Flowchart PDF

| Title | Flowchart |
|---|---|
| Author | Meagan Fitzgerald |
| Course | General Microbiology |
| Institution | University of South Florida |
| Pages | 1 |
| File Size | 150.7 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 76 |
| Total Views | 165 |
Summary
Microbiology Lab flowchart...
Description
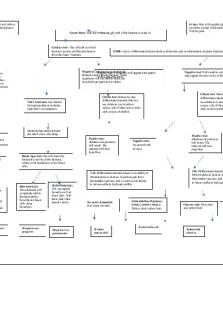
Gram+: Will be purple in color and tells us that the bacteria has a thick peptidoglycan layer.
Gram-Stain: Will show what the cell wall of the bacteria is made of.
Catalase test: This will tell us which bacteria can and can't ferment lactose from the Gram+ bacteria.
NaCl Tolerance test: Selects for bacteria that can tolerate high NaCl concentration.
Bacteria that can tolerate the NaCl: This is the Staph bacteria
MSA: Can ferment mannitol which changes the pH of the agar.
A negative test will produce no color but will still grow on the plate.
Staphylococcus aureus
A positive test will show growth and turn the medium red.
Staphylococcus epidermidis
EMB: Used to differentiate between lactose fermenters and non-fermenters of gram- bacteria.
Negative Catalase testtest: mean that the will appear dark purple Positive Fermenters bacteria cannot ferment lactose. These with a greenish sheen organisms will not bubble when you drop hydrogen peroxide on them.
Positive Catalase test mean that the bacteria can ferment lactose. These organisms will produce bubbles when you drop hydrogen peroxide on them.
NaCl Tolerance test: Selects for bacteria that can tolerate high NaCl concentration.
Gram-: Has a thin peptidoglycan layer which does not allow crystal violet stain to stay within the cell. Will be pink
Negative test: Will result in colorless colonies or may appear the same color of the agar.
Citrate test: Selects for and differentiates bacteria that can use citrate as a sole carbon source, only if there are no other carb. sources available.
Citrate test: Selects for and differentiates bacteria that can use citrate as a sole carbon source, only if there are no other carb. sources available.
Bacteria that cannot tolerate the NaCl: this is the Strep Positive test: Alkaline end produces will result. The medium will turn deep blue
Negative test: No growth will be seen.
Positive test: Alkaline end produces will result. The medium will turn deep blue
Negative test: No growth will be seen.
Blood Agar test: this will show the hemolytic activity of the bacteria, which is the breakdown of red blood cells.
Beta hemolysis: These bacteria will completely utilize the hemoglobin from the red blood cells using hemolysis.
Streptococcus pyogenes
Alpha hemolysis: The incomplete hemolysis of red blood cells. Will leave green halo around colony.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
TSI: Differentiates bacteria based on its ability to ferment glucose, lactose, to produce gas form fermentation process, and or sucrose and ability to reduce sulfur to hydrogen sulfide
No carbs fermented: Red slant/ red butt
Yersinia enterocoliti
Fermentation of glucose, lactose, and/or sucrose: Yellow slant/ yellow butt
Escherichia coli
TSI: Differentiates bacteria based on its ability to ferment glucose, lactose, to produce gas form fermentation process, and or sucrose and ability to reduce sulfur to hydrogen sulfide
Glucose only: Red slant and yellow butt.
Salmonella enterica
Fermentation of glucose, lactose, and/or sucrose: Yellow slant/ yellow butt
Klebsiella pneumoniae...
Similar Free PDFs
Flowchart-acco - flowchart
- 1 Pages

Flowchart
- 8 Pages
Flowchart
- 1 Pages

Negligence Flowchart
- 3 Pages

Bab02 Flowchart
- 7 Pages

civil Flowchart
- 2 Pages
Solubility Flowchart
- 2 Pages

Flowchart Jurnal
- 13 Pages

Remedies Flowchart
- 1 Pages

Evidence Flowchart
- 1 Pages

Flowchart Assignment
- 6 Pages

Flowchart sample
- 1 Pages

Divorce flowchart
- 1 Pages

Hearsay Flowchart
- 1 Pages

Remedies - Flowchart
- 1 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu