9. Drugs of Abuse - Notes taken from the lecture of Mr. Mikhail Valdescona, RMT, MPH PDF

| Title | 9. Drugs of Abuse - Notes taken from the lecture of Mr. Mikhail Valdescona, RMT, MPH |
|---|---|
| Author | Joyce Ann Magsakay |
| Course | Clinical Chemistry 1 |
| Institution | Our Lady of Fatima University |
| Pages | 5 |
| File Size | 152.5 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 128 |
| Total Views | 531 |
Summary
DRUGS OF ABUSE DRUGS OF ABUSE ▪ when a drug is used inconsistently with the medical or the social pattern of a culture TYPES OF DRUG DEPENDENCE: 1. PHYSICAL DEPENDENCE ▪ changes occur in the body after repeated used of drugs that necessitates the continued administration of drug to prevent withdrawa...
Description
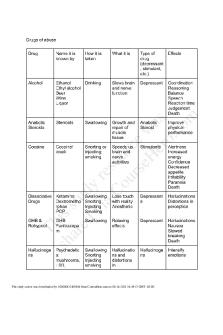
DRUGS OF ABUSE DRUGS OF ABUSE ▪ when a drug is used inconsistently with the medical or the social pattern of a culture TYPES OF DRUG DEPENDENCE: 1. PHYSICAL DEPENDENCE ▪ changes occur in the body afer repeated used of drugs that necessitates the continued administration of drug to prevent withdrawal symptoms ▪ can disappear immediately within days or weeks afer stopping the use of drugs Factors affecting the withdrawal syndrome: > The drugs being used > The dosage & the route of admission > The concurrent use of other drug > Frequency & Duration of drug use > Age, Sex, Health, & Genetic make-up of the user 2. PSYCHOLOGICAL DEPENDENCE ▪ much last longer ▪ primary reason of relapse ▪ the one that causes the addiction CLASSES OF DRUGS: 1. Narcotics 2. Stimulants 3. Depressants 4. Hallucinogens 5. Anabolic Steroids
I. NARCOTICS ▪ also called as “Opioids” ▪ derived from the greek word “Stupor” which means obliviousness, unconsciousness, & insensibility ▪ comes from Poppy Papaver somniferum ▪ refers to opium, opium derivatives, & their synthetic substitute ▪ Examples: > Heroin > Codein > Oxycotin > Morphin > Vicodin > Methadone
1.OPIATES ▪ derived chemically from Opium Poppy ▪ N-Acetylmorphine & Morphine: major metabolites of Heroin ▪ Morphine & Meperidine: can increase the Liver & Pancreatic enzymes ▪ Darvon + Alcoholic overdose: major cause of drugrelated death ▪ Naloxone / Narcan: Antagonist of opiate overdose ▪ capable of Analgesia, Sedation & Anesthesia ▪ Toxic effects: Respiratory acidosis, Myoglobinuria, Cardiopulmonary failure & constriction of pupils ▪ Withdrawal effects: Tremors, muscle cramps, nausea, vomiting, & diarrhea CLASSIFICATION OF OPIATES: ▪ Opoids ▪ Morphine NATURAL ▪ Codeine ▪ Heroin CHEMICAL ▪ Hydromorphone ▪ Oxycodone ▪ Meperidine SYNTHETIC ▪ Methadone ▪ Pentazocine 2.HEROIN ▪ the most rapid-acting narcotics ▪ processed from Morphine Common Names: Chiva, Thunder, Negra, Black tar, Big H, Hell Dust, Horse 3. HYDROMORPHONE ▪ has a great sedative effect ▪ legally manufactured & distributed in USA ▪ Doctor shopping / thef from Pharmacy Common Names: D, Dillies, Footballs, Juice, Smack 4. METHADONE ▪ legally manufactured & distributed in USA ▪ Doctor shopping / thef from Pharmacy Common Names: Pastora, Maria , Amidone, Fizzies, Chocolate chip cookies,Water, Salvia & St. Methadone 5. MORPHONE
▪ the most powerful analgesia known to man ▪ usually gives afer operation Common Names: Mister Blue, Emsel, Hows, Dreamer, God’s Drug, First line, Morf, Morpho & Unkie 6.OPIUM Common Names: Ah-pen-yen, God’s Medicine, Big 0 , Dovers powder, Chinese tobacco, Midnight oil & Aunti Emma 7.OXYCODONE ▪ synthesized from Thebaine ▪ can cause liver damage with Acetaminophen Common Names: OC, Ox, Oxy, Roxy, Parc, Hilliby Heroin, II. STIMULANTS ▪ also called as “Uppers” ▪ it increases the body’s energy & alertness ▪ Examples: > Amphetamines > Methcathion > Methypenidate > Cocaine > Methampethamine > Diet Aid 1. AMPHETAMINES ▪ Old name: Benzedrine ▪ comes from Acacia Berlandieri ▪ similar to Cocaine ▪ has the same structures with Dophamines & Cathecholamines ▪ used to treat Narcolepsy, Obsesity, & ADHD ▪ can be passed into Breastmilk ▪ contraindicated to patients with CVD ▪ Manifestation: Euphoria, heighten mental & physical Activity ▪ Excessive intake: Dilusion, Hallucination, Psychosis, & Panic state ▪ Withdrawal effects: Depression, Parasomias, & Extreme appetite ▪ Laboratory Methods: > Immunoassays > Gas Chromatography Common Names: Bennies, Black beauties, Crank, Ice, Speeds, Uppers 2.COCAINE
▪ comes from Erythroxylon Coca ▪ can cross Blood Brain Barrier (BBB) ▪ can cause sudden death due to direct toxicity on Myocardium ▪ inhibits the uptake of Serotonin, Norepinephrine, & Dopamine ▪ Excessive intake: Violent behavior ▪ Toxic effects: Hypertension, Arrythmia, Seizure, & Myocardial infarction ▪ Urine metabolites: Benzoyl Ecgonine (Half-life: 4-7hrs) ▪ Inhibitor: Prozac ▪ Treatment: Benzodiazepine ▪ Cocaine + Phenylephrine = Treatment for Parkinson’s Disease Common Names: Coca, Coke, Crack, Flake, Snow and Sod, Cot 3.KHAT ▪ comes from “Flowering evergreen shrub” ▪ Cathine & Cathione: Active component of Khat Common Names: Abyssinian tea, African salad, Catha, chat, Kat & Oat 4.FLAKKA ▪ a modifed form of Khat ▪ Chemical Name: Alpha-Pyrrolidinopentiophenone ▪ derived from the Spanish word “Flaca” which means beautiful woman who charms all she meets ▪ common in Florida, USA ▪ has Amphetamine stimulant like-effect Common Names: Zombie drug & Gravel 5. METHAMPETHAMINE ▪ a recreational drug ▪ derived from Ampethamine ▪ Desoxyn: Marketed-form of Methampethamine ▪ Neurotoxic—used before as Aphrodisiac & Europhoriant Common Names: Shabu, Meth, Ice, Crank, Chalk, Crystal, Fire, Go fast & Speed
III. DEPRESSANTS ▪ also known as “Tranquilizers” or “Sedative Hypnotics”
▪ they have therapeutic roles & CNS depressants ▪ this will put you to sleep, relieve pain & anxiety, & muscle spasms & prevent seizure ▪ used to potentiate the effects of Heroin ▪ used to potentiate Gamma-Amino-Butyric-Acid ▪ toxicity agents are initiated by Ethanol ▪ Secobarbital: Major metabolite of Sedative Hypnotics ▪ Diazepam: used for rapid control of Acute Seizure activity ▪ Toxic effects: Respiratory Depression ▪ Two types of Depressants: > Barbiturates > Benzodiazepenes COMMONLY ▪ Secobarbital ▪ Pentobarbital ABUSED ▪ Phenobarbital BARBITURATES ▪Diazepam (Valium) COMMONLY ABUSED ▪ Chlorodiazepoxide (Librium) ▪Lozeparam (Ativan) BENZODIAZEPINE S 1. BARBITURATES ▪ it was frst introduced for Medical use ▪ Short-intermediate acting: Amobarbital,Butabarbital, Butabital, & Pentobarbital ▪ Long acting: Phenobarbital ▪ Signs & Symptoms: Slurred speech, slow mental function, constricted pupils, & CNS depressants ▪ Treatment: Alkalinization of Urine Common Names: Barbs, Pinks, Block Busters, Christmas Trees, Goof balls, Red Devils, Red & Blues, & Yellow Jackets 2. BENZODIAZEPINES ▪ a sedative hypnotics, muscle relaxant, anti-convulsant ▪ it treats anxiety, seizure, & pre-anesthetic sedation ▪ it is available through prescription Common Names: Benzos, Downers 3. ROHYPNOL ▪ a form of Benzodiazepines ▪ Chemical Name: Flunitrazepam ▪ a green/white pill that usually add to the drinks Common Names: Date-Rape Drug, Forget-Me-Pill, Circle, La Rocha, Lunch Money Drug, Mexican Valium, Reynold, Roach, Roapies, Rophies, Wolfes 4. GAMMA-HYDROXYBUTYRIC ACID ▪ it is available as Sodium Oxybate
▪ it is sold as supplement for body building, fat loss, baldness drug addiction & Insomnia ▪ also sold as fsh tank cleaner, ink stain remover, ink cartridge remover, & nail enamel remover Common Names: G, GHB, Goop, Liquid Ecstasy, Liquid X, Scoop, Easy Lay, Grievous bodily Harm, Georgia Home Boy, 5. METHAQUALONE ▪ a 2,3-disubstitue quinazoline with anesthetic, antihistamine, & anti-tussive property ▪ has a sedative hypnotic properties ▪ has a similar symptoms of toxicity to barbiturates, as well as Pyramydal signs (Hypertonicity, Hyperflexa, Myoclonus) IV. HALLUCINOGEN ▪ usually found in Plant & Fungi ▪ it is known to alter human perception & mood ▪ Examples: > Ecstasy / MDMA > Ketamine > K2 / Spice > LSD 1. ECSTASY / MDMA Chemical name: 3,4-Methylenedioxymethampethamine ▪ Half-life: 8-9 hours ▪ most popular recreational drugs ▪ can be incorporated in biscuits ▪ Route: Orally, Inhalation, Ingestion, & Smoking ▪ Signs of Acute Intoxication: Hyperpyrexia ▪ Toxic effects: Hypertension, Cardiac Arrythmias & Convulsion, & Pancytopenia ▪ Effect: Euphoria, Heightened sexual drive, expand consciousness ▪ Excessive intake: Hyperthermia, Tachycardia, Seizure, & DIC Common Names: Disco biscuits, Hug Drug, Harty Drug, Lover’s Speed, Peace, Adams, Eve, E, Clarity, Go, STP, X, XTC, Adams,
2. LSD ▪ most potent pharmacological material known
▪ a semi-synthetic indolalkylamine & hallucinogen ▪ causes blurred / undulating vision ▪ Adverse reaction: Panic reactions Common Names: Acid, Blotter Acids, Dots, Mellow Yellow, Windown Pane 3. MARIJUANA / CANNABIS ▪ comes from “Cannabis sativa” ▪ associated with impairment of short-term memory & intellectual functions ▪ Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): the most potent component / the psychoactive substance of Marijuana ▪ Marijuana-Hash: a naturally occurring cannabinoids ▪ 11-Nor-deltatettrahydrovannabinol: Urine Metabolite ▪ afer a single use, THC-COOH can be detected in urine for 3-5 days & up to 4 weeks for chronic users ▪ Physiologic effects: reddening of the conjunctiva & Tachycardia Common Names: Smoke, Weed, Mary Jane, Aunt Mary, Grass, Herb, Hash, Hash-ish, BC Bud, Blunts, Boom, Dope, Gangster, Ganja, Sinsemilla, Skunk, Kif, Joint, Pot, Reefeer, Yerba 4. PHENCYCLIDINE ▪ a depressant, stimulant, hallucinogenic, & anesthetic effect ▪ Phencyclidine HCl: major metabolites ▪ about 10-15% is unchanged when excreted in urine ▪ detected in urine afer 7-30 days of abstinence ▪ Low dose effect: sense of dissociation, euphoria, & numbness ▪ High dose effect: loss of feeling in lower extremities, disorganize thoughts, & disconnection to reality ▪ Toxic effect: Stupor & Coma V. ANABOLIC STEROIDS ▪ derived from Testosterone ▪ improves athletic performance by ↑ muscle mass ▪ Toxic effects: Chronic Hepatitis, Atherosclerosis, Abnormal Platelet aggregation & Cardiomegaly ▪ Continued Uptake: > Male: Testicular Atrophy, Infertility, Gynecomastia > Female: Masculine traits, breast reduction, sterility Common Names: Amoids, Juice, Pampers, Roids, Stackers, & Weight Gainers SPECIMEN FOR DRUG TESTING: > Urine: 30-45 mL (polyethylene bottle)
> Blood: 10 mL (Red top: Serum) > Saliva: 30 mL—detects active portion of drugs > Hair > Tissue > Fingernails > Sweat: detects Parent drugs URINE REQUIREMENT: > Temperature = 32.5-37°c > Specifc Gravity = 1.003-1.035 > Creatinine = > 20 mg/dL > Electrolytes KINDS OF ADULTERANTS: 1. Water 2. Bleach 3. Cologne 4. Gluteralydehyde 5. Liquid soap 6. Salt vinegar 7. Baking soda 8. Lemon juice METHODS FOR IDENTIFYING & MEASURING DRUG ABUSE: 1. ENZYMATIC TESTING ▪ it is for Alcohol testing ▪ quantify the sum of all Alcohols present in the sample ▪ it doesn’t distinguish alcohol from its metabolites during quantifcation 2. IMMUNOASSAY a. ENZYME MULTIPLIED IMMUNOASSAY TECHNIQUE (EMIT): uses enzyme-labeled drug that competes with the drug in the sample 3. CAPILLARY ELECTROPHORESIS ▪ different analyte selectivity based on different physiochemical principles of separation without changes in instrumental hardware 4. CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS: a. THIN LAYER CHROMATOPGRAHY ▪ uses Serum, Urine, or CSF fluid for analysis ▪ extraction is pH dependent: > Acidic drug @ 4.5 > Alkaline drug @ 9.0 b. LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY
▪ used to confrm positive test results from the screening test ▪ used for poisoning detection, therapeutic drug identifcation & quantifcation, pharmacokinetics, & drug metabolism studies c. HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY ▪ allows quantitative measurement of drugs as well as separation of these same drugs especially antidepressant including active & inactive metabolites d. GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY ▪ a legally accepted method for e. GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY-MASS SPECTROMETRY ▪ for confrming screening methods ▪ allows detection of low levels of drugs ▪ give rise to fngerprint pattern of each compound analyzed EMIT (ng/mL) Amphetamines Marijuana Cocaine Opiates Phencyclidine
500 50 150 2,000 25
GC-MS (ng/mL ) 250 25 100 2,000 25...
Similar Free PDFs

Drugs of Abuse DEA 8
- 17 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu