The Hospitality Business Notes PDF

| Title | The Hospitality Business Notes |
|---|---|
| Course | The Hospitality Business |
| Institution | University of Brighton |
| Pages | 14 |
| File Size | 300.9 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 61 |
| Total Views | 118 |
Summary
Lecture and Seminar notes ...
Description
Krunali Manek
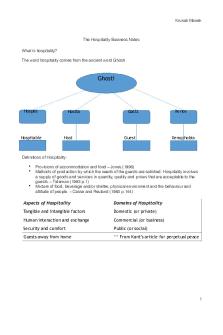
The Hospitality Business Notes What is hospitality? The word hospitality comes from the ancient word Ghosti
Ghosti
Hospes
Hospitable
Hostia
Host
Gatiz
Guest
Xenos
Xenophobia
Definitions of Hospitality: • •
•
Provisions of accommodation and food – Jones (1996) Methods of production by which the needs of the guests are satisfied. Hospitality involves a supply of goods and services in quantity, quality and prices that are acceptable to the guests. – Tideman (1983 p.1) Mixture of food, beverage and/or shelter, physical environment and the behaviour and attitude of people. – Casse and Reuland (1983 p.144)
Aspects of Hospitality
Domains of Hospitality
Tangible and intangible factors
Domestic (or private)
Human interaction and exchange
Commercial (or business)
Security and comfort
Public (or social)
Guests away from home
^^ From Kant’s article for perpetual peace
1
Krunali Manek
The history of hospitality: In Slavic mythology they had a god named Radegast, which meant the god of Hospitality. 3500 BC: • The Summerians (Turkish) were the first people to trade beer 2500 BC: • This was the first type of accommodation as when people came to see the Egyptian pyramids they could stay there overnight. 1750 BC: • The code of Hammurabi 80 AD: • The volcano Vesuvius erupted and destroyed the village of Pompeii. The ruins lead to show that this was the first sign of fast food places as the layout was similar to today’s layout of fast food restaurants. 400 AD: • The fall of the roman empire. They had built a lot of roads and after the fall of the empire people could travel along these roads and stay in buildings known as posthouses. 16th century: • Stagecoaches were invented (horse wagons), during this time period inns and taverns were created in England. 18th century: • The boulanger (1765) was created which was the first restaurant. The word restaurant comes from the French verb restoré, which means to replenish/restore. 19th century: • August Escoffier invented the brigade system in restaurants, which is each person having a specific job within the kitchen. • César Ritz re-invented hospitality as he was the first person to build a hotel with all rooms with their own bathrooms. Early 20th century: • The elevator was created which meant that hotels could add more stories to their building. • Waldorf Astoria – New York was built next to the main station so people could travel directly to the hotel. In the 1920’s the big hotels opened, then in 1929 worldwide depression.
Mid 20th century: • Hitler created a massive area for his soldiers to go have holiday before the war started but was never used. It could account for 20,000 people. It is now being redesigned for a new hotel. • After WWII: transport, baby boom • Tourism boom: build new hotels in accessible areas.
2
Krunali Manek
•
The big hotel chains in the 1950’s they started to build hotels near roads as people started buying more cars.
50’s-80’s: • Fast food (McDonalds, Burger King), hotel buildings • 1990-91: recession • Mergers (Holiday Inn and Intercontinental) • 11th September 2001 (Terrorist attacks in America) the tourism fell • 2009-2012: recession • New mergers Today: • • • • • • • •
Asia, Middle East and Africa Extravaganza (the zoo hotel, underwater hotel) Authenticity Community based tourism (CBT) Favela tours House swaps (Airbnb somewhat) Couch surfing (staying in someone’s place) Airbnb (BIGGEST COMPETION FOR HOTELS)
New experiences: • Dans Le Noir restaurant • Slow food • Healthy food
The relationship between Hospitality and Tourism • • •
Tourisms comes from the Latin word tornare Someone that leaves home for more than 24 hours and less than one year. “Temporary movement of people to destinations outside their places of work and residence, the activities undertaken and facilities created to cater for their needs.”
Tourism involves: • Transfer • Temporary stay • People • Facilities
3
Krunali Manek
Tourism = movement, hospitality = stay
The scope and size of the Hospitality Industry In economic terms hospitality is the provision of accommodation, meals and drinks outside of the home. – BHA (2011) BHA = British Hospitality Association Hospitality involves consumption “on-site” = eating at the place. The context of consumption is important (time to consume, what type of food, the atmosphere) and also the management of consumption. The BHA says there are 4 different sectors in hospitality: • Hotels • Restaurants • Catering • Events The sectors of hospitality are: Barrows, Powers and Reynolds (2012) • • • • • • • • • • • •
Accommodation Food service Cruises Gaming operations (casinos) Private clubs (Gentleman’s club, golf clubs) Managed parks (national parks) Theme parks Contract catering (airplane catering) Consulting services (someone that a company hires and then give you feedback on what you can improve) Hospital Management (looking after people, feed them) Senior living (working with the elderly) MICE; o Meetings o Incentives (motivation factors, awards) o Conferences o Exhibitions
4
Krunali Manek
Direct Hotels restarant Caterings events
Indirect food and beverage
Induced (lead in a indirect way) consumer goods retail
The Scope and Size of the Hospitality Industry: Figures in the UK: • 6th largest contributor for export • Over 180,000 businesses • 4th largest employer • 10% of the workforce • 27% of the UK jobs growth • 44% of the employees are under 30 • 100,000 more jobs until 2020 • More than 1.2 million people in other sectors Sectors: • Accommodation • Found service The International Hospitality Industry: Part of the international business: • import and export of goods and services • foreign investment • Global hotel organisations The 10 largest hotel chains: 1. Marriott/Starwood 2. Hilton 3. Intercontinental 4. Wyndham Hotel Groups
5
Krunali Manek
5. Jin Jiang International/Plateno Hotel Groups 6. Choice Hotel International 7. Accor Hotels 8. Best Western Hotels and Resorts 9. Home ins Hotel Group 10. Carlson Residor Hotel Group Characteristics and Trends of the Hospitality Industry: Characteristics: • Service: • Intangibility (cant be touched) • Inseparability (service, product and customer - all interdependent) • Variability (service is changed, personalised) • Perishability (its a feeling that ends - provide service quickly and 100% booking) • Seasonality: • Relatively fixed supply • High fixed costs • Sensitivity to the economic environment Trends affection the industry: • Business tourism • Leisure tourism • Self gratification • Family tourism • Female tourism • Increase in sophistication • Shrinking of loyalty programmes • Mass Customisation Cons
Pros
physically challenging job
fast career progression
long and unsocial hours
competitive wages at managerial levels
low wages in the beginning
inclusion and diversity
dealing with people
flexibility
quick decisions
dealing with people
highly competitive
highly competitive
Accommodation Sector: Ways of classifying accommodation: • Type: motel, hotel, camping, hostel • Function: resort, connection business • Location: city centre, airports • Size: small, medium, large • Stars: 1-5? 6? 7? • Service Level: budget, standard, luxury
6
Krunali Manek
Serviced accommodation in Britain: • Hotels • Budget Hotel • Guest Accommodation Common Departments in Hotel Management: 1. Rooms Division: • room maintenance • house keeping • electrician, plumber - engineering • reception • reservations • concierge 2. Food and Beverage: • room service • restaurants • bars • mini bars 3. Maintenance and engineering 4. Sales and marketing 5. Accounting 6. Human Resources Management 7. Security 8. Procurement Room types: According to number of guests - Single - Double - Twin - Triple Room types: - Standard - Superior - Deluxe - Junior suite - Suite - Presidential/Royal/Imperial suite - Connecting - Adapted Types of meal plans: - European plan (RO) - Continental plan (BB) - Half Board (MAP or Demi-Pension) - Full Board (FAP or Pension)
7
Krunali Manek
Rates: Rack rate Discount rate • Room night - Number of rooms X Number of nights • Occupancy - Number of occupied rooms/Number of total rooms X 100 • ADR - Average daily rate - Room revenue/Number of occupied rooms • RevPar - Room revenue/Number of total rooms Organisational Forms: Public sector vs Private sector: 1.1. Public Sector • National Government • Department for culture, Media and Sport • Department for Business Innovation and Skills • Local Government • East Sussex County Council • Eastbourne Borough Council • Nationalised Services • National Health Services (NHS) • Agencies and Authorities • Higher Education Funding Council (HEFC) 1.2. Private sector Privately funded 1.2.1. Not for profit organisations • Charities • Social enterprises 1.2.2. For profit organisations • Sole trader • One owner • the person who owns manages their own business • Normally issues their own but can use a business name • Supplies all the capital • Entities to all the profits • limited liability for the depts of the business • Advantages: • Simple and cheap • Total Control • Income = Personal income • Disadvantages: • Total Responsibility • Can incur in personal debt • Partnerships • An agreement between people to carry on a business to aim for profit • A partnership may trade under a business name or the name son the partners • Partners are manager: they can decide how to control business • Partners puppy capital
8
Krunali Manek
• Partner share the profits • Partners pay tax on the share of their profits and pay for the losses he business makes • Partnership agreement can set out rules to reduce the likelihood of disputes • Normally unlimited liability • Limited liability partnership: • A special type of LLP where there no general partners • All of the owners of an LLP have limited personal liability for business debts • Liability for debts is limited to the amount of money partners invest • Limited companies • Set up by individual who want limited liability • Shareholders are but not necessarily managers • Shareholders supply capital • Shareholders share the profit • Shareholder have limited liability for the debts of the business • Public limited companies • Shares are traded publicly • Public can buy shares listed on the stock exchange People: • Aims to make profit • invest capital to start a business • Compete in the market Business affiliation: Three elements: - Name - Structure - Procedures Types of management and associations in hospitality: 1. Company owned • Owned, managed and operated by the company • The company uses its own expertise in • site selection • property development • markering and advertisement • operations management 2. Management contract • “the ownership of the physical asset is separated from its management” • Property managed but not owned by the hotel company • The operational an managerial control of a business is contracted out to a separate company • The company provides: • Operational and marketing expertise • Management and professional staff • Popular method of international growth 3. Franchising • An agreement where the franchisor grants a license to the franchise to distribute products and services under the franchisers name • Franchiser offers (franchisee pays for): • Reservations system • Marketing • Standards and procedures
9
Krunali Manek
• Training • Loyalty • Advantages for the franchise: • Franchisee benefits from a brand and has exclusive rights over it • Franchisee gains from the franchisors experience and knowledge • Easier to recover ROI: lower risk • Advantages for the franchisor: • Brand extension • Fees and profits • Disadvantages for the franchisee: • High fees and royalties • Limited autonomy • Risk that the franchise will deteriorate • Disadvantages for the franchisor: • loss of control • need to scrutinise the abilities os the franchisee • having to with the franchisee as a stakeholder But how about the global economy? View 1: Franchising is good - More efficient - Lower prices for consumers - more consumption - more production - more jobs View 2: Franchising is bad: - less money for workers - less to buy things - less consumption - less production - fewer jobs Consortium: • Independently owned hotels • individual ownerships are maintained • Name is primary - Why consortiums? - International coverage - Central reservations system - Markering expertise - Education and training - Financial resources Referral Property or affiliation: • Independent properties associated for diverse purpose: - mangement - marketing - reservations • Like a consortium but the name is not primary
10
Krunali Manek
The Food and Beverage Sector: Business in F&B: Contract catering: • Business and Industry • Education • Healthcare • Public department and agencies Food service management: • Restaurants • Hotel food service • Motorway and roadside • Fast food and take away Orientation: • Cost: - Budgeted profit - Prefer to cut costs than increase sales - Fixed-pricing policy • Market: - Greater reliance on sales - Unstable market - Fluctuating prices
Restricted Market Market Open Market
- Clubs - Function catering - Hotels - Restaurants - Pubs - Fast food and take away
Employee catering Cost Institutional catering
- Schools - Universities and colleges - Hospitals - Prisons
Key components of F&B Sector: • Product offered • Menu choice • Service • Price and value • Interior design
11
Krunali Manek
• Atmosphere and mood • Location and accessibility • Employees • Consumer demographics SWOT analysis:
Ethnic food: Zeret Restaurant Street food and pop up: - Farmers market - Consumers look for diversity authenticity - Cheap (to eat and run) - Mobile food - Molecular Gastronomy Health: - 1/4 of adolescents leaving school are obese - NHS: 10bn on bad diet-related diseases (40 hospitals) - 1/3 of of 16-24 year olds: trying to lose weight Perfect Competition: - Many buyers and seller - No product differentiation - Perfect knowledge - Freedom of entry Monopoly: Railway - Single producer - changes in prices do not affect demand
12
Krunali Manek
Oligopoly: Washing powder - Small number of suppliers - Various barriers to entry - More non-price competition Monopolistic competition: chocolates - Large number of buyers and suppliers - Independence - Freedom of entry - Product differentiation Collusion: Tacit Collusion: Agenda: - Focus on welfare catering - SWOT analysis of the foodservice sector - Real life examples: Schools, hospitals and prisons - Links to wider social and economic trends Contract catering and foodservice management market - its two sub-categories: - profit such as restaurants and leisure outlets - Costs, which covers catering in - business and industry (B&): the largest segment - education: schools - healthcare: hospitals - catering for the public - the ministry of Defence (MoD): and local authorities (LAs) Key Facts: Food Service 1. Clients or Customers Performance Management: Why Performance management? Measuring how well your company is doing. - Value across the company are uniform - Individual and organisation goals are compatible - Roles and expectations are explained Should be: - Strategic - Integrated Should aim to: - Measure, improve and refine business performance - Manage behaviour - Develop tam work KPI’s: Key Performance Indicators - Reflect on organisations goal - Asses the state of business
13
Krunali Manek
- Measure progress - Prescribe future action KPI;s are: - Quantifiable measurements - Financial or non-financial Bad: - Title of KPI: Sales - Definition: Change in sales from month to month - Measurement: Total sales by region or all regions - Target: Increase each month Good: - Title of KPI: Employee Turnover - Definition: The total number of employees who resign for whatever reason plus the number of employees terminated for performance reasons, and the total divided by the number of employees at the beginning of the year. Employees lost due to reductions in force will not be included in this calculations. - Measurement: The Human Resources department contains record of each employee. The separation section lists reason and date of separation for each employee. Some KPI’s in Hospitality: 1. Physical • Furniture.equipment/linen loss and turnover • Energy use • 2. Financial and Operational • Room nights • Occupancy • ADR • RevPar • Yield • RevPas • Seat turnover • Fixed costs • Variable costs • Profit: • Gross: Profit-Cost • Operational: Gross-Operational expenses • Net: Operational expenses-Taxes • Productivity Index • Mystery Shopper • Benchmarking 3. External
14...
Similar Free PDFs
The Hospitality Business Notes
- 14 Pages

Hospitality study notes
- 10 Pages

Hospitality Law Lecture Notes
- 32 Pages

Hospitality Questionnaire
- 3 Pages

Italian Hospitality in Australia
- 3 Pages

Pricing in Tourism and Hospitality
- 15 Pages

THE Business Policy GAME
- 233 Pages

The Business Model Canvas
- 11 Pages

The business model canvas
- 1 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu






