Topic 5- Diffusion and membrane transport Notes PDF

| Title | Topic 5- Diffusion and membrane transport Notes |
|---|---|
| Author | Renee Magnan |
| Course | Principles of Cell Biology |
| Institution | University of Victoria |
| Pages | 3 |
| File Size | 110.1 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 35 |
| Total Views | 183 |
Summary
Topic 5 - Diffusion and Membrane Transport Notes...
Description
TOPIC 5: Diffusion and Membrane Transport Electrochemical Gradient
These pumps work against 2 gradients at the same time: o The concentration gradient: Inside = low concentration of sodium ions (Na+) o The electrochemical gradient (dif. in charge on either side of cells membrane): Inside = Negative (-) Outside = Positive (+)
Pump works against both of these gradients: take in 3 (+) charged Na+ and pushes them outside into the Na+ rich environment.
To get the energy to do this, the protein pump breaks up a molecule of ATP. o When ATP (3 P, 1 A) connects to the protein pump an enzyme breaks a covalent bond of one of the phosphate groups, releasing a burst in excited energy. o The bond break releases enough energy to change the shape of the pump so that it opens outward and releases 3 Na+. o This new shape allows it to transport 2 potassium ions (K+) in.
Topic 2c: Carbohydrates (Polysaccharides) Monosaccharides
1 sugar unit
Typically sweet-tasting
Function as an immediate energy source for cells. o Glucose o Galactose o Fructose
Disaccharides
2 sugar units
Small enough to be soluble in water
Function as a transport form. o Lactose ( B-D-galactose + B-D-glucose = B glycosidic bond) B-glycosidic bond: cause the hydroxyl groyp on C-atom 1 of the galactose is in the B-configuration. Some ppl lack the enzyme needed to hydrolyze this Bglycosidic bond and are considered lactose intolerant (have difficulty metabolizing this disaccharide). o Maltose (a-D-glucose + a-D-glucose = a glycosidic bond) Both in a-form: glycosidic bond forms between C atom 1 of one glucose and C atom 4 of the other. o Sucrose (a-D-glucose + B-D-fructose = a glycosidic bond)
2
a-Glycosidic Bond: involves a C-atom 1 with its hydroxyl group in the aconfiguration.
B-Glycosidic Bond: the hydroxyl group on C-atom 1 is in the Bconfiguration.
In polysaccharides, the 3-D configuration and the biological role of the polymer depend critically on the nature of the bond between the repeating monosaccharide units.
3...
Similar Free PDFs
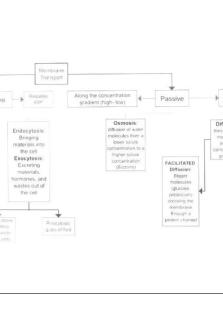
Membrane Transport Flow Chart
- 1 Pages

Week 2 Membrane transport lab
- 6 Pages

Chapter 7 HW Membrane Transport
- 1 Pages

Lab 5 Diffusion and Osmosis
- 1 Pages

Math1081-topic 5-notes
- 38 Pages

Topic 5 Credibility Notes
- 8 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu









