Chapter 6-01 - Pearson - Homework PDF

| Title | Chapter 6-01 - Pearson - Homework |
|---|---|
| Course | Biological Principles For Non-Majors |
| Institution | Broward College |
| Pages | 14 |
| File Size | 773.7 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 84 |
| Total Views | 144 |
Summary
Pearson - Homework...
Description
Chapter 6-01 Due: 10:59pm on Tuesday, November 30, 2021 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy
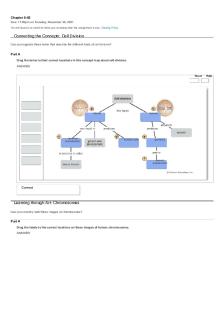
Learning through Art: Nutrient Cycling and Energy Flow in Ecosystems Can you label this diagram showing how nutrients and energy flow in an ecosystem?
Part A First drag the blue labels to their correct locations. Then drag the pink labels to their correct locations to show how O2 and CO2 cycle in the ecosystem. ANSWER: Reset
sunlight
heat producers
Correct
BioFlix Quiz: Cellular Respiration Watch the animation before answering the questions.
chemical energy
consumers
Help
Part A Select the correct sequence of steps as energy is extracted from glucose during cellular respiration.
Hint 1. Think about the order of the steps in the Cellular Respiration Road Map Tutorial.
ANSWER:
citric acid cycle → electron transport chain → glycolysis → acetyl CoA acetyl CoA → citric acid cycle → electron transport chain → glycolysis electron transport chain → citric acid cycle → glycolysis → acetyl CoA glycolysis → citric acid cycle → acetyl CoA → electron transport chain glycolysis → acetyl CoA → citric acid cycle → electron transport chain
Correct Glycolysis produces pyruvic acid, which enters the mitochondrion. There, it is converted to acetyl CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle. Electron carriers bring electrons from the first three steps to the electron transport chain, and ATP is made.
Part B What is the correct general equation for cellular respiration?
Hint 1. C6H12O6 is the chemical formula for glucose, a fuel molecule that we break down in cellular respiration for energy.
ANSWER:
6 O2 + 6 H2O + ATP energy → C6H12O6 + 6 CO2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP energy C6H12O6 + 6 H2O → 6 CO2 + 6 O2 + ATP energy C6H12O6 + 6 CO2 → 6 O2 + 6 H2O + ATP energy
Correct Cellular respiration extracts energy from glucose (C6H12O6) to produce smaller energy packets (ATP).
Part C Which of the following processes takes place in the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell?
Hint 1. The cytosol is the fluid that is inside the cell but outside the organelles. Think about the process that took place in the cytosol in the Cellular Respiration Animation.
ANSWER:
electron transport chain ATP production by ATP synthase acetyl CoA formation citric acid cycle glycolysis
Correct Glycolysis, the breakdown of glucose into two molecules of pyruvic acid, takes place in the cytosol, outside the mitochondria.
Part D In what organelle would you find acetyl CoA formation, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain?
Hint 1. Think about where these processes occurred in the Cellular Respiration Animation.
ANSWER:
lysosome Golgi apparatus mitochondrion nucleus chloroplast
Correct All of the steps of cellular respiration except glycolysis take place in the mitochondrion.
Part E Which statement describes glycolysis?
Hint 1. Review your Study Sheet or the Summary Tutorial for Cellular Respiration.
ANSWER:
This process produces some ATP and carbon dioxide in the mitochondrion. This process splits glucose in half and produces 2 ATPs for each glucose. This process joins 2 pyruvic acid molecules into a molecule of glucose. This process converts pyruvic acid to acetyl CoA. This process uses energy captured from electrons flowing to oxygen to produce most of the ATPs in cellular respiration.
Correct In glycolysis, glucose is split into two molecules of pyruvic acid. The released energy is stored in ATP and the electron carrier NADH.
Part F
Which statement describes the citric acid cycle?
Hint 1. Review your Study Sheet or the Summary Tutorial for Cellular Respiration.
ANSWER:
This process uses energy captured from electrons flowing to oxygen to produce most of the ATPs in cellular respiration. This process converts pyruvic acid to acetyl CoA. This process splits glucose in half and produces 2 ATPs for each glucose. This process produces some ATP and carbon dioxide in the mitochondrion. This process joins 2 pyruvic acid molecules into a molecule of glucose.
Correct The citric acid cycle breaks down carbon molecules, releasing carbon dioxide and forming some ATP.
Part G Which statement describes the electron transport chain?
Hint 1. Review your Study Sheet or the Summary Tutorial for Cellular Respiration.
ANSWER:
This process joins 2 pyruvic acid molecules into a molecule of glucose. This process splits glucose in half and produces 2 ATPs for each glucose. This process uses energy captured from electrons flowing to oxygen to produce most of the ATPs in cellular respiration. This process produces some ATP and carbon dioxide in the mitochondrion. This process converts pyruvic acid to acetyl CoA.
Correct In the electron transport chain, electrons move from one electron carrier to another, eventually reaching oxygen. The released energy is used to make ATPs.
BioFlix Activity: Cellular Respiration – Cell Work Do you know how cells use energy-rich molecules? To review cellular respiration, watch this BioFlix animation: Cellular Respiration.
Part A - Fuel for cellular respiration Which of the following molecules is broken down in cellular respiration, providing fuel for the cell? ANSWER:
Correct
Part B - Energy for cell work Which energy-rich molecule produced by cellular respiration directly powers cell work? ANSWER:
Correct
BioFlix Activity: Cellular Respiration -- Food as Fuel Can you identify how food relates to cellular respiration? To review cellular respiration, watch this BioFlix animation: Cellular Respiration.
Part A - How food fuels cellular respiration Drag the labels onto the flowchart to indicate how food molecules reach the body’s cells and fuel cellular respiration. Start with the ingestion of food on the left. ANSWER:
Reset
Eating food provides fuel and building blocks for your body.
After food is broken down in the digestive system, it is transported to cells via the circulatory system.
Fuel molecules are broken down further in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle (also called the Krebs cycle).
Correct
BioFlix Activity: Cellular Respiration -- The Stages Can you identify the stages of cellular respiration? To review the stages of cellular respiration, watch this BioFlix animation: Cellular Respiration.
Part A - Stages of cellular respiration Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the stages of cellular respiration. ANSWER:
ATP is produced with the help of the electron transport chain.
Help
Reset
Glycolysis
Citric Acid Cycle
Help
Electron Transport
Correct
MP3 Tutor Session: Cellular Respiration Part 1 - Glycolysis Click the image below to listen to the MP3 Tutor Session. You can also download the MP3 or view the text of the tutor session to read while you are listening. Estimated time: 8 minutes, 52 seconds. After you have listened to the tutor session, answer the questions.
Part A Cellular respiration requires fuel (glucose) and oxygen gas. The main process that produces these inputs is _____. ANSWER:
photosynthesis glycolysis electron transport the Citric Acid cycle
Correct
Part B Which part(s) of cellular respiration require(s) oxygen gas? ANSWER:
the Citric Acid cycle the electron transport chain glycolysis a, b, and c a and b, but not c
Correct
Part C What is/are the most important output(s) of glycolysis? ANSWER:
two net ATP molecules four net ATP molecules two pyruvic acid and two NADH molecules carbon dioxide one glucose molecule
Correct
Part D Unlike the Citric Acid cycle and electron transport, glycolysis occurs _____. ANSWER:
in the cytoplasm directly on the surface of the mitochondrial membrane within the mitochondrial membrane within the cell nucleus
Correct
Part E Glycolysis is the multi-step breakdown of _____. Several different _____ play a role in this process. ANSWER:
pyruvic acid ... sugars glucose ... enzymes ATP ... complex carbohydrates glucose ... organelles
Correct
MP3 Tutor Session: Cellular Respiration Part 2 - Citric Acid and Electron Transport Chain Click the image below to listen to the MP3 Tutor Session. You can also download the MP3 or view the text of the tutor session to read while you are listening. Estimated time: 11 minutes, 57 seconds. After you have listened to the tutor session, answer the questions.
Part A Which part(s) of cellular respiration take(s) place in the mitochondria? ANSWER:
the Citric Acid cycle glycolysis the electron transport chain the Citric Acid cycleand the electron transport chain All of the above.
Correct
Part B What is the role of oxygen in cellular respiration? ANSWER:
Oxygen provides high-energy electrons for transfer to glucose. Oxygen accepts high-energy electrons after they are stripped from glucose. Oxygen is required to convert ADP to ATP. Oxygen is involved in the initial breakdown of glucose to pyruvic acid.
Correct
Part C Cellular respiration accomplishes two major processes: (1) it breaks glucose down into smaller molecules, and (2) it harvests the chemical energy released and stores it in ATP molecules. By the end of _____, the breakdown of glucose is complete; most ATPmolecules are produced during _____. ANSWER:
glycolysis ... the Citric Acid cycle the Citric Acid cycle ... glycolysis the Citric Acid cycle ... electron transport electron transport ... glycolysis
Correct
Part D NADH and FADH 2 are important in cellular respiration because they deliver high-energy electrons to the electron transport system. Electron transport produces _____ ATP molecule(s) per NADH molecule and _____ ATP molecules(s) perFADH 2 molecule. ANSWER:
three ... two two ... three one ... one zero ... zero
Correct
Part E In electron transport, high-energy electrons "fall" to oxygen through a series of reactions. The energy released is used to _____. ANSWER:
synthesize ATP directly. transport protons into the intermembrane space of the mitochondria, where they become concentrated. They then flow back out into the the inner compartment (matrix) of the mitochodria. On the way back, protons turn ATP synthase turbines and produce ATP. transport electrons out of the mitochondria, resulting in ATP production. move phosphate groups into the mitochondria. When they reach a high enough concentration, they spontaneously join with ADP to form ATP.
Correct
BioFlix Activity: Cellular Respiration -- Inputs and Outputs Can you fill in the cellular respiration equation? To review cellular respiration, watch this BioFlix animation: Cellular Respiration.
Part A - Cellular respiration equation Drag the labels onto the equation to identify the inputs and outputs of cellular respiration. ANSWER:
Reset
Correct
Activity: Fermentation
Click here to complete this activity. Then answer the questions.
Part A In muscle cells, fermentation produces _____. ANSWER:
pyruvate lactate and NADH lactate and NAD+ carbon dioxide, ethanol, NAD+, and ATP carbon dioxide, ethanol, NADH, and ATP
Help
Correct These are the products of fermentation as it occurs in muscle cells.
Learning through Art: Organic Molecules as Fuel for Cellular Respiration Can you label these components of pathways that break down various food molecules?
Part A Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in this diagram of pathways that break down organic molecules. ANSWER: Reset
carbohydrates
fats
Help
proteins
fatty acids
amino acids
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
ATP
Correct
Interpreting Data: Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) The basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the amount of energy that must be consumed by a person at rest to maintain his or her body weight. BMR depends on several factors, including sex, age, height, and weight. This graph shows the BMR for a 6-foot tall 45-year-old male.
Part A - Interpreting the graph How many more calories would a 240-pound man need to consume than a 170-pound man to maintain a constant weight? ANSWER:
70 calories 100 calories 300 calories 2000 calories
Correct According to the graph, the BMR for a 240-pound man is 2000 calories, while the BMR for a 170-pound man is 1700 calories. By subtracting 1700 from 2000, you can determine that the difference in caloric needs between the two men is 300 calories.
Part B - Thinking critically Which two statements about basal metabolic rate are true? ANSWER:
If all other factors are identical, a person who weighs more will have a higher BMR than a person who weighs less. Basal metabolic rate includes the energy consumed by the body during cellular respiration. The basal metabolic rate determines exactly how many calories to consume each day. If you exercise vigorously, you will need to consume fewer calories than your BMR suggests to maintain a constant weight. If you lose weight, your BMR will not change.
Correct The graph shows a positive correlation between BMR and weight. That is, as weight increases, the BMR also increases. BMR depends on weight because many of the energy-consuming processes that take place in the body (moving muscles, thermoregulation to maintain a constant body temperature, etc.) require more energy for a larger body to accomplish.
Identifying Major Themes – Chapter 6
Part A Can you identify the major theme illustrated by each of the following examples? If necessary, you may review the themes in Chapter 1 of your book. Match the themes on the left with the examples on the right. Not all themes will be used.
ANSWER:
Reset
Help
For many endurance athletes, the rate at which oxygen is provided from the lungs, to the blood, to Information flow
working muscles, is the limiting factor in their performance. Interactions within biological systems
The fact that glycolysis occurs in almost all organisms suggests that it was used by very early ancestors common to all the domains of life. Evolution The inner membrane of a mitochondrion is folded within the outer membrane. The space between the membranes acts as a temporary reservior for hydrogen ions, which cannot pass through the membranes. Relationship of structure to function
Electrons captured from food by the NADH formed in the first two stages of electron transport are stripped of their energy, a little bit at a time, until they are finally combined with oxygen to form water. Pathways that transform energy and matter
Correct As you become skilled at identifying themes, your thinking about biology will become more sophisticated.
Score Summary: Your score on this assignment is 99.4%. You received 9.94 out of a possible total of 10 points....
Similar Free PDFs
Chapter 8-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 22 Pages

Chapter 8-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 15 Pages

Chapter 3-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 17 Pages

Chapter 7-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 17 Pages

Chapter 9-01 - Pearson Homework
- 17 Pages
Chapter 5-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 13 Pages

Chapter 5-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 16 Pages

Chapter 13-01 - Pearson Homework
- 14 Pages

Chapter 7-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 18 Pages

Chapter 9-02 - Pearson Homework
- 12 Pages

Chapter 10-03 - Pearson Homework
- 8 Pages

Chapter 10-02 - Pearson Homework
- 12 Pages

Chapter 6-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 14 Pages

Chapter 10-01 - Pearson Homework
- 20 Pages

P141 - Pearson
- 1 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu
