Mental Health SBAR Plan of Care PDF

| Title | Mental Health SBAR Plan of Care |
|---|---|
| Course | Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing of Individuals |
| Institution | The University of Texas at Arlington |
| Pages | 4 |
| File Size | 183.7 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 13 |
| Total Views | 147 |
Summary
SBar Assisngment...
Description
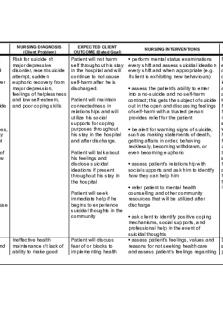
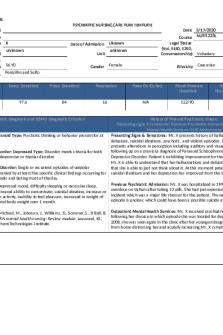
SBAR NURSING CARE PLAN Student Name: Alexander Pham Client Initials: AA Age: 14- DOB: 01/23/2007 Current issues (Chief Complaint, Precipitating Factors) Psychiatric Diagnoses: Major depressive S: disorder with increased levels of anxiety Situation aggravated from environmental stressors. The chief complaint was described as having suicidal ideations as evidenced by holding a knife close to the Medical Problems: history of autism and abdomen for two minutes but did not follow through with also experiences alcohol, nicotine, and puncturing through the skin. The girlfriend was the person cannabis use disorder that adds on to the who made the call for the police to show up when he was patient’s physical symptoms of the experiencing this episode. psychiatric diagnose. B: Background
Psychosocial/Environmental History (Predisposing Factors): Family history of mental illness but states, “I do not know exactly what they are called but they are related to drug abuse.” Neurological / Genetic History (Predisposing Factors): The client stated that the environmental factors of living situation, family relationships, and availability of substances subject to abuse, are predisposing factors to the diagnoses. Patient states, “I started drinking alcohol when I was 12, then smoked cigarettes and cannabis when I was about 14.”
A: Assessment
Mental Status Assessment Appearance: Dress is appropriate for age, red hair that is messy but grooming overall adequate for situation. Behavior: Able to maintain eye contact with normal mannerisms, body is erect with no signs of slumping of the shoulders. Speech: Normal volume and rate of speech that is clear and with precise tone. Mood: Normal mood at the moment that question was asked but patient stated feelings of worthlessness two days ago as evidenced by stating, “I sometimes don’t have the energy that I was had before.” Affect: No negative emotions or mood noted, client was cooperative and able to answer questions in a professional manner. Cognition: “alert and oriented x 4-, short- and long-term memory appropriate, abstract ability present. Thought Process: clear, consistent and linear. No flight of ideas when not under the influence, the client confirms this by saying that “I need to maintain and really take my sobriety serious if I want to actually feel better.” Thought Content: Patient’s thought content is consistent with the context of conversation. No thoughts of suicidal or homicidal ideations at the time question was asked, the client does place blame on himself many times by restating that, “the reason that I am here was because I wanted to commit suicide.” Perceptual Disturbances: Patients reports no perceptual audible or visual disturbances. Insight/Judgment: Good insight and judgement but dependent on willingness to maintain the current level of sobriety. Suicide ideation: Patients reports history of suicidal ideation as reason for admission. Reports no current suicidal ideation. Prior SI included the plan of inflicting physical harm first through the head smashing with various objects, then followed by puncturing the abdominal wall with a knife. Homicide ideation: No homicidal ideation; patient denies having HI Aggression: precautions placed for increased levels of aggression related to physical symptoms of depression and increased levels of anxiety aggravated by certain stressors. Psychosis: No evidence of psychosis noted. Falls: Patient reports no issues with falls. Staff have no noted fall risk measure implemented. Substance use: the client is a chronic alcohol, nicotine, and cannabis user due to availability and environment within the household in which he grew up, this knowledge and accessibility is one of the
1
reasons why he is so dependent on these drugs. Maslow Hierarchy of Needs/Rational (top 2 priorities) 1. Safety: “Do you have any thoughts of killing yourself or the want to harm anyone else around you?” 2. Willingness to comply to care plan: “What are some goals that you have for today?” 3. The patient responded to this patient with the following, “I want to practice my coping skills that I have learned but I want to cope, I do not think that they work.” 4. In response to this I said, “you mentioned earlier that deep breathing helped you at moments, could you show me how you do it exactly?” and followed up with proving additional teaching on other methods to cope with stress. Current Medications (Include Therapeutic & Side Effects) 1. This client is currently not taking any medications and is not on any medications prior to this admission, this is evidenced by the client’s chart. One of the care plan interventions consisted of starting the client on Wellbutrin 100 mg po daily, as indicated for the psychiatric diagnoses. 2. The patient denies any major side effects experienced; however, complains of slightly having less energy and temporary loss of appetite. 3. The client also mentions ibuprofen a couple times was taken due to his physical injury that was experienced at home. Current Psychiatric Therapies: 1. Check on the client every 15 minutes or as needed upon the willingness of the patient and how much they want to talk. 2. Client to be started on Wellbutrin 100 mg po daily as indicated for diagnoses and continued monitoring of the client for any signs of an adverse reaction. 3. The family psych educated about the risk of substance use and how it links to the client’s suicidal ideations.
R: Recommended Actions
1.Priority Problem Statement/Nursing Diagnosis Risk for suicide related to feelings of worthlessness AEB decreased energy levels and from the client stating, “suicidal ideations was the reason for admittance.” Smart Goals: S/T: Patient will remain safe throughout my shift. L/T: Patient will display understanding of coping methods at time of discharge. Nursing Interventions S/T : “Nurse will closely monitor the patient and offer to talk with the client when the needs arise with the frequency be at least every 15 minutes/” 1. “Nurse will review coping strategies and the medication with client as well as the client’s family.” 2. “Nurse should ask the client to display one of the coping skills learned through group sharing to evaluate the effectiveness of patient education.”
2. Problem Statement /Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective coping related to environmental stressors of nicotine, alcohol, and cannabis use AEB patient being extremely hard on himself by once again restating the fact that, “I am here because I tried to commit suicide. I feel so stupid for doing that. I don’t know what I was thinking.” Smart Goals: S/T: “Patient will learn at least 1 effective coping method that he can use correctly during times of experiencing physical symptoms of depression.” L/T: Teach the client to notice for signs of certain stressors that can aggravate the situation. Nursing Interventions S/T 1. “Provide the patient with information on coping methods and asking the client to show the correct way of using that coping skill.” 2. “Encourage the patient to actively participate in group therapy.”
L/T
2
1. “Nurse will explore the causative factors and triggers that cause patients to have SI” and provide methods of coping such as teaching the client to verbalize certain fears associated with these thoughts and as well as practicing the skill of positive self-talk. 2. “Patient will be educated on methods of compliance with prescription medication regimens to prevent decrease in therapeutic levels, in order to subjectively state feeling better.” 3. The effectiveness of care plan and medication is dependent on the client’s willingness to accept and be consistent with the treatment plan.
L/T 1. “Teach the patient when to recognize signs of stress specific to patient.” 2. “Provide the patient with resources for support groups specific to the patient’s issue.”
Patient Teaching: Patient teaching will include methods of coping with stress specific information related to the physical symptoms of the psychiatric diagnose of major depressive disorder. Additional teaching provided to parents about how the effectiveness of the client’s individualized care plan is dependent on the client’s willingness to maintain his current status of sobriety.
Resources and/or Referrals needed: Potential referral to support groups in order continue helping the client develop more coping skills and through verbalization of positive self-talk that is exercised through the group sessions that are held. This group therapy has the foundational goal of helping the client to initiate the sense of well-being through sharing personal experiences with others, with the hopes of shared experiences between group members.
References 3
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association. Boyd, M. A. (2018). Psychiatric nursing: Contemporary practice (6th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer. Qaseem, A., et al. (2016). Nonpharmacologic versus pharmacologic treatment of adult patients with major depressive disorder: A clinical practice guideline from the American college of physicians. Annals of Internal Medicine, 164(5), 350–359. (Level I). Taylor, C., Lynn, P., & Bartlett, J. L. (2019). Fundamentals of nursing: The art and science of person-centered nursing care (9th ed.). Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Wolters Kluwer. Varcarolis, E. (2017). Essentials of psychiatric nursing: A communication approach to evidencebased care. Evolve Health Sciences.
4...
Similar Free PDFs

Mental Health SBAR Plan of Care
- 4 Pages

Mental Health Care Plan
- 8 Pages

Mental Health Clinical Care Plan
- 1 Pages
Med Sur Care plan SBAR George
- 18 Pages

History of Mental Health
- 1 Pages

Foundation of Health Care
- 13 Pages

Plan of Care: Osteoporosis
- 21 Pages

UTI Care Plan - Care Plan
- 7 Pages

Care plan 3 - Care Plan
- 3 Pages

Care Plan 1 - Care plan
- 7 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu