Freud, Jung, Adler, and Erikson Study Guide PDF

| Title | Freud, Jung, Adler, and Erikson Study Guide |
|---|---|
| Course | Personality And Individual Differences |
| Institution | Baruch College CUNY |
| Pages | 2 |
| File Size | 62.6 KB |
| File Type | |
| Total Downloads | 60 |
| Total Views | 145 |
Summary
Study guide from Dr. Milano's Exam I. Contains all important information from the lectures and slides with short descriptions to review for the test. ...
Description
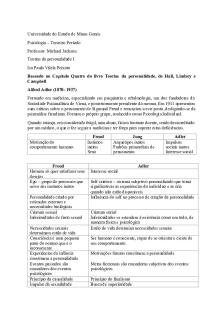
BARUCH COLLEGE – Spring 2018 PSY 3064: Personality and Individual Differences Exam I Study Sheet Freud Freud’s Influences- Mother, Darwin, Joseph Breuer/Anna O Id- genetic inheritance, reflexes, instincts, and drives that motivate us Ego- develops in order to realistically meet the wishes of the id Superego- represents internalized values, ideals, and moral standards Primary Process- visualizations Wish fulfillment- woman with T-pain and love letters/dreaming about food when hungry Secondary ProcessPleasure Principle- seeking pleasure and avoiding pain Reality Principle- distinguishing between reality and fantasy Ego Ideal- ideal representation of one’s moral self, consisting of rewarding and approved behaviors Conscience- scolds the ego Psychosexual Stages: 1. Oral- Fixation in this stage is associated with schizophrenia 2. Anal- Fixation in this stage is associated with OCD 3. Phallic- The oedipal and Electra complexes are associated with this stage as well as castration anxiety, leading to Freud’s belief woman are morally inferior to men 4. Latency- the age from seven until puberty 5. Genital- To love and work in a socially approved way and work productively in society Defense Mechanisms: Repression, Denial, Regression, Projection, Displacement, identification, reaction formation, Rationalization, and sublimation Executory Function of the Ego Relationship of the Id, Ego & Superego to Consciousness: The Id is completely unconscious while the ego and superego both have parts in the conscious. Transference- making therapist into mother figure Neuro-psychoanalysis: Combines the study of the brain with the study of the mind and its inner processes. E.g. Unconscious vs. conscious thought: limbic system vs. cortex and biological underpinnings for drives, instincts, and the pleasure principal. Jung Ego- The conscious mind and part of the psyche that selects perceptions, thoughts, feelings and memories that may enter consciousness. It is responsible for feelings of identity and continuity. Jung also did not consider it the true center of personality like Freud. Personal Unconscious- Perceptions, thoughts, feelings and memories that have been put aside can be retrieved. It includes those experiences of an individual’s life history that have been repressed or forgotten. Complex- clustered groups of life experiences, thoughts, and feelings about a particular concept Confession & Catharsis Collective Unconscious- The shared transpersonal aspects of human psyche Archetypes- A universal thought form or predisposition to respond to the world in certain ways
Persona/Shadow Anima/Animus
Synchronicity- coincidences like the beetle Ego vs Self Mandala Attitudes: Extraversion Introversion
Functions: Sensation Intuition Thinking Feeling
Myers-Briggs Adler Intrapsychic vs. Interpsychic/Interpersonal Social Interest Finalism Fictional finalisms Striving for superiority Goal of superiority Inferiority feelings Masculine protest Style of Life Family Constellation Family Atmosphere Birth Order The Creative Self Erikson Psychosocial Stages: 1. Trust vs. Mistrust 2. Autonomy vs. Shame and doubt 3. Initiative vs. Guilt 4. Industry vs. Inferiority 5. Identity vs. Role confusion 6. Intimacy vs. Isolation 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation 8. Integrity vs. Despair...
Similar Free PDFs

Freud et Erikson
- 7 Pages

Differenze fra Freud e Jung
- 2 Pages

Sigmund Freud y Carl Jung
- 3 Pages

Teoría Freud VS Teoría Jung
- 8 Pages

Erikson Case Study
- 2 Pages
Popular Institutions
- Tinajero National High School - Annex
- Politeknik Caltex Riau
- Yokohama City University
- SGT University
- University of Al-Qadisiyah
- Divine Word College of Vigan
- Techniek College Rotterdam
- Universidade de Santiago
- Universiti Teknologi MARA Cawangan Johor Kampus Pasir Gudang
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Yogyakarta
- Baguio City National High School
- Colegio san marcos
- preparatoria uno
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico Industrial y de Servicios No. 107
- Dalian Maritime University
- Quang Trung Secondary School
- Colegio Tecnológico en Informática
- Corporación Regional de Educación Superior
- Grupo CEDVA
- Dar Al Uloom University
- Centro de Estudios Preuniversitarios de la Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería
- 上智大学
- Aakash International School, Nuna Majara
- San Felipe Neri Catholic School
- Kang Chiao International School - New Taipei City
- Misamis Occidental National High School
- Institución Educativa Escuela Normal Juan Ladrilleros
- Kolehiyo ng Pantukan
- Batanes State College
- Instituto Continental
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kesehatan Kaltara (Tarakan)
- Colegio de La Inmaculada Concepcion - Cebu