Chapter 9-01 - Pearson Homework PDF

| Title | Chapter 9-01 - Pearson Homework |
|---|---|
| Course | Biological Principles For Non-Majors |
| Institution | Broward College |
| Pages | 17 |
| File Size | 1 MB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 107 |
| Total Views | 159 |
Summary
Pearson Homework...
Description
Chapter 9-01 Due: 11:59pm on Tuesday, November 30, 2021 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy
Building Vocabulary: Mendelian Genetics Can you match each genetics term with its description?
Part A Drag the terms on the left to the appropriate blanks on the right to complete the sentences. ANSWER:
Reset
1. A character
2. A trait
Help
is an inherited feature that varies from individual to individual.
is one particular variation of a character.
3. A genetic cross involving parents that differ in a single character is called a monohybrid cross .
4. Most human genes come in alternate versions called alleles .
5. If an organism has two non-identical versions of a gene, the one that is expressed in the organism is called the dominant
allele.
6. If an organism has two non-identical versions of a gene, the one that is not expressed in the organism is called the recessive
allele.
7. The physical traits of an organism are called its phenotype .
8. The genotype
Correct
Figure Walkthrough: The Law of Segregation Watch this video and then answer the questions.
Part A
is the genetic makeup of an organism.
The figure illustrates the law of genetic segregation. Can you identify the processes and F2 genotypes? Drag the labels to their appropriate locations on the figure. Labels of Group 1 represent genotypes, and labels of Group 2 represent processes. ANSWER: Reset
Help
Alleles segregate in meiosis
Fertilization Fertilization Alleles segregate in meiosis Alleles segregate in meiosis
pp
Pp Fertilization PP
PP
Pp
Pp
pp
Answer Requested
Part B Crossing a plant with white flowers and a plant that is homozygous for purple flowers results in offspring with what color combinations? ANSWER:
Approximately 3/4 will have purple flowers, and 1/4 will have white flowers. Half will have white flowers, and half will have purple flowers. The ratios cannot be predicted because the genotype of the plant with white flowers is unknown. All flowers will be purple.
Correct All of the offspring will have the heterozygous genotype and the dominant phenotype.
Part C Can two plants with purple flowers produce offspring with white flowers? ANSWER:
Yes, if both parents are heterozygous for the trait. No, the only way to be purple is to be homozygous dominant. Yes, the plant with white flowers could be heterozygous recessive. No, because purple is dominant.
Correct If both parents are heterozygous for the trait, you would expect approximately 1/4 of the offspring to be white.
MP3 Tutor Session: Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Click the image below to listen to the MP3 Tutor Session. You can also download the MP3 or view the text of the tutor session to read while you are listening. Estimated time: 7 minutes, 51 seconds. After you have listened to the tutor session, answer the questions.
Part A Mendel formulated his principles of inheritance based on _____. ANSWER:
a detailed understanding of meiosis, fertilization, and the other chromosomal processes that are involved. observations on the outcomes of breeding experiments. The underlying processes were unknown at the time. little-known works by earlier scientists. existing knowledge of chromosomal processes that he combined with insights from his own breeding experiments.
Correct
Part B Mendel observed that pairs of alleles were separated or segregated in gametes and that they were rejoined in fertilization. We know that pairs of _____ are segregated in _____ and then are rejoined through fertilization. ANSWER:
linked genes ... meiosis homologous chromosomes ... crossing over homologous chromosomes ... meiosis gametes ... meiosis
Correct
Part C As we now understand it, the Law of Independent Assortment applies _____. ANSWER:
to all pairs of genes to pairs of genes that are on different chromosomes, but NOT to pairs of genes that are close together on the same chromosome only to pairs of genes that are close together on the same chromosome only to sex-linked genes
Correct
Part D If you are a male, the Law of Independent Assortment indicates that your gametes contain _____. ANSWER:
only the chromosomes and alleles you inherited from your father only the chromosomes you inherited from your father, although some of the alleles you inherited from your mother may have been spliced in through recombination a random mix of the chromosomes you inherited from each parent only the chromosomes and alleles you inherited from your mother
Correct
Part E How have Mendel's laws fared as we have learned more about cell biology and processes such as meiosis? ANSWER:
Our new knowledge has confirmed all of Mendel's predictions and laws. Our new knowledge has led to the rejection of all of Mendel's laws. Our new knowledge shows that the Law of Segregation is incorrect, but it has proved the Law of Independent Assortment to be valid. Our new knowledge has helped to explain some of the exceptions to Mendel's laws of inheritance.
Correct
Activity: Monohybrid Cross
Click here to complete this activity. Then answer the questions.
Part A
The result of the following cross indicates the orange eyes are _____ black eyes. ANSWER:
dominant to incompletely dominant to recessive to co-dominant to larger than
Correct The result of this cross indicates that both parents are heterozygous for eye color.
Part B If B represents the allele for black eyes (dominant) and b represents the allele for orange eyes (recessive), what would be the genotypic ratio of a cross between a heterozygous black-eyed MendAlien and an orange-eyed MendAlien? ANSWER:
2 homozygous black (BB): 1 heterozygote (black) (Bb): 1 homozygous orange (bb) 0 homozygous black (BB): 0 heterozygote (black) (Bb): 1 homozygous orange (bb) 0 homozygous black (BB): 1 heterozygote (black) (Bb): 1 homozygous orange (bb) 1 homozygous black (BB): 1 heterozygote (black) (Bb): 1 homozygous orange (bb) 1 homozygous black (BB): 0 heterozygote (black) (Bb): 1 homozygous orange (bb)
Correct The heterozygous black-eyed MendAlien has the genotype Bb. The orange-eyed MendAlien has the genotype bb. The result of this cross is two Bb offspring and two bb offspring. This 2:2 ratio reduces to 1:1.
Part C If B represents the allele for black eyes (dominant) and b represents the allele for orange eyes (recessive), what would be the phenotypic ratio of a cross between a heterozygous black-eyed MendAlien and an orange-eyed MendAlien? ANSWER:
1 black : 3 orange 1 black : 1 orange 0 black : 1 orange 3 black : 1 orange 1 black : 0 orange
Correct The heterozygous black-eyed MendAlien has the genotype Bb. The orange-eyed MendAlien has the genotype bb. The result of this cross is two Bb offspring and two bb offspring. This means that two of the offspring have black eyes and two of the offspring have orange eyes. This 2:2 ratio then reduces to 1:1.
Part D
The result of the following cross indicates that the genotype of the female parent is _____. ANSWER: B Bb BB bb b
Correct The result of this cross indicates that the flat headtop allele is dominant to the wild-type headtop. Thus, the only way to express a wild-type headtop is to be homozygous recessive.
Part E
The result of the following cross indicates that the genotype of the male parent is _____. ANSWER:
BB Bb bb b B
Correct Since all of the offspring have flat headtops, it is reasonable to conclude that the allele for flat headtop is dominant to the wild-type headtop allele.
Part F
The result of the following cross indicates that genotypically the offspring _____. ANSWER:
exhibit a 1 BB : 2 Bb : 1 bb ratio are all bb are all Bb are all BB exhibit a 3 BB : 1 bb ratio
Correct This cross indicates that the flat headtop allele is dominant to the wild-type headtop allele, so all offspring are indeed Bb.
Part G Which of these is a testcross? ANSWER:
aa x aa A? x A? A? x AA A? x Aa A? x aa
Correct A testcross is used to determine whether an individual expressing the dominant phenotype is homozygous dominant or heterozygous.
Part H
That each gamete contains a single allele of the eye color gene is an illustration of _____. ANSWER:
Darwin's theory of natural selection Mendel's law of independent assortment only Both Mendel's law of segregation and Mendel's law of independent assortment. Mendel's law of segregation only Beadle and Tatum's one gene - one enzyme hypothesis
Correct Mendel's law of segregation is based on gametes getting only one copy of each allele of each gene.
Learning through Art: Monohybrid Cross Can you correctly label the genotypes and phenotypes in this Punnett square of a monohybrid cross?
Part A Mendel discovered that the allele for green seed pods (G) is dominant to the allele for yellow seed pods (g). He crossed true-breeding (homozygous) parental plants with green (GG) and yellow (gg) seed pods to produce an F1 generation, all of which were heterozygous (Gg) with green seed pods. He then crossed two of these F1 plants to produce an F2 generation. Drag the genotypes and phenotypes from the left to correctly complete the Punnett square for the F2 generation. Drag only blue labels to blue targets and pink labels to pink targets. Labels may be used more than once. ANSWER:
Reset
GG
Gg GG
Gg
Gg
gg
gg
Correct
Activity: Dihybrid Cross
Click here to complete this activity. Then answer the questions.
Part A What is the genotype of the parent with orange eyes and white skin? (Note: orange eyes are recessive.)
ANSWER:
Help
BBGG bbGG bbGg bbgg BbGg
Correct This result of the cross indicates that both orange eyes and white skin are recessive.
Part B Black eyes are dominant to orange eyes, and green skin is dominant to white skin. Sam, a MendAlien with black eyes and green skin, has a parent with orange eyes and white skin. Carole is a MendAlien with orange eyes and white skin. If Sam and Carole wereto mate, the predicted phenotypic ratio of their offspring would be _____. ANSWER:
1 black eyes, green skin : 1 black eyes, white skin : 1 orange eyes, green skin : 1 orange eyes, white skin 1 black eyes, green skin : 3 black eyes, white skin : 3 orange eyes, green skin : 9 orange eyes, white skin 9 black eyes, green skin : 3 black eyes, white skin : 3 orange eyes, green skin : 1 orange eyes, white skin 3 black eyes, green skin : 3 black eyes, white skin : 9 orange eyes, green skin : 1 orange eyes, white skin There is insufficient information to determine Sam's genotype.
Correct Sam's genotype is BbGg, and Carole's genotype is bbgg.
Part C In order to determine the genotype of a MendAlien with black eyes and green skin, you would cross this individual with a(n) _____ individual. ANSWER:
BBGG bbGG bbgg BBgg BbGg
Correct This is an extension of the single character testcross you worked with in the activity on monohybrid crosses.
Part D A cross between two individuals with black eyes and green skin which results in an individual with orange eyes and white skin is an example of a _____ cross. ANSWER:
dihybrid trihybrid difficult test monohybrid
Correct The cross is examining two characters.
Part E A phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 in the offspring of a cross indicates that _____. ANSWER:
one parent is homozygous dominant and one parent is heterozygous one parent is homozygous dominant and one parent is homozygous recessive both parents are homozygous dominant one parent is heterozygous and one parent is homozygous recessive both parents are heterozygous for both genes
Correct Such a result indicates that the genes assort independently and that, for each gene, the alleles exhibit a dominant/recessive relationship.
Part F The observed distribution of alleles into gametes is an illustration of _____.
ANSWER:
Mendel's law of independent assortment only Thienemann's rule Eimer's principle Mendel's law of segregation only Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment
Correct The events seen here illustrate both the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment.
Part G An individual heterozygous for eye color, skin color, and number of eyes mates with an individual who is homozygous recessive for all three characters; what would be the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? [Hint: B = black eyes, b = orangeeyes; G = green skin, g = white skin; C = two eyes, c = one eye]
ANSWER:
9 black eyes, green skin, two eyes : 3 black eyes, green skin, one eye : 3 black eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, white skin, one eye : 9 orange eyes, green skin, two eyes : 3 orange eyes, green skin, one eye : 3 orange eyes, white skin, twoeyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, one eye 9 black eyes, green skin, two eyes : 3 black eyes, green skin, one eye : 3 black eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, white skin, one eye 1 black eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, green skin, one eye : 1 black eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, one eye 9 orange eyes, green skin, two eyes : 9 orange eyes, green skin, one eye : 9 orange eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, one eye 1 black eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, green skin, one eye : 1 black eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, white skin, one eye : 1 orange eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, green skin, one eye : 1 orange eyes, white skin, twoeyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, one eye
Correct This is a tough problem; you had to expand your Punnett square to accommodate another character. However, 1:1:1:1:1:1:1:1 ratio is the expected outcome of a BbGgCc x ooggcc cross.
Part H A BbGg x bbgg cross yields a phenotypic ratio of approximately 5 black eyes, green skin : 5 orange eyes, white skin : 1 black eyes, white skin : 1 orange eyes, green skin. Which of the following best explains these results? ANSWER:
The heterozygous individual is male, and the homozygous individual is female. The genes for eye color and skin color are co-dominant. Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment are being violated. Mendel's law of segregation is being violated. Mendel's law of independent assortment is being violated.
Correct If the genes for eye color and skin color assorted independently, then the outcome of this cross would have been a 1:1:1:1 ratio.
Part I In the following cross the genotype of the female parent is BbGg. What is the genotype of the male parent? [Hint: B = black eyes, b = orange eyes, G = green skin, g = white skin]
ANSWER:
BBGg BbGG BbGg BBGG bbGG
Correct All of the offspring have black eyes, and there is a 3:1 ratio of skin color.
Part J In a situation in which genes assort independently, what is the ratio of the gametes produced by an AaBB individual? ANSWER:
1A:1B 3A:1B 3 AA : 1 BB 3 AB : 1 ab 1 AB : 1 aB
Correct This is the correct ratio of gametes.
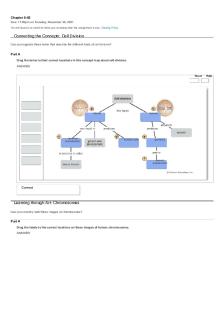
Connecting the Concepts: Genetics Concept Map Can you correctly organize these terms associated with Mendelian genetics?
Part A Drag the terms to their correct locations in this concept map. ANSWER:
Reset
Help
chromosomes
genes
alleles
homozygous
heterozygous
dominant
sex-linked traits
Correct
Building Vocabulary: Chromosome Structure Can you place each word in the appropriate sentence?
Part A Drag the terms on the left to the appropriate blanks on the right to complete the sentences. Not all terms will be used. ANSWER:
Reset
1. DNA and protein together form a complex called chromatin .
2. Chromosomes contain most of the cell's DNA
which acts as the molecule of heredity.
3. Before a cell divides, it copies all of its chromosomes. While the two copies of a chromosome are attached they are called sister chromatids . 4. A duplicated chromosome remains tightly paired with its partner at a region called the centromere . microtubules protein
5. The DNA of every eukaryotic cell is stored in one or more chromosomes nucleus .
located in the
Help
Correct
Learning through Art: Genes and Chromosomes Can you label these chromosomes with the correct genetic terms?
Part A Drag the terms to their correct locations on the figure below. ANSWER:
Reset
homologous chromosomes
dominant allele
Help
gene locus
recessive allele
alleles
centromere
sister chromatids
Correct
Learning through Art: Human Pedigree Analysis Can you identify the genotypes in this human pedigree for deafness?
Part A The human pedigree shown here is for an inherited form of deafness caused by a recessive allele (d). Drag the labels to the pedigree to identify the genotypes of individual family members. If you can't tell with certainty whether an individual is homozygous dominant or heterozygous for the trait, place the label "DD or Dd" in that box. ANSWER:
Reset
Help
Dd
Dd
DD
DD or Dd
DD or Dd
DD or Dd
dd
DD or Dd
dd
dd
Correct
Interpreting Data: Inheritance Patterns As shown in this Punnett square, one variety of deafness in humans is caused by an autosomal recessive allele (d). Two parents who do not show any signs of the disease but are carriers (Dd) could therefore have a child who is deaf, because that child could inherit one recessive deafness-causing allele from each parent (dd). Parents
Hearing (Dd)
Offspring
Hearing (Dd) Sperm
Eggs
D
d
D
DD Hearing
Dd Hearing (carrier)
d
Dd Hearing (carrier)
dd Deaf
Part A - Interpreting Punnett squares Imagine that a deaf male has a child with a hearing female. You know that the male must have the genotype dd, but the female could be either Dd or DD. If the couple's first child has hearing, can you determine the mother’s genotype? (Hint: Draw Punnett squares for the two possible crosses.) ANSWER:
Her genotype must be DD. Her genotype must be Dd. Her genotype must be dd. Her genotype cannot be determined.
Correct A hearing child with a deaf father (dd) must have the genotype Dd. This means that the mother must have contributed a D allele, which would be possible if she is either DD or Dd . The mother’s genotype cannot be deduced from this child's genotype.
Part B - Thinking critically Use the Punnett square from the in...
Similar Free PDFs
Chapter 8-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 22 Pages

Chapter 8-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 15 Pages

Chapter 3-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 17 Pages

Chapter 7-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 17 Pages

Chapter 9-01 - Pearson Homework
- 17 Pages
Chapter 5-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 13 Pages

Chapter 5-02 - Pearson - Homework
- 16 Pages

Chapter 13-01 - Pearson Homework
- 14 Pages

Chapter 7-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 18 Pages

Chapter 9-02 - Pearson Homework
- 12 Pages

Chapter 10-03 - Pearson Homework
- 8 Pages

Chapter 10-02 - Pearson Homework
- 12 Pages

Chapter 6-01 - Pearson - Homework
- 14 Pages

Chapter 10-01 - Pearson Homework
- 20 Pages

PSYC 218 Syllabus 901
- 10 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu
