Chapter 5-01 - Pearson - Homework PDF

| Title | Chapter 5-01 - Pearson - Homework |
|---|---|
| Course | Biological Principles For Non-Majors |
| Institution | Broward College |
| Pages | 13 |
| File Size | 861.1 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 58 |
| Total Views | 164 |
Summary
Pearson - Homework...
Description
Chapter 5-01 Due: 10:59pm on Tuesday, November 30, 2021 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy
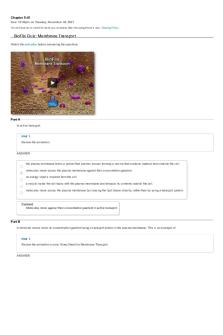
BioFlix Quiz: Membrane Transport Watch the animation before answering the questions.
Part A In active transport,
Hint 1. Review the animation.
ANSWER:
the plasma membrane forms a pocket that pinches inward, forming a vesicle that contains material from outside the cell. molecules move across the plasma membrane against their concentration gradient. no energy input is required from the cell. a vesicle inside the cell fuses with the plasma membrane and releases its contents outside the cell. molecules move across the plasma membrane by crossing the lipid bilayer directly, rather than by using a transport protein.
Correct Molecules move against their concentration gradient in active transport.
Part B A molecule moves down its concentration gradient using a transport protein in the plasma membrane. This is an example of
Hint 1. Review the animation or your Study Sheet for Membrane Transport.
ANSWER:
facilitated diffusion. active transport. exocytosis. endocytosis. diffusion.
Correct In facilitated diffusion, molecules use a transport protein to move across the plasma membrane. There is a net movement of molecules down the concentration gradient -- that is, there is a net movement of molecules from where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated.
Part C Water crosses the plasma membrane
Hint 1. Review the animation.
ANSWER:
through cotransport. through active transport. through facilitated diffusion or diffusion. against its concentration gradient. using a process that requires energy from the cell.
Correct Water can cross the plasma membrane through the process of facilitated diffusion. However, water molecules can also cross the lipid bilayer directly.
Part D The sodium-potassium pump uses energy from ATP to move sodium ions out of the cell, and potassium ions into the cell. This is an example of
Hint 1. Review the animation.
ANSWER:
diffusion. facilitated diffusion. exocytosis. active transport. passive transport.
Correct The sodium-potassium pump moves ions across the plasma membrane against their concentration gradients. This requires energy and is an example of active transport.
Part E The plasma membrane forms a pocket that pinches inward, forming a vesicle that contains material from outside the cell. This describes the process of
Hint 1. Review the animation or your Study Sheet for Membrane Transport.
ANSWER:
diffusion. endocytosis. passive transport. exocytosis. active transport.
Correct In endocytosis, the plasma membrane forms a pocket that pinches inward, forming a vesicle that contains material from outside the cell.
Activity: Diffusion
Click here to complete this activity. Then answer the questions.
Part A Drag the terms on the left to complete the sentences on the right. ANSWER:
Reset
active transport
Help
When molecules move down their concentration gradient, they move from where they are more concentrated
to where they are less concentrated .
Diffusion across a biological membrane is called passive transport .
Correct
BioFlix Activity: Membrane Transport -- Diffusion Certain molecules use diffusion to cross the plasma membrane. To review the process of diffusion, watch this BioFlix animation: Diffusion.
Part A - Diffusion Drag the labels to their appropriate locations on the diagram. ANSWER: Reset
Side with higher concentration of molecules
Diffusion causes a net movement of molecules down their concentration gradient.
Correct
Activity: Facilitated Diffusion
Plasma membrane
Side with lower concentration of molecules
Help
Click here to complete this activity. Then answer the questions.
Part A Facilitated diffusion is a type of _____. ANSWER:
active transport pinocytosis passive transport phagocytosis
Correct During facilitated diffusion, the cell is not expending energy to move the particles across the membrane; therefore, facilitated diffusion is a form of passive transport.
Part B Structure A is a _____.
ANSWER:
phospholipid solute water molecule transport protein solvent
Correct A solute is crossing the plasma membrane.
Part C Structure B is a _____.
ANSWER:
solvent transport protein solute water molecule phospholipid
Correct The transport protein facilitates the movement of solute across the plasma membrane..
BioFlix Activity: Membrane Transport -- Facilitated Diffusion Certain molecules use facilitated diffusion to cross the plasma membrane. To review the process of facilitated diffusion, watch this BioFlix animation: Facilitated diffusion.
Part A - Facilitated diffusion Drag the labels to their appropriate locations on the diagram. ANSWER:
Reset
Plasma membrane
Side with higher concentration of molecules
Side with lower concentration of molecules
Transport protein
Correct
Facilitated diffusion causes a net movement of molecules down their concentration gradient.
Help
Activity: Osmosis and Water Balance in Cells
Click here to complete this activity. Then answer the questions.
Part A What name is given to the process by which water crosses a selectively permeable membrane? ANSWER:
osmosis diffusion phagocytosis passive transport pinocytosis
Correct Osmosis is the passive transport of water.
Part B This cell is in a(n) _____ solution.
ANSWER:
hypertonic hypotonic isotonic hypotonic and isotonic hypertonic or isotonic
Correct There is a greater concentration of solute outside the cell.
Part C You know that this cell is in a(n) _____ solution because the cell _____.
ANSWER:
hypertonic ... lost water isotonic ... neither lost nor gained water hypotonic ... swelled hypertonic ... gained water hypotonic ... shrunk
Correct A cell will gain water when placed in a hypotonic solution.
Part D You know that this cell is in a(n) _____ solution because it _____.
ANSWER:
hypotonic ... is turgid hypotonic ... lysed hypertonic ... lysed hypertonic ... gained water hypertonic solution ... lost water
Correct A cell will lose water when placed in a hypertonic solution.
Building Vocabulary: Water Balance in Cells Can you match these three tonicity terms with their descriptions?
Part A Drag the terms on the left to the appropriate blanks to complete the sentences. Terms can be used more than once. ANSWER:
Reset
hypotonic
1. The ideal osmotic environment for an animal cell is a(n) isotonic
environment.
isotonic 2. An animal cell placed in a(n) hypotonic hypertonic
solution will gain water, swell, and
possibly burst. 3. There is a net diffusion of water out of an animal cell when it is placed in a(n) hypertonic
solution.
4. The ideal osmotic environment for a plant cell is a(n) hypotonic
5. A plant cell placed in a(n) hypertonic
solution will be flaccid (limp).
Correct
Activity: Active Transport
Click here to complete this activity. Then answer the questions.
Part A Which of these statements is TRUE with regard to this animation? ANSWER:
Potassium ions are transported down their concentration gradient. The cell is not expending energy. The cell does not expend ATP. Sodium and potassium ions are transported against their concentration gradients. Sodium ions are transported down their concentration gradient.
environment.
solution will lose water and plasmolyze.
6. A plant cell surrounded by a(n) isotonic
Help
Correct Energy in the form of ATP is required for the sodium-potassium pump to pump both sodium and potassium ions against their concentration gradients. Three positively charged sodium ions are exchanged for two positively charged potassium ions. Thus, the cell experiences a net loss of positive ions.
BioFlix Activity: Membrane Transport -- Active Transport Certain molecules cross the plasma membrane through the process of active transport. Active transport requires an input of energy and moves molecules against their concentration gradient. To review the process of active transport, watch this BioFlix animation: Active transport.
Part A - Active transport Drag the labels to their appropriate locations on the diagram. ANSWER: Reset
Side with lower concentration of square molecules
Transport protein
Energy input from the cell
Plasma membrane
Side with higher concentration of square molecules
Correct
Activity: Exocytosis and Endocytosis
Click here to complete this activity.
Help
Then answer the questions.
Part A Endocytosis moves materials _____ a cell via _____. ANSWER:
out of ... diffusion into ... facilitated diffusion out of ... membranous vesicles into ... a transport protein into ... membranous vesicles
Correct The prefix "endo-" means "inward."
Part B You can recognize the process of pinocytosis when _____.
ANSWER:
a receptor protein is involved the cell is engulfing a large particle the cell is engulfing extracellular fluid
Correct Pinocytosis is "cell drinking."
Part C A white blood cell engulfing a bacterium is an example of _____. ANSWER:
receptor-mediated endocytosis pinocytosis phagocytosis exocytosis facilitated diffusion
Correct Phagocytosis occurs when a cell engulfs a large particle.
BioFlix Activity: Membrane Transport -- Exocytosis and Endocytosis
Some large molecules move into or out of cells by exocytosis or endocytosis. To review these processes, watch this BioFlix animation: Exocytosis and Endocytosis.
Part A - Exocytosis and endocytosis Drag the correct label under each diagram. ANSWER:
Reset
Exocytosis
Correct
BioFlix Activity: Membrane Transport -- Vocabulary Review Can you match the processes involved in membrane transport to their descriptions? To review the processes involved in membrane transport, watch this BioFlix animation: Membrane Transport.
Part A - Vocabulary review Drag the labels onto the chart to match each process with its description. ANSWER:
Endocytosis
Help
Reset
Exocytosis
Correct
Score Summary: Your score on this assignment is 100%. You received 9 out of a possible total of 9 points.
Facilitated Diffusion
Endocytosis
Diffusion
Active Transport
Help...
Similar Free PDFs
Chapter 8-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 22 Pages

Chapter 8-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 15 Pages

Chapter 3-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 17 Pages

Chapter 7-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 17 Pages

Chapter 9-01 - Pearson Homework
- 17 Pages
Chapter 5-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 13 Pages

Chapter 5-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 16 Pages

Chapter 13-01 - Pearson Homework
- 14 Pages

Chapter 7-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 18 Pages

Chapter 9-02 - Pearson Homework
- 12 Pages

Chapter 10-03 - Pearson Homework
- 8 Pages

Chapter 10-02 - Pearson Homework
- 12 Pages

Chapter 6-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 14 Pages

Chapter 10-01 - Pearson Homework
- 20 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu

