Chapter 14 INFORMAL DESIGN GUIDELINES FOR RELATION SCHEMAS FOUR INFORMAL MEASURES: 1. Semantics of Attributes. 2. Reducing redundant values in TUPLES. 3. Reducing Null values in TUPLES. 4. Disallowing possibility of Generating Spurious Tuples DOC

| Title | Chapter 14 INFORMAL DESIGN GUIDELINES FOR RELATION SCHEMAS FOUR INFORMAL MEASURES: 1. Semantics of Attributes. 2. Reducing redundant values in TUPLES. 3. Reducing Null values in TUPLES. 4. Disallowing possibility of Generating Spurious Tuples |
|---|---|
| Author | Sharans Kumar |
| Pages | 43 |
| File Size | 1.7 MB |
| File Type | DOC |
| Total Downloads | 96 |
| Total Views | 286 |
Summary
Chapter 14 INFORMAL DESIGN GUIDELINES FOR RELATION SCHEMAS FOUR INFORMAL MEASURES: 1. Semantics of Attributes. 2. Reducing redundant values in TUPLES. 3. Reducing Null values in TUPLES. 4. Disallowing possibility of Generating Spurious Tuples. 1. SEMANTICS OF ATTRIBUTES: Whenever we group attributes...
Description
Chapter 14 INFORMAL DESIGN GUIDELINES FOR RELATION SCHEMAS FOUR INFORMAL MEASURES: 1. Semantics of Attributes. 2. Reducing redundant values in TUPLES. 3. Reducing Null values in TUPLES. 4. Disallowing possibility of Generating Spurious Tuples. 1. SEMANTICS OF ATTRIBUTES: Whenever we group attributes to form relation, We assume certain meaning associated with attributes. This meaning we call "SEMANTICS". It tells how to interpret the values stored. Easier the semantics, better the relation schema would be. Guideline 1 Design relation schema so that it is easy to explain the meaning. Do not combine attributes from multiple entity types into single relation. Note: A relation schema should always correspond to one entity type or one relationship type, for the meaning to be clear. Refer fig 10.3 for bad relation schema design. Combines two entities into one schema. 1. Reducing redundant values in TUPLES.: If Redundant values are not reduced.. We face the following problems. Redundant information increases storage space. Redundant information in Tuples introduces "UPDATE ANAMOLIES"....
Similar Free PDFs

Informal Introduction in Japanese
- 37 Pages

REDUCING THE DURATION OF PROJECTS
- 11 Pages
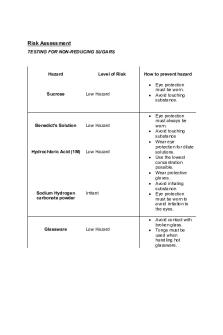
Testing for non-reducing sugars
- 4 Pages

Informal letter
- 1 Pages

Density of Water Values
- 1 Pages

Reducing Balance Loans Notes
- 3 Pages

Reducing Stress - sbs
- 2 Pages

NSW Police Statement of Values
- 1 Pages

Informal Contractions
- 3 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu






