bans banks from using customer funds to make risky bets for their our account (Volcker Rule)
Beyond the law ○ Make changes in Board of Directors ● More board diversity (backgrounds & experiences) ● A greater ratio of outside directors to inside directors ● Outside directors are independent from the firm and management ● Inside directors are usually the top managers of a firm ○ Use Board Committees to: ● Ensure that financials are not misleading ● Ensure that internal controls are adequate ● Follow-up allegations of irregularities ● Ratify the selection of an external director The role of SEC ● The Securities and Exchanges Commissions: a gov agency that is responsible for protecting investor interests ○ Overseas companies issues ○ Financial report need to be looked by SEC ○ Routines monitor executives of insider trading ○ Routines look for misleading the stakeholders ● The SEC requires public companies to make period filings and disclosures ● The SEC is not perfect and critics believe it favors businesses. ○ It failed to stop the Bernard Madoff Ponzi scheme before investors lost billions, although they has been warned of the scheme a decade earlier Insider trading ● The practice of buying or selling a security by an insider who has access to material, confidential info that is not available to the public ○ "Material information" is info that a reasonable investor might want to use and is likely to affect the price of the firm's stock ○ A "tipper" provides that info ● Gives info to friends, family, collages ○ A "tippee" receives that info ● If receives but not trade - not a insider trading ● Trades on this ●
Lecture 2 Corporate Social Responsibility Corporate social responsibility began as allegations (指控) against business started Business ● Has little concern for the consumer ● Exploits employees ● Cares nothing abt the deteriorating social order ● Has no concept ethical behavior ● Is indifferent to the problems of minorities & the environment These claims have generated an unprecedented number of pleas (请求) for companies to be more socially responsible CSR as a concept Early def. ● CSR means seriously considering the impact of a company's action on society & environment ● CSR requires the individual to consider his/her acts in terms of a whole social system, and holds him or her responsible for the effects of his/her acts anywhere in that system Carroll 4-part def. of CSR CSR encompass the: ● Economic ○ Be profitable - min the was...
Similar Free PDFs
SM 131 Midterm Review
- 22 Pages

MATH 131 Midterm - Grade: A
- 4 Pages

131 263 1 SM - No hay
- 9 Pages

Biology 131 final exam review
- 16 Pages

Midterm Review
- 8 Pages

PHY 131 Midterm 2 Study Sheet
- 7 Pages

Midterm review
- 11 Pages

Midterm Review
- 12 Pages

LS7B Midterm Review
- 1 Pages

Psychology midterm 1 review
- 19 Pages

Midterm Review - HLTH 230X
- 7 Pages

Midterm 3 Review
- 18 Pages

Communications Midterm Review
- 12 Pages

Biol 207 (midterm review)
- 96 Pages

Public Speaking Midterm Review
- 3 Pages

Midterm Review Sheet
- 6 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu