Memory flowchart Team BDone PDF

| Title | Memory flowchart Team BDone |
|---|---|
| Course | Cognitive Psychology |
| Institution | University of Phoenix |
| Pages | 5 |
| File Size | 194.1 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 22 |
| Total Views | 171 |
Summary
Memory flowchart...
Description
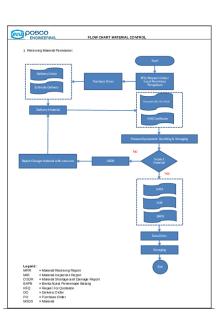
MEMORY FLOWCHART
Gabriela Milligan, Amanda Williams and Jennifer Holland Team B PSY/360 December 10. 2018 Jennifer Doran
Memory Visual, acoustic, semantic. This is the surroundings and encodes or stores in our brain Encoding is the first step in creating a memory. Stimuli enter the brain through the senses, and memory is formed (The Human Memory 2018).
Memory allows the brain to encode, store, and retrieve information in three basic forms. Storage – short term, long term (short term up to 30 seconds, long term whole life time) Storing refers to the method of placing newly received information into memory, which is modified in the brain for more accessible storage (The Human Memory 2018).
The NEXT Stage
The brain processes the number either short- or long-term memory. If we are not able to recall the information this is where we have memory loss. Recall or retrieval of memory refers to the following re-accessing of events or information from the past, which has been earlier encoded and stored in the brain (The Human Memory 2018).
Implicit Memory
Explicit Memory
Referred as unconsious memory or automatic memory. Uses experiences to remember things whitout thinking about them. ( Driving a car, bike, buttoning a shirt, and rutine task)
Information consciously recollected. (Things that happen in a vacation, in school, and remembering peoples names)
Sensory Memory Holds presented stimuli for a very small period of time
Types of Memory Storage
Long-Term Memory Houses all of the experiences, knowledge, and skills in our lifetime Short-Term Memory The rehearse or recycle information and flows back and forth between long and short term memory
Working Memory Model
VisualSpatial Scratch Pad
Sensory Memory (Attention)
Central Executive
Long-Term Memory
Phonological Loop Articulatory Control Phonological Store
FORGETTING
DECAY: loss of information from immediate memory due to aging, or memory not bein recall as often
INTERFERENCE: Loss of information from immediate memory because information is being negatively influence
References
McLeod, S. (2008). Simply Psychology Working Memory . Retrieved from https://ecampus.phoenix.edu/secure/aapd/cwe/citation_generator/index.html
Robinson-Riegler, B., & Robinson-Riegler, G. L. (2017). Cognitive Psychology: Applying the Science of the Mind, Fourth Edition. New York: Pearson Education, Inc.Simply Psychology Working Memory (2012) Unknown. (2018). Stages of memory. Psychestudy. Retrieved from https://www.psychestudy.com/cognitive/memory/stages...
Similar Free PDFs

Memory flowchart Team BDone
- 5 Pages
Flowchart-acco - flowchart
- 1 Pages

Flowchart
- 8 Pages

Memory
- 3 Pages
Memory
- 5 Pages
Flowchart
- 1 Pages

Negligence Flowchart
- 3 Pages

Bab02 Flowchart
- 7 Pages

civil Flowchart
- 2 Pages
Solubility Flowchart
- 2 Pages

Flowchart Jurnal
- 13 Pages

Remedies Flowchart
- 1 Pages

Evidence Flowchart
- 1 Pages

Flowchart Assignment
- 6 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu