Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy PDF

| Title | Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy |
|---|---|
| Course | Chemistry |
| Institution | Higher School Certificate (New South Wales) |
| Pages | 1 |
| File Size | 38.5 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 23 |
| Total Views | 131 |
Summary
What is Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy?...
Description
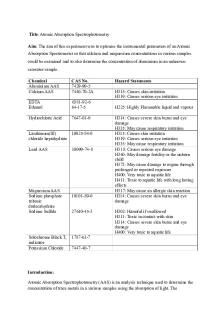
Explain how Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) works and its importance in its applications. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) is a quantitative analysis technique, used to identify the amount of an element present in a sample. This analysis technique uses the absorption of light by electrons in the sample to determine the amount of an element present in a sample of a given substance. The process of AAS uses an Atomic Absorption Spectrometer. AAS works by first selecting a certain element to analyse. After an element has been selected, a lamp made of the same element is selected. This is because the light emitted will be of a wavelength specific to the element being tested. The sample is then vaporised, changing the substance into atoms. Light is then passed through the sample, with the element being tested for, absorbing this light. This is because, the atoms which emitted the light from the lamp are of the same energy levels as the element being tested. Any other elements within the sample will be unable to absorb the light, as their energy levels are different. As the light passes through the sample, it is focused through a slit, and proceeds to enter a monochromator. The monochromator selects one wavelength of light for it to be analysed by the detector. The detector measures the intensity of the light emitted, and is displayed as a number. This number is representative of the amount of light, which has passed through the sample, without being absorbed. This value is known as the absorbance value of the element. This absorbance value allows for the determination of the amount of an element present. This is because a higher concentration of an element, will lead to more light being absorbed. Hence, less light will reach the detector, lowering the absorbance value. AAS is used widely to determine the amount of metal ions present within particular substances, especially those ions, toxic to humans. This is because particular metal ions, if ingested, can lead to severe illness, Mutations, and death. This analysis technique is highly importance as the measure of the amount of an element present within a substance can prevent negative impacts to humans. For example, aluminium within the human body can have negative effects on the individual, as this substance can cause osteoporosis, headaches, and problems with liver and kidney function. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy can be used to analyse the amount of aluminium present within sources of this substance such as deodorants, drinking water, and medication. Through AAS, the amount of aluminium present is able to be determined, thus reducing the chances of problems occurring within the human body. In addition, substances such as lead, arsenic, mercury, and cadmium are found in small amounts within the human body. This is sure to everyday contact with materials within the environment. High concentrations of these substances can have severe effects on a human being. Through AAS, the amount of these substances present within a sample can be determined. This would prevent events from occurring, in which these substances could have a negative impact on individuals. For example, if lead was leaked into a water supply, this could cause lead poisoning and could have severe negative impacts. By determining the amount of lead present within water supplies, through AAS, lead poisoning can be prevented. Therefore, AAS is a qualitative technique, which is used to determine the amount of an element present within a sample. It is highly important in its application as it can help determine the amount of a particular substance within a given sample to prevent negative impacts on humans such as Mutations, severe illness, improper liver and kidney functioning and death....
Similar Free PDFs

Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
- 271 Pages

Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
- 9 Pages

Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
- 1 Pages

Chem 1411 Atomic Spectroscopy
- 3 Pages

Spectroscopy
- 5 Pages

Mass Spectroscopy
- 14 Pages

Cour absorption
- 15 Pages

TD Absorption
- 4 Pages

Spectroscopy Lab
- 2 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu