Wk 7 - corporate lvl strategy PDF

| Title | Wk 7 - corporate lvl strategy |
|---|---|
| Author | Anaisee LJ |
| Course | Introduction to Strategic Management |
| Institution | University of Sunderland |
| Pages | 4 |
| File Size | 90.3 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 56 |
| Total Views | 157 |
Summary
corporate lvl strategy...
Description
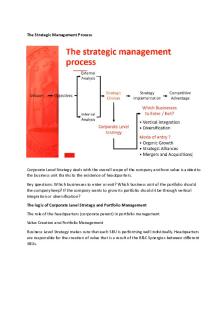
Corporate Level Strategy What is Corporate Strategy? Defines the scope of the different industries and markets the organization competes within -in order to achieve its organizational purpose “What business or businesses should we be in?” “How should we allocate resources across different businesses?”
Corporate parenting Corporate parenting (corporate headquarters)is concerned with how a parent company adds value across the businesses that make up the organization To achieve synergy –the whole is greater than the parts Corporate parent refers to all those levels of management that are not part of customer facing and profit run business units in multi-business companies Allow SBU’s to perform better collectively than they would as stand-alone units Growth Strategies Organizations can pursue number of different strategies …depending on level of risk they are willing to take on their internal resources and capabilities, and their management expertise. Ansoff (1965) suggests organizations can pursue 4 different growth strategies: The first of the 4 is an expansion of an existing business but the others probably involve new businesses.
Market penetration Increase market share in your existing markets using your existing products •Market development Entering new markets with your existing products •Product development Developing new products to sell in yourexisting markets •Diversification Developing new products to serve new markets
Related Diversification Entry into ‘Related’industry in which there is still some link with the organization’s value chain Example:
has distinctive capabilities in engine design & this capability can be applied in number of related businesses Honda Automobiles Acura Automobiles Honda Powersports HondaJet Honda Power Equipment Honda Marine Honda Engines
•‘RELATED’ Vertical integration -when an organization goes upstreami.e. it moves towards its resource inputs, or downstream; it moves closer to its ultimate consumer refining oil OR distribution i.e. retailer of fuels to customer •‘RELATED’ Horizontal integration -when an organization takes over a competitor or offers complementary products (economies of scale) at the same stage within the supply chain formed through the acquisition ofHBOSbyLloyds TSB. Unrelated Diversification Where an organization moves into a totally unrelated industry; this is sometimes called conglomerate diversification **Conglomerate**…meaning; a combination of two or more corporations engaged in entirely different businesses that fall under one corporate group
Reasons for diversification: •Existing markets are saturated or declining e.g. Tesco’s diversification into finance and insurance (and more recently into film production and in 1992; “Dobbies” garden centres •Restrictions at homemarket e.g. Tesco’s diversification into overseas markets •Too spread risk •failure of one business will not cause the company to fail •skills to manage business are common to each business; organization can leverage management skills across range of different businesses i.e. production, R&D, finance and/or retailing skills
Implementing Growth Strategies •Mergers and Acquisitions •Internal Development •Joint ventures and Strategic Alliances
Mergers and Acquisitions Merger –when two (equal) organizations join together to share their combined resources Acquisition –when one organization seeks toacquire another, often smaller,organization (sometimes hostile) Criteria for acquisitions (Porter 1987) •Attractiveness •Cost of entry-should not be so high that they prevent the organization from recouping its investment •Competitive advantage –profit/market share
Internal Development An alternative route to growth ‘Internal development’ or ‘organic growth’ involves the organization using its own resources and developing capabilities it believes will be necessary to compete in the future. International B&Q trial of products?? Less risky [financially] but slower! However easier to manage
Joint ventures and Strategic Alliances Joint Venture-when two organizations form a separate independent company in which they own shares equally e.g. Sony Ericsson Strategic Alliance–when two or more separate organizations share some of their resources and capabilities but stop short of forming a separate organization e.g. European Airbus formed by British, French, German and Italian aircraft manufacturers.
Portfolio Analysis A portfolio is the different business units that an organization possesses Portfolio analysis allows organization to assess the competitive position and identify the rate of return it is receiving from its various business units By disaggregating (separate into its component parts) the organization into its individual SBUs, the organization can devise appropriate strategies for each Aim being to maximise the return on investment by allocating resources between SBUs to achieve a balanced portfolio.
Boston Consulting Group Matrix A business unit can fall within one of four strategic categories: •Stars •Question Mark (problem child) •Cash Cows •Dog Criticisms of the BCG matrix Based on industry/market growth rate and relative market share
Corporate Parenting Campbell, Goold and Alexander (1995) argue: •Multi-business organizations (corporate parents) create value by influencing or parentingthe businesses they own •Sound corporate strategies create value through parenting advantage •Parenting advantageoccurs when an organization creates more value than any of its rivals could if theyowned the same businesses
Goold, Campbell and Alexander (1994) argue •Successful parents create parenting advantage through their value creation insights •Parenting advantage also involves creating a fitbetween the parent’s distinctive characteristics, and the opportunities that exist within the business units •In order to create value the parent’s characteristics must be compatible with the critical success factorsneeded for the business...
Similar Free PDFs

Wk 7 - corporate lvl strategy
- 4 Pages

Corporate objectives and strategy
- 14 Pages

Corporate strategy directions
- 3 Pages

Corporate Diversification Strategy
- 11 Pages
3. Corporate Level Strategy
- 18 Pages

8 Corporate Strategy Diversification
- 44 Pages

Riassunto corporate strategy -3
- 1 Pages

Riassunto corporate strategy -17
- 1 Pages

Assignment - Corporate Strategy
- 1 Pages

Music Notes Wk #7
- 4 Pages

CH 6 - Corporate Level Strategy
- 9 Pages

Chapter 6 - Corporate-Level Strategy
- 10 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu



