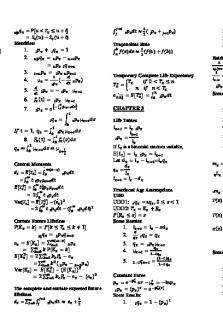Summary 394-5 - Contains list of formulas from MATH 394,395 that you will need for MATH 396 PDF

| Title | Summary 394-5 - Contains list of formulas from MATH 394,395 that you will need for MATH 396 |
|---|---|
| Course | Probability Iii |
| Institution | University of Washington |
| Pages | 2 |
| File Size | 73.9 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 31 |
| Total Views | 136 |
Summary
Contains list of formulas from MATH 394,395 that you will need for MATH 396...
Description
MATH/STAT 395A
Final Exam: Formula Sheet
Winter 2018, Wed March 14
1. Permutations and combinations Qn There are n! = i=1 i = 1.2.3.4. . . . n permutations of n objects. n There are ( ) = n!/(k!(n − k)!) ways of choosing a given k objects from n. k 2. Joint and conditional probabilities S T If C and D are any events: P(C D) = P(C) + P(D) − P(C D).
The conditional probability of C given D is P(C | D) = P(C T C and D are independent if P(C D) = P(C).P(D).
T
D) / P(D).
3. Laws and theorems T S S S Suppose E1 , . . . , Ek is a partition of Ω. That is Ei Ej is empty, and E1 E2 . . . Ek = Ω. Pk T Pk The law of total probability states that: P(D) = j=1 P(D | Ej ) P(Ej ) j=1 P(D Ej ) = Bayes’ Theorem states that: P(Ei | D) = P(D | Ei ) P(Ei )/P(D) 4. Random variables and distributions Probability mass/density function Cumulative dist. func. CDF, P(X ≤ x) Joint mass/density func. of (X, Y ) Marginal mass/density of X
Conditional of X given Y = y Independence of X and Y
discrete (mass) pmf: P(X = x) = pX (x) FX (x) =
w≤x p X (w)
P
pX,Y (x, y) = P(X = x, Y = y) P pX (x) = y pX,Y (x, y)
pX|Y (x|y) = pX,Y (x, y)/pY (y) pX,Y (x, y) = pX (x).pY (y)
or All assumed to hold for
pX|Y (x|y) = pX (x) all X ∈ X , y ∈ Y
continuous (density) pdf: fX (x) R FX (x) = x−∞ fX (w)dw fX,Y (x, y ) R∞ y=−∞ fX,Y (x, y)dy fX|Y (x|y) = fX,Y (x, y)/fY (y) fX,Y (x, y) = fX (x)fY (y) fX (x) =
fX|Y (x|y) = fX (x) −∞ < x < ∞, − ∞ < y < ∞
5. Moments of random variables: (provided the relevant sums/integrals converge absolutely.) Expectation:
E(X) E(g(X))
Conditional expectation E(g(X)|Y = y)
xx
P(X = x) P x g(x) P(X = x) P
x g(x)
P
P(X = x | Y = y)
R∞
xfX (x)dx −∞ g(x)fX (x)dx R∞ −∞ g(x)fX|Y (x|y)dx R ∞−∞
(i) For any random variables X : Variance: var(X) = E((X − E(X))2 ) = E(X 2 ) − (E(X ))2 Note: E(aX + b) = aE(X) + b, var(aX + b) = a2 var(X ). (ii) For any random variables X, Y , Z and W : Covariance: cov(X, Y ) = E((X − E(X))(Y − E(Y ))) = E(XY ) − E(X )E(Y ) p Correlation: ρ(X, Y ) = cov(X, Y )/ var(X )var(Y ), − 1 ≤ ρ(X, Y ) ≤ 1 Note: E(X + Y ) = E(X) + E(Y ), var(X + Y ) = var(X) + var(Y ) + 2cov(X, Y ) cov(aX +b, cW +d) = ac cov(X, W ), cov(X +Y, W +Z) = cov(X, W )+cov(X, Z )+cov(Y, W )+cov(Y, Z ) (iii) Conditional expectation and variance Expectation of h(Y ) = E(X | Y ): E(h(Y )) = E(E(X|Y )) = E(X). Or more generally for E(g(X) | Y ): E(E(g(X)|Y )) = E(g(X). Variance of X: var(X) = E(var(X|Y )) + var(E(X|Y )) 6. A note about Normal (Gaussian) random variables (a) Linear transformations of Normal random variables are Normal (b) Linear combinations of independent Normal r.vs are Normal (c) Different linear combinations of independent Normal r.vs are called jointly Normal (d) If X and Y are jointly Normal and cov(X, Y )=0, then X and Y are independent.
pmf or pdf
7. Standard distributions: (a) Binomial; B(n, p) index n, parameter p (b) Geometric; Geom(p); parameter p (c) Neg. Binomial; N egB(r, p); index r, parameter p (d) Poisson: Po(µ) (e) Uniform on (a, b); U (a, b); (f) Normal; N (µ, σ 2 ) (g) Exponential; E(λ) rate parameter λ (h) Gamma, G(α, λ) shape α, rate λ
P(X = k) =
(
n k
)pk (1 − p)n−k
k = 0, 1, 2, ..., n P(X = k) = p(1 − p)k−1 k = 1, 2, 3, 4, ......
mean
variance
np
np(1 − p)
1/p
(1 − p)/p2
k−1
)pr (1 − p)k−r r/p r−1 k = r, r + 1, r + 2, .... P(X = k) = exp(−µ)µk /k!, k=0,1,2,... µ fX (x) = 1/(b − a), a < x < b (b + a)/2 √ 2 2 2 fX (x) = (1/ 2πσ ) exp(−(x − µ) /2σ ) µ P(X = k) =
(
fX (x) = λ exp(−λx) 0≤x...
Similar Free PDFs

Nanda list - math
- 11 Pages

Forex market that you need
- 2 Pages

, MATH
- 8 Pages

Math 1431 - Math 1431
- 3 Pages

Math Worksheets simple math.
- 14 Pages

Math for nurses 2 - math notes
- 74 Pages

MATH FOR NURSING
- 23 Pages

Notes For MAth HW
- 1 Pages

MATH FOR NURSING
- 18 Pages

Medical term list - It will help you
- 21 Pages

Math IA - curve of a flight math
- 14 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu